Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Geometric Progression
We will discuss here about the Geometric Progression along with examples.
A sequence of numbers is said to be Geometric Progression if the ratio of any term and its preceding term is always a constant quantity.
Definition of Geometric Progression:
A sequence of non-zero number is said to be in Geometric Progression (abbreviated as G.P.) if each term, after the first, is obtained by multiplying the preceding term by a constant quantity (positive or negative).
The constant ratio is said to be the common ratio of the Geometric Progression and is denoted by dividing any term by that which immediately precedes it.
In other words, the sequence {a1, a2, a3, a4, ..................., an, ................. } is said to be in Geometric Progression, if an+1an = constant for all n ϵ N i.e., for all integral values of a, the ratio an+1an is constant.
Examples on Geometric Progression
1. The sequence 3, 15, 75, 375, 1875, .................... is a Geometric Progression, because 155 = 7515 = 37575 = 1875375 = .................. = 5, which is constant.
Clearly, this sequence is a Geometric Progression with first term 3 and common ratio 5.
2. The sequence 13, -12, 34, -98, is a Geometric Progression with first term 13 and common ratio −1213 = -32
3. The sequence of numbers {4, 12, 36, 108, 324, ........... } forms a Geometric Progression whose common ratio is 3, because,
Second term (12) = 3 × First term (4),
Third term (36) = 3 × Second term (12),
Fourth term (108) = 3 × Third term (36),
Fifth term (324) = 3 × Fourth term (108) and so on.
In other words,
Secondterm(12)Firstterm(4) = Thirdterm(36)Secondterm(12) = Fourthterm(108)Thirdterm(36) = Fifthterm(324)Fourthterm(108) = ................. = 3 (a constant)
Solved example on Geometric Progression
Show that the sequence given by an = 3(2n), for all n ϵ N, is a Geometric Progression. Also, find its common ratio.
Solution:
The given sequence is an = 3(2n)
Now putting n = n +1 in the given sequence we get,
an+1 = 3(2n+1)
Now, an+1an = 3(2n+1)3(2n) = 2
Therefore, we clearly see that for all integral values of n, the an+1an = 2 (constant). Thus, the given sequence is an Geometric Progression with common ratio 2.
Geometric Series:
If a1, a2, a3, a4, ..............., an, .......... is a Geometric Progression, then the expression a1 + a2 + a3 + ......... + an + .................... is called a geometric series.
Notes:
(i) The geometric series is finite according as the corresponding Geometric Progression consists of finite number of terms.
(ii) The geometric series is infinite according as the corresponding Geometric Progression consists of infinite number of terms.
● Geometric Progression
- Definition of Geometric Progression
- General Form and General Term of a Geometric Progression
- Sum of n terms of a Geometric Progression
- Definition of Geometric Mean
- Position of a term in a Geometric Progression
- Selection of Terms in Geometric Progression
- Sum of an infinite Geometric Progression
- Geometric Progression Formulae
- Properties of Geometric Progression
- Relation between Arithmetic Means and Geometric Means
- Problems on Geometric Progression
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Geometric Progression to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
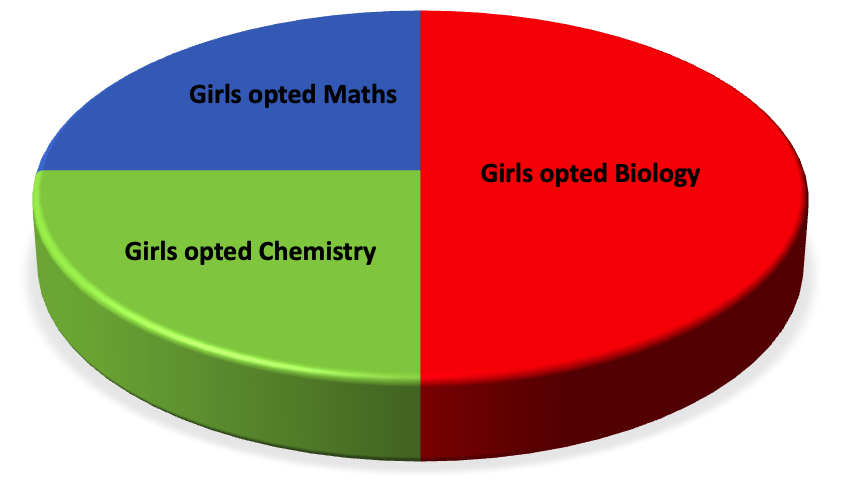
5th Grade Pie Chart | Definition of Pie Chart | Construction |Examples
Jul 31, 25 05:12 PM
Data can also be represented in a circle. This method, to represent data, is called a pie chart. Let us understand this method with the help of an example. -
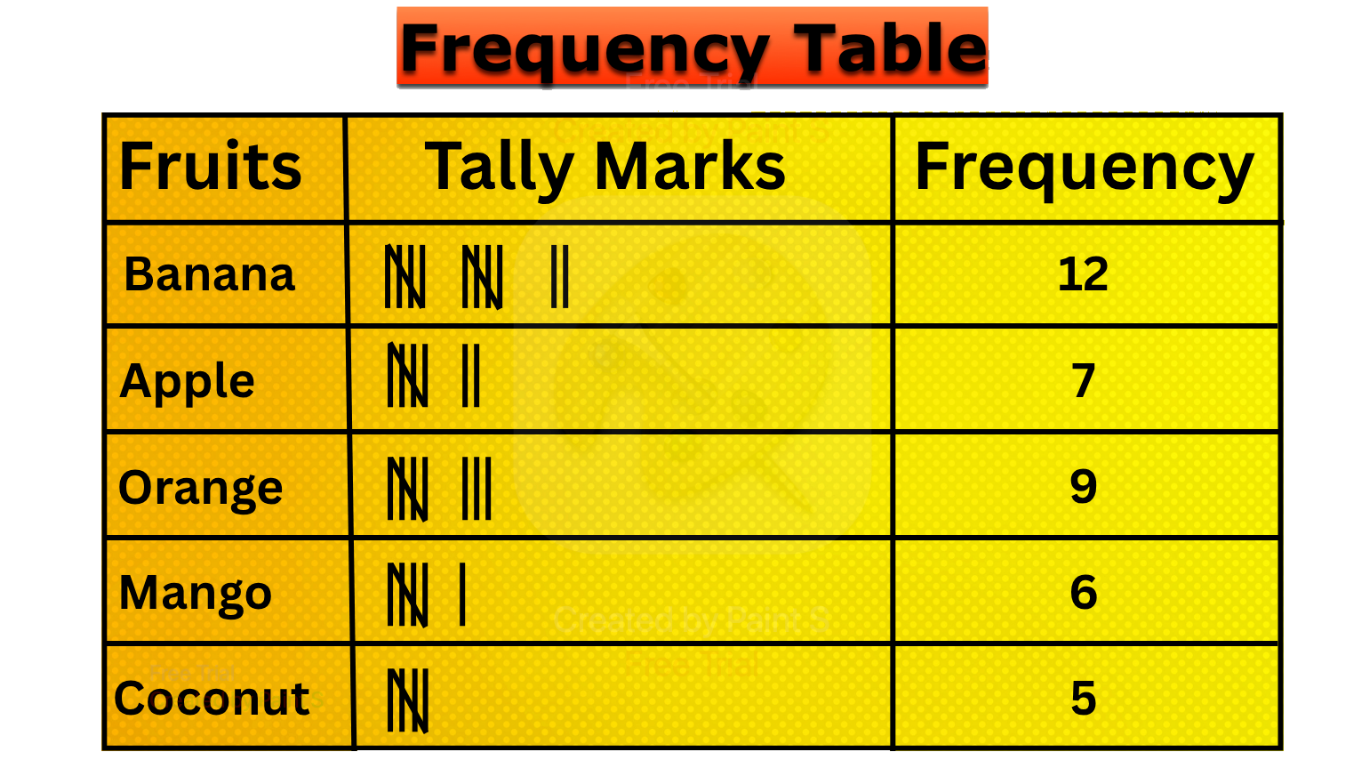
Frequency Distribution |Tally Marks |Frequency Distribution Table
Jul 31, 25 12:23 PM
What is frequency distribution?The number of times a particular observation occurs in a given data is called its frequency. In 7ᵗʰ grade and 8ᵗʰ grade frequency distribution, -
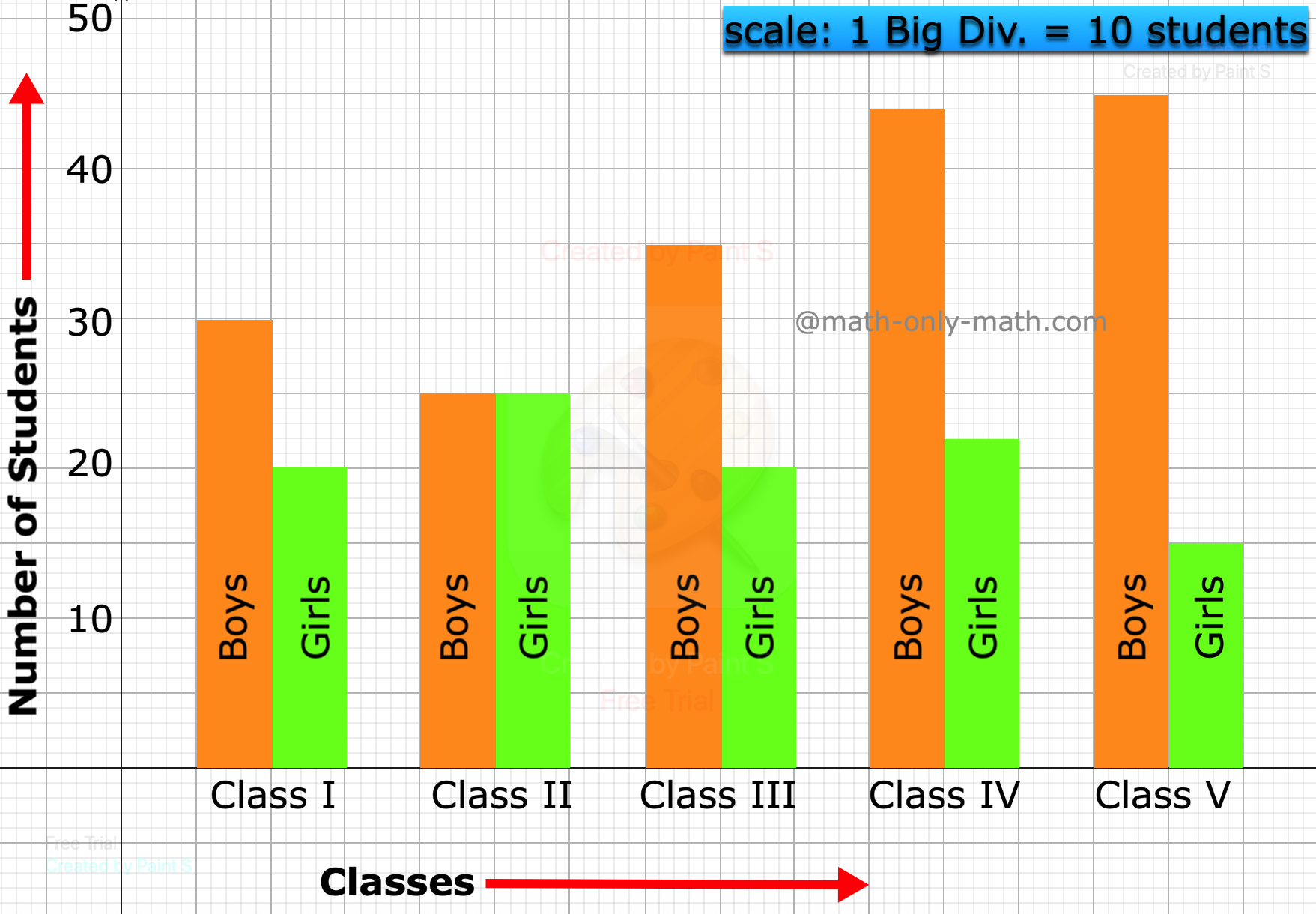
5th Grade Bar Graph | Definition | Interpret Bar Graphs|Free Worksheet
Jul 31, 25 05:16 AM
We learn how to represent the data on the bar graph. Data can be represented by bars (like rectangle) whose lengths represent numerical values. One can use horizontal or vertical bars. Instead of rect… -
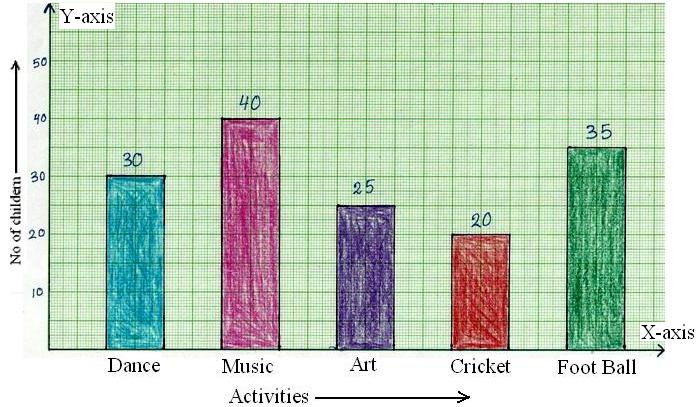
Construction of Bar Graphs | Examples on Construction of Column Graph
Jul 31, 25 03:35 AM
Now we will discuss about the construction of bar graphs or column graph. In brief let us recall about, what is bar graph? Bar graph is the simplest way to represent a data. In consists of rectangular… -
Successor and Predecessor | Successor of a Whole Number | Predecessor
Jul 29, 25 12:59 AM
The number that comes just before a number is called the predecessor. So, the predecessor of a given number is 1 less than the given number. Successor of a given number is 1 more than the given number…

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.