Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
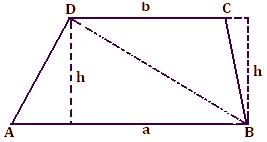
Area of Trapezium
Here we will learn how to use the formula to find the area of trapezium.
Area of trapezium ABCD = Area of ∆ ABD + Area of ∆ CBD
= 1/2 × a × h + 1/2 × b × h
= 1/2 × h × (a + b)
= 1/2 (sum of parallel sides) × (perpendicular distance between them)
Worked-out examples on area of trapezium
1. The length of the parallel sides of a trapezium are in the rat: 3 : 2 and the distance between them is 10 cm. If the area of trapezium is 325 cm², find the length of the parallel sides.
Solution:
Let the common ration be x,
Then the two parallel sides are 3x, 2x
Distance between them = 10 cm
Area of trapezium = 325 cm²
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (p₁ + p₂) h
325 = 1/2 (3x + 2x) 10
⇒ 325 = 5x × 5
⇒ 325 = 25x
⇒ x = 325/25
Therefore, 3x = 3 × 13 = 39 and 2x = 2 × 13 = 26
Therefore, the length of parallel sides area are 26 cm and 39 cm.
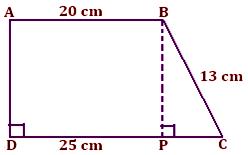
2. ABCD is a trapezium in which AB ∥ CD, AD ⊥ DC, AB = 20 cm, BC = 13 cm and DC = 25 cm. Find the area of the trapezium.
Solution:
From B draw BP perpendicular DC
Therefore, AB = DP = 20 cm
So, PC = DC - DP
= (25 - 20) cm
= 5 cm
Now, area of trapezium ABCD = Area of rectangle ABPD + Area of △ BPC
△BPC is right angled at ∠BPC
Therefore, using Pythagoras theorem,
BC² = BP² + PC²
13² = BP² + 5²
⇒ 169 = BP² + 25
⇒ 169 - 25 = BP²
⇒ 144 = BP²
⇒ BP = 12
Now, area of trapezium ABCD = Area of rectangle ABPD + Area of ∆BPC
= AB × BP + 1/2 × PC × BP
= 20 × 12 + 1/2 × 5 × 12
= 240 + 30
= 270 cm²
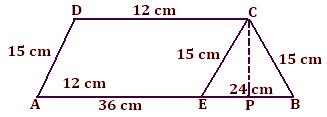
3. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides are AB = 12 cm, CD = 36 cm and the non-parallel sides are BC = 15 cm and AG = 15 cm.
Solution:
In trapezium ABCD, draw CE ∥ DA.
Now CE = 15 cm
Since, DC = 12 cm so, AE = 12 cm
Also, EB = AB - AE = 36 - 12 = 24 cm
Now, in ∆ EBC
S = (15 + 15 + 24)/2
= 54/2
= 27
= √(27 × 12 × 12 × 3)
= √(3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3)
= 3 × 3 × 3 × 2 × 2
= 108 cm²
Draw CP ⊥ EB.
Area of ∆EBC = 1/2 × EB × CP
108 = 1/2 × 24 × CP
108/12 = CP
⇒ CP = 9 cm
Therefore, h = 9 cm
Now, area of triangle = √(s(s - a) (s - b) (s - c))
= √(27 (27 - 15) (27 - 15 ) (27 - 24))
Now, area of trapezium = 1/2(p₁ + p₂) × h
= 1/2 × 48 × 9
= 216 cm²
4. The area of a trapezium is 165 cm² and its height is 10 cm. If one of the parallel sides is double of the other, find the two parallel sides.
Solution:
Let one side of trapezium is x, then other side parallel to it = 2x
Area of trapezium = 165 cm²
Height of trapezium = 10 cm
Now, area of trapezium = 1/2 (p₁ + p₂) × h
⇒ 165 = 1/2(x₁ + 2x) × 10
⇒ 165 = 3x × 5
⇒ 165 = 15x
⇒ x = 165/15
⇒ x = 11
Therefore, 2x = 2 × 11 = 22
Therefore, the two parallel sides are of length 11 cm and 22 cm.
These are the above examples explained step by step to calculate the area of trapezium.
● Mensuration
Perimeter and Area of Rectangle
Area and Perimeter of the Triangle
Area and Perimeter of the Parallelogram
Circumference and Area of Circle
Practice Test on Area and Perimeter of Rectangle
Practice Test on Area and Perimeter of Square
● Mensuration - Worksheets
Worksheet on Area and Perimeter of Rectangles
Worksheet on Area and Perimeter of Squares
Worksheet on Circumference and Area of Circle
Worksheet on Area and Perimeter of Triangle
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Area of Trapezium to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.