Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
sin θ = 0
How to find the general solution of the equation sin θ = 0?
Prove that the general solution of sin θ = 0 is θ = nπ, n ∈ Z
Solution:
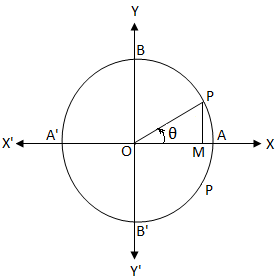
According to the figure, by definition, we have,
Sine function is defined as the ratio of the side opposite divided by the hypotenuse.
Let O be the centre of a unit circle. We know that in unit circle, the length of the circumference is 2π.If we started from A and moves in anticlockwise direction then at the points A, B, A', B' and A, the arc length travelled are 0, π2, π, 3π2, and 2π.
Therefore, from the above unit circle it is clear that
sin θ = PMOP
Now, sin θ = 0
⇒ PMOP = 0
⇒ PM = 0.
So when will the sine be equal to zero?
Clearly, if PM = 0 then the final arm OP of the angle θ coincides with OX or, OX'.
Similarly, the final arm OP coincides with OX or OX' when θ = 0, π, 2π, 3π, 4π, 5π …………….., -π, , -2π, -3π, -4π, -5π ………., i.e., when θ = 0 or an integral multiples of π i.e., when θ = nπ where n ∈ Z (i.e., n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….)
Hence, θ = nπ, n ∈ Z is the general solution of the given equation sin θ = 0
1. Find the general solution of the equation sin 2θ = 0
Solution:
sin 2θ = 0
⇒ 2θ = nπ, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,……., [Since, we know that θ = nπ, n ∈ Z is the general solution of the given equation sin θ = 0]
⇒ θ = nπ2, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
Therefore, the general solution of the equation sin 2θ = 0 is θ = nπ2, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
2. Find the general solution of the equation sin 3x2 = 0
Solution:
sin 3x2 = 0
⇒ 3x2 = nπ, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….[Since, we know that θ = nπ, n ∈ Z is the general solution of the given equation sin θ = 0]
⇒ x = 2nπ3, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
Therefore, the general solution of the equation sin 3x2 = 0 is θ = 2nπ3, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
3. Find the general solution of the equation tan 3x = tan 2x + tan x
Solution:
tan 3x = tan 2x + tan x
⇒ sin3xcos3x = sin2xcos2x + sinxcosx
⇒ sin3xcos3x = sin2xcosx+cos2xsinxcos2xcosx
⇒ cos 3θ sin (2x + x) = sin 3x cos 2x cos x
⇒ cos 3x sin 3x = sin 3x cos 2x cosx
⇒ cos 3x sin 3x - sin 3x cos
2x cos x = 0
⇒ sin 3x [cos (2x + x) - cos 2x cos x] = 0
⇒ sin 3x . sin 2x sin x = 0
Either either, sin 3x = 0 or, sin 2x = 0 or, sin x = 0
⇒ 3x = nπ or, 2x = nπ or, x = nπ
⇒ x = nπ3 …..... (1) or, x = nπ2 …..... (2) or, x = nπ …..... (3), where n ∈ I
Clearly, the value of x given in (2) are∶ 0, π2, π, 3π2, 2π, 5π2 ……………., - π2,- π, - 3π2 , …………
It is readily seen that the solution x = π2, 3π2, 5π2………, - π2, - 3π2,………
Of the above solution do not satisfy the given equation.
Further to not that the rest solutions of (2) and the solution of (3) are contained in the solutions (1).
Therefore, the general solution of the equation tan 3x = tan 2x + tan x is x = 3π2,, where n ∈ I
4. Find the general solution of the equation sin2 2x = 0
Solution:
sin2 2x = 0
sin 2x = 0
⇒ 2x = nπ, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,……., [Since, we know that θ = nπ, n ∈ Z is the general solution of the given equation sin θ = 0]
⇒ x = nπ2, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
Therefore, the general solution of the equation sin2 2x = 0 is x = nπ2, where, n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3,…….
- General solution of the equation sin x = ½
- General solution of the equation cos x = 1/√2
- General solution of the equation tan x = √3
- General Solution of the Equation sin θ = 0
- General Solution of the Equation cos θ = 0
- General Solution of the Equation tan θ = 0
- General Solution of the Equation sin θ = sin ∝
- General Solution of the Equation sin θ = 1
- General Solution of the Equation sin θ = -1
- General Solution of the Equation cos θ = cos ∝
- General Solution of the Equation cos θ = 1
- General Solution of the Equation cos θ = -1
- General Solution of the Equation tan θ = tan ∝
- General Solution of a cos θ + b sin θ = c
- Trigonometric Equation Formula
- Trigonometric Equation using Formula
- General solution of Trigonometric Equation
- Problems on Trigonometric Equation
11 and 12 Grade Math
From sin θ = 0 to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.