Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem is also known as ‘Pythagoras theorem’ and is related to the sides of a right angled triangle.
Statement of ‘Pythagoras theorem’:
In a right triangle the area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares of its remaining two sides.
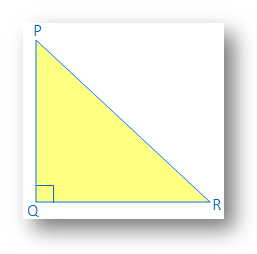
(Length of the hypotenuse)2 = (one side)2 + (2nd side)2In the given figure, ∆PQR is right angled at Q;
PR is the hypotenuse and PQ, QR are
|
the remaining two sides, then (PR)2 = PQ2 + QR2 (h)2 = p2 + b2 [Here h → hypotenuse, p → perpendicular, b → base] |
Verification of Pythagoras theorem by the method of dissection:
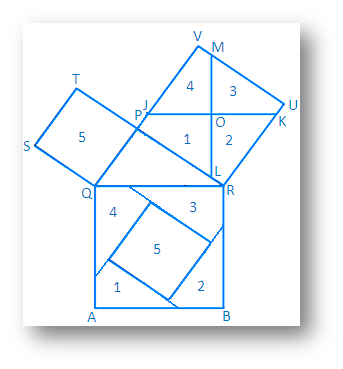
In the adjoining figure, ∆ PQR is a right angled triangle where QR is its hypotenuse and PR > PQ.
Square on QR is QRBA, square on PQ is PQST and the square on PR is PRUV.
The point of intersection of the diagonal of the square PRUV is O.
The straight line through the point O parallel to the QR intersects PV and RU at the point J and K respectively.
Again the straight line through the point O perpendicular to JK intersects PR and VU at the point L and respectively.
As a result, the square PRUV is divided into four parts which is marked as 1, 2, 3, 4 and the square PQST is marked 5.
You can draw the same figure on a thick paper and cut it accordingly and now cut out the squares respectively from this figure. Cut the squares PRUV along JK and LM dividing it in four parts. Now, place the parts 1, 2, 3, 4and 5 properly on the square QRBA.
Note:
(i) these parts together exactly fit the square. Thus, we find that QR2 = PQ2 + PR2(ii) Square drawn on side PQ, which means the area of a square of side PQ is denoted by PQ2.
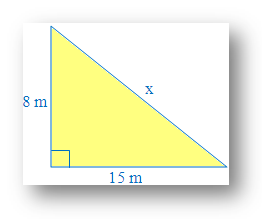
1. Find the value of x using Pythagorean theorem:
Solution:
Identify the sides and the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle.
The one sides length = 8 m and the other side length = 15.
'X' is the length of hypotenuse because it is opposite side of the right angle.
Substitute the values into the Pythagorean formula (here 'x' is the hypotenuse)
(h)2 = p2 + b2[Here h → hypotenuse, p → perpendicular, b → base]
x2 = 82 + 152
Solve to find the known value of ‘x’
x2 = 64 + 225
x2 = 289
x = √289
x = 17
Therefore, value of x (hypotenuse) = 17 m
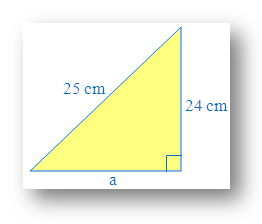
2. Use the formula of Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of ‘a’.
Solution:
Identify the perpendicular, base and the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle.
Length of perpendicular = 24 cm and the length of base = a.
Length of hypotenuse = 25 cm. Since hypotenuse is the opposite side of the right angle.
Substitute the values into the Pythagorean formula (here 'a' is the base)
(h)2 = p2 + b2[Here h → hypotenuse, p → perpendicular, b → base]
252 = 242 + a2
Solve to find the known value of ‘a’
625 = 576 + a2
625 – 576 = 576 – 576 + a2
49 = a2
a2 = 49
a = √49
a = 7
Therefore, length of ‘a’ (base) = 7 cm
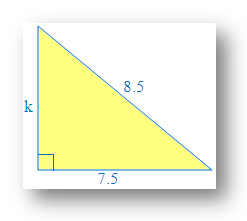
3. Solve to find the missing value of the triangle using the formula of Pythagorean Theorem:
Solution:
Identify the perpendicular, base and the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle.
Perpendicular = k and Base = 7.5
Hypotenuse = 8.5, since hypotenuse is the opposite side of the right angle.
Substitute the values into the Pythagorean formula (here 'k' is the perpendicular)
(h)2 = p2 + b2[Here h → hypotenuse, p → perpendicular, b → base]
8.52 = k2 + 7.52
Solve to find the known value of ‘k ’
72.25 = k2 + 56.25
72.25 – 56.25 = k2 + 56.25 – 56.25
16 = k2
k2 = 16
k = √16
k = 4
Therefore, missing value of the triangle ‘k’ (perpendicular) = 4
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Pythagorean Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.