Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Cross-Multiplication Method
Here we will discuss about simultaneous linear equations by using cross-multiplication method.
General form of a linear equation in two unknown quantities:
ax + by + c = 0, (a, b ≠ 0)
Two such equations can be written as:
a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0 ----------- (i)
a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0 ----------- (ii)
Let us solve the two equations by the method of elimination, multiplying both sides of equation (i) by a₂ and both sides of equation (ii) by a₁, we get:
a₁a₂x + b₁a₂y + c₁a₂ = 0
a₁ a₂x + a₁b₂y + a₁c₂ = 0
Subtracting, b₁a₂y - a₁b₂y + c₁a₂ - c₂a₁ = 0
or, y(b₁ a₂ - b₂a₁) = c₂a₁ - c₁a₂
Therefore, y = (c₂a₁ - c₁a₂)/(b₁a₂ - b₂a₁) = (c₁a₂ - c₂a₁)/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) where (a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) ≠ 0
Therefore, y/(c₁a₂ - c₂a₁) = 1/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁), ------------- (iii)
Again, multiplying both sides of (i) and (ii) by b₂ and b₁ respectively, we get;
a₁b₂x + b₁b₂y + b₂c₁ = 0
a₂b₁x + b₁b₂y + b₁c₂ = 0
Subtracting, a₁b₂x - a₂b₁x + b₂c₁ - b₁c₂ = 0
or, x(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) = (b₁c₂ - b₂c₁)
or, x = (b₁c₂ - b₂c₁)/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁)
Therefore, x/(b₁c₂ - b₂c₁) = 1/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) where (a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) ≠ 0 -------------- (iv)
From equations (iii) and (iv), we get:
x/(b₁c₂ - b₂c₁) = y/(c₁a₂) - c₂a₁ = 1/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) where (a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) ≠ 0
This relation informs us how the solution of the simultaneous equations, co-efficient x, y and the constant terms in the equations are inter-related, we can take this relation as a formula and use it to solve any two simultaneous equations. Avoiding the general steps of elimination, we can solve the two simultaneous equations directly.
So, the formula for cross-multiplication and its use in solving two simultaneous equations can be presented as:
If (a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) ≠ 0 from the two simultaneous linear equations
a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0 ----------- (i)
a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0 ----------- (ii)
we get, by the cross-multiplication method:
x/(b₁c₂ - b₂c₁) = y/(c₁a₂ - c₂a₁) = 1/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁) ---------- (A)
That means, x = (b₁c₂ - b₂c₁)/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁)
y = (c₁a₂ - c₂a₁)/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁)
Note:
If the value of x or y is zero, that is, (b₁c₂ - b₂c₁) = 0 or (c₁a₂ - c₂a₁) = 0, it is not proper to express in the formula for cross- multiplication, because the denominator of a fraction can never be 0.
From the two simultaneous equations, it appears that the formation of relation (A) by cross-multiplication is the most important concept.
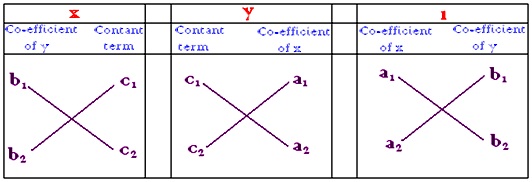
At first, express the co-efficient of the two equations as in the following form:
Now multiply the co-efficient according to the arrow heads and subtract the upward product from the downward product. Place the three differences under x, y and 1 respectively forming three fractions; connect them by two signs of equality.
Worked-out examples on simultaneous linear equations by using cross-multiplication method:
1. Solve the two variables linear equation:
8x + 5y = 11
3x – 4y = 10
Solution:
On transposition, we get
8x + 5y – 11 = 0
3x – 4y – 10 = 0
Writing the co-efficient in the following way, we get:
Note: The above presentation is not compulsory for solving.
By cross-multiplication method:
x/(5) (-10) – (-4) (-11) = y/(-11) (3) – (-10) (8) = 1/(8) (-4) – (3) (5)
or, x/-50 – 44 = y/-33 + 80 = 1/-32 – 15
or, x/-94 = y/47 = 1/-47
or, x/-2 = y/1 = 1/-1 [multiplying by 47]
or, x = -2/-1 = 2 and y = 1/-1 = -1
Therefore, required solution is x = 2, y = -1
2. Find the value of x and y by using the using cross-multiplication method:
3x + 4y – 17 = 0
4x – 3y – 6 = 0
Solution:
Two given equations are:
3x + 4y – 17 = 0
4x – 3y – 6 = 0
By cross-multiplication, we get:
x/(4) (-6) – (-3) (-17) = y/(-17) (4) – (-6) (3) = 1/(3) (-3) – (4) (4)
or, x/(-24 – 51) = y/(-68 + 18) = 1/(-9 – 16)
or, x/-75 = y/-50 = 1/-25
or, x/3 = y/2 = 1 (multiplying by -25)
or, x = 3, y = 2
Therefore, required solution: x = 3, y = 2.
3. Solve the system of linear equations:
ax + by – c² = 0
a²x + b²y – c² = 0
Solution:
x/(-b + b²) = y/(- a² + a) = c²/(ab² - a²b)
or, x/-b(1 - b) = y/- a(a - 1) = c²/-ab(a - b)
or, x/b(1 - b) = y/a(a - 1) = c²/ab(a - b)
or, x = bc²(1 – b)/ab(a – b) = c²(1 – b)/a(a – b) and y = c²a(a – 1)/ab(a – b) = c²(a – 1)/b(a – b)
Hence the required solution is:
x = c²(1 – b)/a(a – b)
y = c²a(a – 1)/b(a – b)
● Simultaneous Linear Equations
Solvability of Linear Simultaneous Equations
Word Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Word Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Practice Test on Word Problems Involving Simultaneous Linear Equations
● Simultaneous Linear Equations - Worksheets
Worksheet on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Worksheet on Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
8th Grade Math Practice
From Cross-Multiplication Method to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
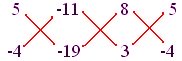


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.