Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Domain Co-domain and Range of Function
Here we will discuss about domain, co-domain and range of function.
Let : A → B (f be function from A to B), then
● Set A is known as the domain of the function ‘f’
● Set B is known as the co-domain of the function ‘f’
● Set of all f-images of all the elements of A is known as the range of f. Thus, range of f is denoted by
f(A).
Note:
Range ∈ co-domain
Example on Domain, co-domain and range of function:
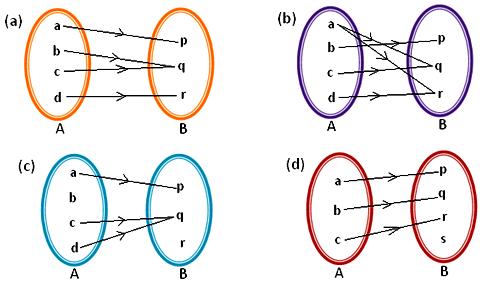
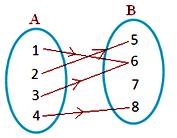
1. Which of the arrow diagrams given below represents a mapping? Give reasons to support your answer.
Solution:
(a) a has unique image p.
(b) has unique image q.
(c) has unique image q.
(d) has unique image r.
Thus, each element of A has a unique image in B.
Therefore, the given arrow diagram represents a mapping.
(b) In the given arrow diagram, the element ‘a’ of set A is associated with two elements, i.e., q and r of set B. So, each element of set A does not have a unique image in B.
Therefore, the given arrow diagram does not represent a mapping.
(c) The element ‘b’ of set A is not associated with any element of set B. So b ∈ A does not have any image. For a mapping from A to B, every element of set A must have a unique image in set B which is not represented by this arrow diagram. So, the given arrow diagram does not represent a mapping.
(d) a has a unique image p. b has a unique image q. c has a unique image r. Thus, each element in set A has a unique image in set B.
Therefore, the given arrow diagram represents a mapping.
2. Find out if R is a mapping from A to B.
(i) Let A = {3, 4, 5} and B= {6, 7, 8, 9} and R = {(3, 6) (4, 7) (5, 8)}
Solution:
Since, R = {(3, 6); (4, 7); (5, 8)} then Domain (R) = {3, 4, 5} = A
We observe that no two ordered pairs in R have the same first component.
Therefore, R is a mapping from A to B.
(ii) Let A = {1, 2, 3} and B= {7, 11} and R = {(1, 7); (1, 11); (2, 11); (3, 11)}
Solution:
Since, R = {(1, 7); (1, 11); (2, 11); (3, 11)} then Domain (R) = {1, 2, 3} = A
But the ordered pairs (1, 7) (1, 11) have the same first component.
Therefore, R is not a mapping from A to B.
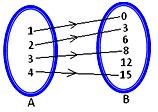
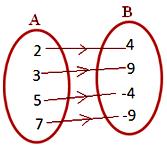
3. Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {0, 3, 6, 8, 12, 15}
Consider a rule f (x) = x² - 1, x∈A, then
(a) show that f is a mapping from A to B.
(b) draw the arrow diagram to represent the mapping.
(c) represent the mapping in the roster form.
(d) write the domain and range of the mapping.
Solution:
Using f (x) = x² - 1, x ∈ A we have
f(1) = 0,
f(2) = 3,
f(3) = 8,
f(4) = 15
We observe that every element in set A has unique image in set B.
Therefore, f is a mapping from A to B.
(b) Arrow diagram which represents the mapping is given below.
(c) Mapping can be represented in the roster form as
f = {(1, 0); (2, 3); (3, 8); (4, 15)}
(d) Domain (f) = {1, 2, 3, 4} Range (f) = {0, 3, 8, 15}
Representation of a function by an arrow diagram:
In this, we represent the sets by closed figures and the elements are represented by points in the closed figure.
The mapping f : A → B is represented by arrow which originates from elements of A and terminates at the elements of B.
Some examples of functions:
figure (i)
Each element of A has a unique image in B
figure (ii)
Two elements of A are associated with same element in B
figure (iii)
Each element of A has a unique image in B
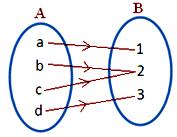
figure (iv)
Every element of A has a unique image in B
Note:
• Observe in figure (i) and figure (ii), there are some elements in B which are not f-images of any elements of A.
• In figure (iii), figure (iv), two elements of A have the same image in B.
Function as a special type of relation:
If A and B are two non-empty sets, A relation f from A to B is called a function from A to B if every element of A (say x) has one and only one image (say y) in B. The f-image of x is denoted by f (x) and so we write y = f (x). The element x is called the pre-image of y under ‘f’.
Real valued function of a real variable: :
If the domain and range of a function ‘f' are subsets of R (set of real numbers), then f is said to be the real valued function of real variable or simply a real function. It may be defined as
A function f A → B is called a real valued function if B is a subset of R. If A and B are subsets of R then f is called a real function.
More examples on domain, co-domain and range of function:
1. Let N be the set of natural number if f: N → N by f (x) = 3x +2, then find f (1), f (2), f (-3), f (-4).
Solution:
Since for f(x) = 3x + 2
then f(1) = 3 × 1 + 2 = 3 + 2 = 5
f(2) = 3 × 2 + 2 = 6 + 2 = 8
there for f(-3) = 3 × (-3) + 2 = -9 + 2 = -7
f(-4) = 3 × -4 + 2 = -12 + 2 = -10
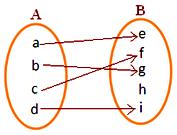
2. Let A = {a, b, c, d} and B= {c, d, e, f, g}
Let R₁ = {(a, c) (b, d) (c, e)}
R₂ = {(a, c) (a, g) (b, d) (c, e) (d, f)}
R₃ = {(a, c) (b, d) (c, e) (d, f)}
Justify which of the given relation is a function from A to B.
Solution:
We have,
(i) Domain R₁ {a, b, c} ≠ A
Therefore, R₁ is not a function from A to B.
(ii) Two different ordered pairs (a, c) (a, g) have the same first component.
Therefore, R₂ is not a function from A → B.
(iii) Domain R₃ = {a, b, c, d} = A and not two different ordered pair have same first component.
Therefore, R₃ is a function from A to B.
● Relations and Mapping
Domain and Range of a Relation
Domain Co-domain and Range of Function
● Relations and Mapping - Worksheets
Worksheet on Functions or Mapping
8th Grade Math Practice
From Domain Co-domain and Range of Function to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.