Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Systems of Measuring Angles
The following three different systems of units are used in the measurement of trigonometrical angles :
(a) Sexagesimal System ( or English System)
(b) Centesimal System ( or French System)
(c) Circular System
If a straight line stands on another line and if the two adjacent angles thus formed are equal to one another then by geometry, each of these angles is called a right angle. This right angle forms the basis in defining the different systems for the measurement of angles.
Definition of systems of measuring angles:
(a) Sexagesimal System: In Sexagesimal System, an angle is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds.
A complete rotation describes 360°. In this system, a right angle is divided into 90 equal parts and each such part is called a Degree (1°); a degree is divided into 60 equal parts and each such part is called a Sexagesimal Minute (1’) and a minute is further sub-divided into 60 equal parts, each of which is called a Sexagesimal Second (1’’). In short,
|
1 right angle 1 degree (or 1°) and 1 minute ( or 1’ ) |
= 90 degrees (or 90°) = 60 minutes ( or 60’) = 60 seconds ( or 60’’). |
(b) Centesimal System: In Centesimal System, an angle is measured in grades, minutes and seconds. In this system, a right angle is divided into 100
|
1 right angle 1 grade ( or 1g) and 1 minute (or 1‵) |
= 100 grades (or, 100g) = 100 minutes (or, 100‵) = 100 seconds ( or, 100‶). |
Note: (i) Clearly, minute and second in sexagesimal and centesimal systems are different.
For example,
1 right angle = 90 × 60 = 5400 sexagesimal minutes = (5400)’
and 1 right angle = 100 × 100 = 10000 centesimàl minutes = (10000)‶
Therefore, 90° = 100g
or, 1° = (10/9) g and 1g = (9/10)°
The first relation is used to reduce an angle of sexagesimal system to centesimal system and the second is used to reduce an angle of centesimal system to sexagesimal system.
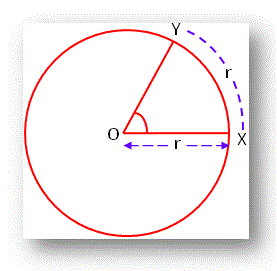
(c) Circular System: In this System, an angle is measured in radians. In higher mathematics angles are usually measured in circular system. In this system a radian is considered as the unit for the measurement of angles.
Definition of Radian: A radian is an angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius.
A radian defined as follows:
Circular (radian) measure of an angle:
The circular measure of an angle is the number of radians it contains.
Thus the circular (radian) measure of a right angle is π/2.
If an angle is given without mentioning units, it is assumed to be in radians. The relation between degree measures and circular (radian) measures of some standard angles are given below:
Degrees0° 30° 45° 60° 90° 120° 135° 150° 180° 270° 360° |
Radians0 π/6 π/4 π/3 π/2 2π/3 3π/4 5π/6 π 3π/2 2π |
● Measurement of Angles
- Sign of Angles
- Trigonometric Angles
- Measure of Angles in Trigonometry
- Systems of Measuring Angles
- Important Properties on Circle
- S is Equal to R Theta
- Sexagesimal, Centesimal and Circular Systems
- Convert the Systems of Measuring Angles
- Convert Circular Measure
- Convert into Radian
- Problems Based on Systems of Measuring Angles
- Length of an Arc
- Problems based on S R Theta Formula
From Systems of Measuring Angles to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Successor and Predecessor | Successor of a Whole Number | Predecessor
Jul 29, 25 12:59 AM
The number that comes just before a number is called the predecessor. So, the predecessor of a given number is 1 less than the given number. Successor of a given number is 1 more than the given number… -
Worksheet on Area, Perimeter and Volume | Square, Rectangle, Cube,Cubo
Jul 28, 25 01:52 PM
In this worksheet on area perimeter and volume you will get different types of questions on find the perimeter of a rectangle, find the perimeter of a square, find the area of a rectangle, find the ar… -
Worksheet on Volume of a Cube and Cuboid |The Volume of a RectangleBox
Jul 25, 25 03:15 AM
We will practice the questions given in the worksheet on volume of a cube and cuboid. We know the volume of an object is the amount of space occupied by the object.1. Fill in the blanks: -
Volume of a Cuboid | Volume of Cuboid Formula | How to Find the Volume
Jul 24, 25 03:46 PM
Cuboid is a solid box whose every surface is a rectangle of same area or different areas. A cuboid will have a length, breadth and height. Hence we can conclude that volume is 3 dimensional. To measur… -
Volume of a Cube | How to Calculate the Volume of a Cube? | Examples
Jul 23, 25 11:37 AM
A cube is a solid box whose every surface is a square of same area. Take an empty box with open top in the shape of a cube whose each edge is 2 cm. Now fit cubes of edges 1 cm in it. From the figure i…




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.