Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The Law of Sines
We will discuss here about the law of sines or the sine rule which is required for solving the problems on triangle.
In any triangle the sides of a triangle are proportional to the sines of the angles opposite to them.
That is in any triangle ABC,
\(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\)
Proof:
Let ABC be a triangle.
Now will derive the three different cases:
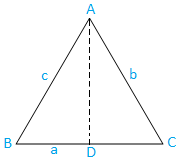
Case I: Acute angled triangle (three angles are acute): The triangle ABC is acute-angled.
Now, draw AD from A which is perpendicular to BC. Clearly, D lies on BC
Now from the triangle ABD, we have,
sin B = AD/AB
⇒ sin B = AD/c, [Since, AB = c]
⇒ AD= c sin B ……………………………………. (1)
Again from the triangle ACD we have,
sin C = AD/AC
⇒ sin C = AD/b, [Since, AC = b]
⇒ AD = b sin C ...………………………………….. (2)
Now, from (1) and (2) we get,
c sin B = b sin C
⇒ b/sin B = c/sin c………………………………….(3)
Similarly, if we draw a perpendicular to AC from B, we will get
a/sin A = c/sin c………………………………….(4)
Therefore, from (3) and (4) we get,
\(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\)
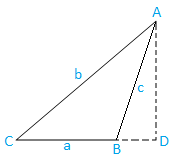
Case II: Obtuse angled triangle (one angle is obtuse): The triangle ABC is obtuse angled.
Now, draw AD from A which is perpendicular to produced BC. Clearly, D lies on produced BC.
Now from the triangle ABD, we have,
sin ∠ABD = AD/AB
⇒ sin (180 - B) = AD/c, [Since ∠ABD = 180 - B and AB = c]
⇒ sin B = AD/c, [Since sin (180 - θ) = sin θ]
⇒ AD = c sin B ……………………………………. (5)
Again, from the triangle ACD, we have,
sin C = AD/AC
⇒ sin C = AD/b, [Since, AC = b]
⇒ AD = b sin C ……………………………………. (6)
Now, from (5) and (6) we get,
c sin B = b sin C
b/sin B = c/sin C ……………………………………. (7)
Similarly, if we draw a perpendicular to AC from B, we will get
a/sin A = b/sin B ……………………………………. (8)
Therefore, from (7) and (8) we get,
\(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\)
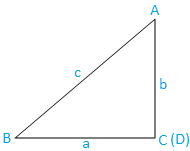
Case III: Right angled triangle (one angle is right angle): The triangle ABC is right angled. The angle C is a right angle.
Now from triangle ABC, we have,
sin C = sin π/2
⇒ sin C = 1, [Since, sin π/2 = 1], ……………………………………. (9)
sin A = BC/AB
⇒ sin A = a/c, [Since, BC = a and AB = c]
⇒ c = a/sin A ……………………………………. (10)
and sin B = AC/AB
⇒ sin B = b/c, [Since, AC = b and AB = c]
⇒ c = b/sin B ……………………………………. (11)
Now from (10) and (11) we get,
a/sin A = b/sin B = c
⇒ a/sin A = b/sin B = c/1
Now from (9) we get,
⇒ \(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\)
Therefore, from all three cases, we get,
\(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\). Proved.
Note:
1. The sine rule or the law of sines can be expressed as
\(\frac{sin A}{a}\) = \(\frac{sin B}{b}\) = \(\frac{sin C}{c}\)
2. The sine rule or the law of sines is a very useful rule to
express sides of a triangle in terms of the sines of angles and vice-versa in
the following manner.
We have \(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{c}{sin C}\) = k\(_{1}\) (say)
⇒ a = k\(_{1}\) sin A, b = k\(_{1}\) sin B and c = k\(_{1}\) sin C
Similarly, sin A/a = sin B/b = sin C/c = k\(_{2}\) (say)
⇒ sin A = k\(_{2}\) a, sin B = k\(_{2}\) b and sin C = k\(_{2}\) c
Solved problem using the law of sines:
The triangle ABC is isosceles; if ∠A = 108°, find the value of a : b.
Solution:
Since the triangle ABC is isosceles and A = 108°, A + B + C = 180°, hence it is evident that B = C.
Now, B + C = 180° - A = 180° - 108°
⇒ 2B = 72° [Since, C = B]
⇒ B = 36°
Again, we have, \(\frac{a}{sin A}\) = \(\frac{b}{sin B}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{a}{b}\) = \(\frac{sin A}{sin B}\) = \(\frac{sin 108°}{sin 36°}\) = \(\frac{cos 18°}{sin 36°}\)
Now, cos 18° = \(\sqrt{1 - sin^{2} 18°}\)
= \(\sqrt{1 - (\frac{\sqrt{5} - 1}{4})^{2}}\)
= ¼\(\sqrt{10 + 2\sqrt{5}}\)
and sin 36° = \(\sqrt{1 - cos^{2} 36°}\)
= \(\sqrt{1 - (\frac{\sqrt{5} + 1}{4})^{2}}\)
= ¼\(\sqrt{10 - 2\sqrt{5}}\)
Therefore, a/b = \(\frac{\frac{1}{4}\sqrt{10 + 2\sqrt{5}}}{\frac{1}{4}\sqrt{10 - 2\sqrt{5}}}\)
= \(\frac{\sqrt{10 + 2\sqrt{5}}}{\sqrt{10 - 2\sqrt{5}}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{(10 + 2\sqrt{5})^{2}}{10^{2} - (2\sqrt{5})^{2}}}\)
= \(\frac{10 + 2\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{80}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = \(\frac{2√5(√5 + 1)}{4 √5}\)
⇒ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = \(\frac{√5 + 1}{2}\)
Therefore, a : b = (√5 + 1) : 2
- The Law of Sines or The Sine Rule
- Theorem on Properties of Triangle
- Projection Formulae
- Proof of Projection Formulae
- The Law of Cosines or The Cosine Rule
- Area of a Triangle
- Law of Tangents
- Properties of Triangle Formulae
- Problems on Properties of Triangle
From The Law of Sines to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.