Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
3rd Grade Basic Shapes
In geometry we know basic shapes involve plane figures and solid figures.
Plane Figures:
The figures that lie in the plane are called plane figures. A closed, flat figure is known as plane shape. Plane shapes can be drawn on a paper or any flat surface. Rectangle, square, circle and triangle are known as basic plane shapes.
For example, square, rectangle, triangle, diamond and circle. They are also called flat shapes.
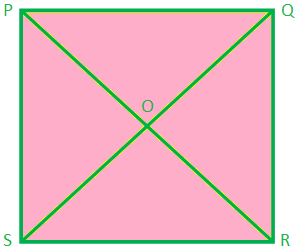
Square: It has 4 sides and 4 corners. Area enclosed inside is called the square region.
PQRS is a square.
It has four sides – PQ, QR, RS and SP
It has four corners- P, Q, R, S
All the sides of a square are equal – PQ = QR = RS = SP
Join P to R and Q to S. PR and QS are the diagonals of a square.
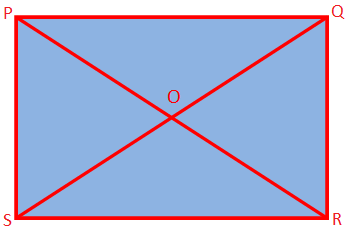
Rectangle: It has 4 sides and 4 corners and the area enclosed inside is called the rectangular region.
PQRS is a rectangle.
It has four sides – PQ, QR, RS and SP
It has four corners- P, Q, R, S
Opposite sides of a rectangle are equal – PS = QR and PQ = SR
Join P to R and Q to S. PR and QS are the diagonals of a rectangle.
Note: Since, opposite sides of square are equal, it is also a rectangle. But rectangle cannot be a square.
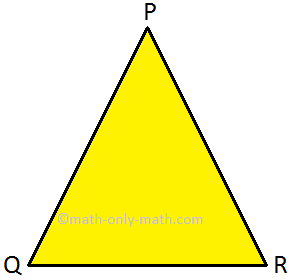
Triangle: It has 3 sides and 3 vertices or corners. Area enclosed inside the triangle is called the triangular region.
PQR is a triangle.
It has three sides – PQ, QR and RP
It has three corners – P, Q and R
We cannot draw diagonals in a triangle.
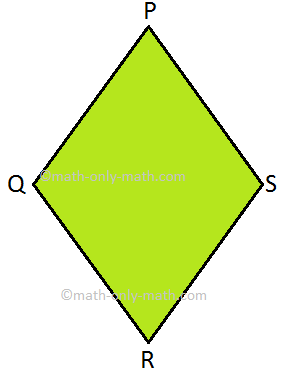
Diamond: It has 4 sides and 4 corners and area enclosed is called the region of diamond.
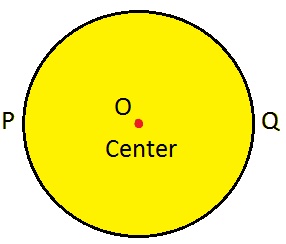
Circle: It has no sides and no corners. Area enclosed inside the circle is called the circular region.
Circle is a simple closed shape made up of curved lines.
It is round in shape with no sides and no corners.
O is the centre point of the circle.
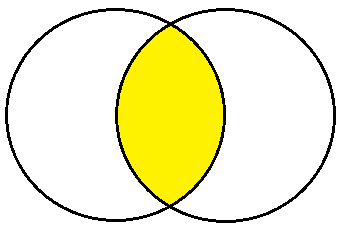
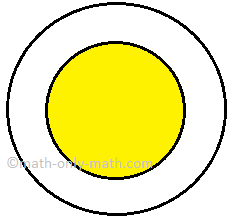
Region enclosed between the two circles:
(i) If two circles cross each other
Area enclosed between the two circles is shown by the shaded region.
(ii) If one circle lies inside the other circle
Area enclosed between the two circles is shown by the shaded region.
Difference between square and rectangle: Square has all sides equal and rectangle has opposite sides equal.
Note: In all figures number of sides and number of corners are the same. Figure with no corner have no sides.
Solid Figures:
We see many objects of solid shapes in our daily life. Some solid shapes have their own characteristics as under.
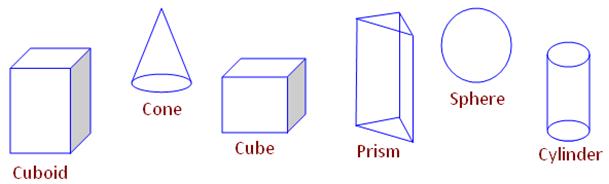
Solid shapes are 3-dimensional shapes. It means solid shapes have length, width and height. We know, about some of the geometrical shapes like cuboid, cube, cylinder, cone, sphere, triangular prism, etc. These are called solid figures or solids. They are also known as three dimensional (3-D) figures. They occupy space. In real life many objects which are seen in our surroundings have the shape of any one or many of the solids mentioned above.
Third grade geometry lessons encourage the kids to develop the basic concept to increase the knowledge on geometry.
Types of solid shapes:
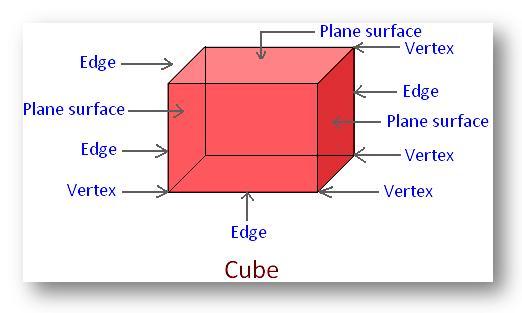
Cube:
Every face of a cube is a square.
It has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 corners (vertices).
All the sides of a cube are equal.
|
Number of faces = 6 Number of vertices = 8 Number of edges = 12 All surfaces are plane. All edges are not equal. Example: Dice |
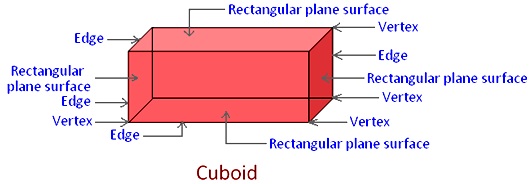
Cuboid:
Every face of a cube is a rectangle.
It has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 corners (vertices).
Opposite sides of a cuboid are equal.
|
Number of faces = 6 Number of vertices = 8 Number of edges = 12 All surfaces are plane. All edges are not equal. Example: Brick |
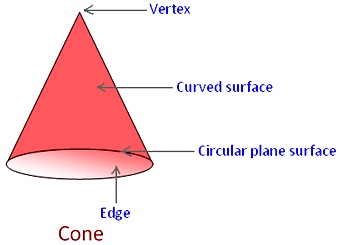
Cone:
It has one flat face and one curved face.
It has one edge and one corner (vertex).
|
Number of faces = 2 Number of vertices = 1 Number of edges = 1 Number of plane surfaces = 1 Number of curved surface = 1 Example: Birthday cap |
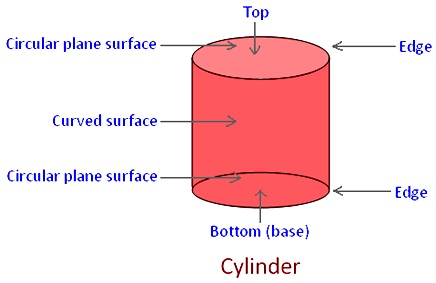
Cylinder:
It has 2 flat faces, both are circles and 1 curved face.
It has 2 edges and no corner/vertex
|
Number of faces = 3 Number of vertices = 0 Number of edges = 2 Number of plane surfaces = 2 Number of curved surface = 1 Example: Dust bin |
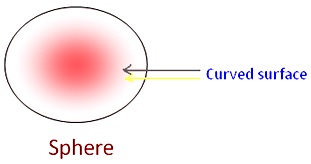
Sphere:
It has no flat face and has only a curved face.
It has no edges and corners.
|
Number of faces = 1 Number of vertices = 0 Number of edges = 0 Number of curved surface = 1 Example: Football |
Surfaces of the Solids: the two types of surfaces such as plane surfaces, curved surfaces.
Common solid figures: Some of the solid shapes such as cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone, sphere.
Important Points about Basic Geometrical Shapes:
We have learnt about solid shapes and plane shapes. Let us recall some important points about shapes.
1. Solid objects have different shapes like cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone and sphere.
2. Solid shapes have two types of surfaces; plane surfaces and curved surfaces. Objects like book, match box, ruler have plane surfaces, whereas objects like football, apple, watermelon have curved surfaces.
3. Plane shapes are made up of straight or curved lines. Rectangle, circle, square, triangle are plane shapes.
Questions and Answers on 3rd Grade Basic Shapes:
1. Choose the correct shapes:
(i)
(a) Cone; (b) Cylinder; (c) Sphere; (d) Cube
(ii)
(a) Cone; (b) Cylinder; (c) Sphere; (d) Cube
(iii)
(a) Cone; (b) Cylinder; (c) Sphere; (d) Cuboid
(iv)
(a) Cone; (b) Cylinder; (c) Sphere; (d) Cube
(v)
Answer:
1. (i) → (a)
(ii) → (c)
(iii) → (d)
(iv) → (b)
(v) → (d)
2. Choose the correct answer:
I. Shape of the base of a cuboid is a ……
(i) circle
(ii) rectangle
(iii) square
II. Shape of the bangle is like a …….
(i) circle
(ii) triangle
(iii) square
III. Shape of a postcard is like a …….
(i) circle
(ii) rectangle
(iii) square
IV. Shape of the base of a match box is like a ……
(i) circle
(ii) triangle
(iii) rectangle
V. Shape of the base of a bucket is like a ……
(i) circle
(ii) triangle
(iii) rectangle
Answer:
2. I → (ii)
II → (i)
III → (ii)
IV → (iii)
V → (i)
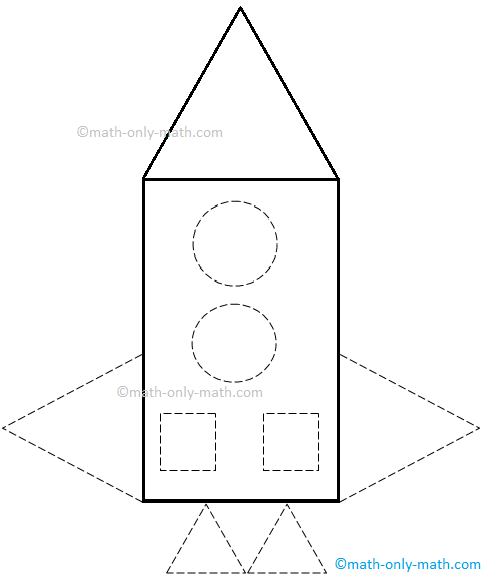
3. Trace and color the rocket. Answer the following questions.
My rocket has
(i) _____ circles
(ii) _____ rectangles
(iii) _____ squares
(iv) _____ triangles
Answer:
3. (i) 2 circles
(ii) 1 rectangle
(iii) 2 squares
(iv) 5 triangles
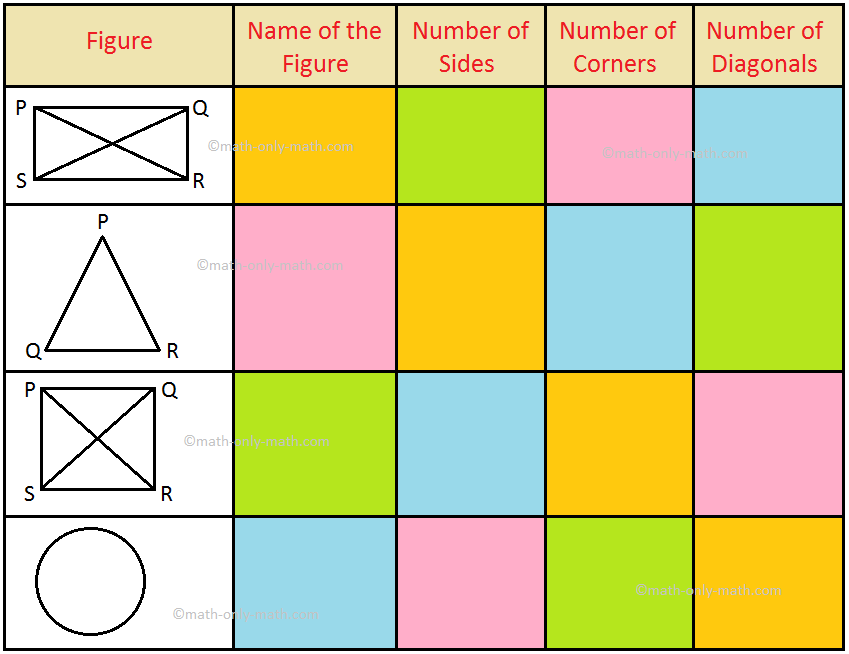
4. Complete the table.
Answer:
4. Rectangle - 4, 4, 2
Triangle - 3, 3, 0
Square - 4, 4, 2
Circle - 0, 0, 0
Related Concepts
● Geometrical Design and Models
From 3rd Grade Basic Shapes to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.












New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.