Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Divisibility Rules From 2 to 18
To find out factors of larger numbers quickly, we perform divisibility test. There are certain rules to check divisibility of numbers.
In divisibility rules (test) we find whether a given number is divisible by another number, we perform actual division and see whether the remainder is zero or not.
A number is said to be exactly divisible by another number if there is no remainder left We use the test of divisibility to know if a given number is divisible by another given number or not. This is done without actually dividing the number. Let's learn some simple divisibility rules:
We will recall how to apply the test for divisibility by 2, 3, 4, 5, 9 and 10.
But divisibility tests of a given number by any of the number 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 can be perform simply by examining the digits of the given number.
Divisibility Rules:
These tests are as under:
Divisibility by 2
A number is divisible by 2 if its units place is either 0 or multiple of 2.
In other words, a number is divisible by 2, if the digit at ones place is an even number, that is the number ends in 0, 2, 4 or 8.
For example:
346, 3818, 14626, 100, 1994, 1252
All these number is divisible by 2 because their units place in multiple of 2.
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility Rule for 2 Video
Divisibility by 3
A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of digits is a multiple of 3.
In other words, a number is divisible by 3, if sum of all its digits is divisible by 3.
For example:
79851 is divisible by 3 as the sum of its digits, i.e., 7 + 9 + 8 + 5 + 1 = 30 is divisible by 3.
Divisibility Rule for 3 Video
Observe the table of 3 carefully. We find the multiples in this table
|
Sum of digits of the multiples of 3 | |
|
3 × 1 = 3 |
3 |
|
3 × 2 = 6 |
6 |
|
3 × 3 = 9 |
9 |
|
3 × 4 = 12 |
1 + 2 = 3 |
|
3 × 5 = 15 |
1 + 5 = 6 |
|
3 × 6 = 18 |
1 + 8 = 9 |
|
3 × 7 = 21 |
2 + 1 = 3 |
|
3 × 8 = 24 |
2 + 4 = 6 |
|
3 × 9 = 27 |
2 + 7 = 9 |
|
3 × 10 = 30 |
3 + 0 = 3 |
Sum of the digits in the multiples in always divisible by 3. Therefore, we can say that
If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, the number will be divisible by 3.
Let us check a large number for its divisibility by 3.
1. Take the number 5,90,121
Sum of digits: 5 + 9 + 0 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 18
18 is exactly divisible by 3.
Therefore, the number 5,90,121 is divisible by 3.
2. Take the number 8,94,322
Sum of digits: 8 + 9 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 2 = 28
28 is not divisible by 3
Therefore, the number 8,94,322 is not divisible by 3.
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility by 4
A number is divisible by 4 if the number formed by its digits in tens and units place is divisible by 4.
In other words, a number is divisible by 4, if the number formed by its last 2 digits is divisible by 4.
For example:
88312 is divisible by 4 because the number formed by its last two digits i.e., 12 is divisible by 4.
Divisibility Rule for 4 Video
We know that 100 ÷ 4 = 25, i.e., 100 is divisible by 4.
All the multiples of 100, i.e., 100, 200, 300, ...., 900 will also be divisible by 4.
Now let us check the divisibility of a number like 652.
We break 652 as 600 + 52 (sum of hundreds and ones).
As 600 is divisible by 4, we are left to check the divisibility of only 52 by 4.
Because 52 ÷ 4 gives quotient = 13, remainder = 0, we can say that 52 is divisible by 4.
Therefore, 652 which is 600 + 52 will also be divisible by 4.
This leads us to say that:
A number is divisible by 4, if the number formed by its last two digits is divisible by 4.
To verify this rule, let us apply this rule to a number which is not divisible by 4.
We take the number 214, which is not divisible by 4.
We see that the number formed by its last two digits is 14, which is not divisible by 4.
Therefore, 214 will not be divisible by 4.
Divisibility by 5
A number is divisible by 5 if its units place is 0 or 5.
In other words, a number is divisible by 5, if it ends in 0 or 5.
For example:
1. 75325 is divisible by 5 as its last digit is 5.
2. 3,220; 1,240; 8,155; 4,440; 2,345; 8,440. These numbers are divisible by 5 as each of them has either 0 or 5 in the end.
Divisibility Rule for 5 Video
A number is exactly divisible by 5 if the digit on the ones place is either 0 or 5.
Divisibility by 6
A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by 2 and 3 both.
For example:
85806 is divisible by 6 because it is an even number so divisible by 2 and sum of its digits, i.e., 8 + 5 + 8 + 0 + 6 = 27, which is divisible by 3.
Divisibility Rule for 6 Video
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility by 7
A number of 2 digits is divisible by 7 because 3 × 6 + 3 = 21. 21 is divisible by 7.
A number of three or more digits is divisible by 7 if the sum of the numbers formed by the last two digits and twice the number formed by the remaining digits is divisible by 7.
For example:
(i) 574 is divisible by 7 because 74 + 5 × 2 = 74 + 10 = 84 is divisible by 7.
(ii) 2268 is divisible by 7 because 68 + 22 × 2 = 68 + 44 = 112 is divisible by 7.
Divisibility Rule for 7 Video
Alternate method for divisible by 7:
To check whether a number is divisible by 7, we take the last digit of the number and double it. Subtract this new number from the truncated number formed by the remaining digits and continue this process until only one digit remains. If the digit is 0 or 7, then the given number is divisible by 7.
For example:
Is 5502 divisible by 7?
Solution:
5502
Double the last or unit digit i.e., 4
Subtract 4 from the remaining number
550 – 4 = 546
Double the last or unit digit i.e., 12
Subtract 12 from the remaining number
54 – 12 = 42
Double the last or unit digit i.e., 4
Subtract 4 from the remaining number
4 – 4 = 0
Therefore, 5502 is divisible by 7.
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility by 8.
A number is divisible by 8 if the numbers formed by the last three digits is divisible by 8.
For example:
54136 is divisible by 8 because if the numbers formed by the last three digits i.e., 136 is exactly divisible by 8.
136 ÷ 8 = 17, Remainder = 0
Divisibility by 9
A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
For example:
3888 is divisible by 9 because 3 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 27 is divisible by 9.
Let us write the multiples of 9. They are 9, 18, 27, 36, 45,....
If we add the digits of each multiple of 9, we notice that their sum is always 9 or 18 or multiple of 9, when we take larger multiples of 9.
We can write the rule:
|
Multiples of 9 |
Sum of Digits of the Multiples of 9 |
|
9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81 90 99 108 |
0 + 9 = 9 1 + 8 = 9 2 + 7 = 9 3 + 6 = 9 4 + 5 = 9 5 + 4 = 9 6 + 3 = 9 7 + 2 = 9 8 + 1 = 9 9 + 0 = 9 9 + 9 = 18 1 + 0 + 8 = 9 |
Divisibility Rule for 7 Video
A number will be divisible by 9, if the sum of the digits of the given number is divisible by 9.
For example, let us take the number 9,25,218
Sum of its digits is 9 + 2 + 5 + 2 + 1 + 8 = 27
Since 27 is divisible by 9, we say that 9,25,218 is divisible by 9.
Divisibility by 10.
A number is divisible by 10 if it has zero (0) in its units place.
In other words, a number is divisible by 10, if all numbers ends in 0.
For example:
80, 210, 790, 9990, 1000, 2658970 are divisible by 10 because all numbers ends in 0.
Divisibility Rule for 10 Video
A number which has 0 at one's place is divisible by 10.
For example, 20, 40, 160, 2480, all are divisible by 10.
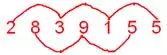
Divisibility by 11.
A number is divisible by 11 if the sum of the digits in the odd places and the sum of the digits in the even places difference is a multiple of 11 or zero.
For example:
Sum of the digits in the even places = 5 + 9 + 8 = 22
Sum of the digits in the odd places = 5 + 1 + 3 + 2 =11
Difference between the two sums = 22 – 11= 11
11 is divisible by 11.
Hence, 2839155 is divisible by 11.
In other words,
To check whether a number is divisible by 11, we find the sum of the digits in the even places and the odd places separately. Now, check the difference between the two sums if it is 0 or divisible by 11, then the given number is divisible by 11.
For example:
Is 5676 divisible by 11?
Solution:
Sum of digits in even places = 6 + 6 = 12
Sum of digits in odd places = 5 + 7 = 12
Difference = 0
Therefore, 5676 is divisible by 11.
Notes:
A number is divisible by another number if it is also by its co-prime factors.
The co-prime factors of 15 are 3 and 5.
Divisibility by 12:
A number is divisible by 12, if it is divisible by co-prime 12 i.e., 3 and 4.
For example:
5436 is divisible by 12 because it is divisible by both 3 and 4.
5436 ÷ 3 = 1812, Remainder = 0
Again, 5436 ÷ 4 = 1359, Remainder = 0
Divisibility by 13:
Divisibility by 15:
A number is divisible by 15, if it is divisible by co-prime 15 i.e., 3 and 5.
For example:
1875 is divisible by 15 because it is divisible by both 3 and 5.
1875 ÷ 3 = 625, Remainder = 0
Again, 1875 ÷ 5 = 375, Remainder = 0
Divisibility by 18:
A number is divisible by 18, if it is divisible by co-prime 18 i.e., 2 and 9.
For example:
2322 is divisible by 18 because it is divisible by both 2 and 9.
2322 ÷ 2 = 1161, Remainder = 0
Again, 2322 ÷ 9 = 258, Remainder = 0
Divisibility by 45:
A number is divisible by 45, if it is divisible by co-prime 45 i.e., 5 and 9.
For example:
5805 is divisible by 45 because it is divisible by both 5 and 9.
5805 ÷ 5 = 1161, Remainder = 0
Again, 5805 ÷ 9 = 645, Remainder = 0
Let us summarise what we have learnt.
Divisibility Rules from 2 to 10:
|
A Number is Divisible by |
Rule |
|
2 |
if the number ends in 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8. (an even number) |
|
3 |
if the sum of the digits is divisible by 3. |
|
4 |
if the number formed by the last two digits is divisible by 4 or the last two digits are zeroes. |
|
5 |
if the number ends in 0 or 5. |
|
6 |
if the number is divisible by 2 and 3. |
|
7 |
double the last digit of the number and then subtract it from the remaining number. If the result is divisible by 7, then the original number will also be divisible by 7. |
|
8 |
if the numbers formed by the last three digits is divisible by 8. |
|
9 |
if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9. |
|
10 |
if the last digit is 0. |
Frequently Asked Questions on Divisibility Rules:
1. What is Test of Divisibility?
Answer:
In order to find whether or not a number is divisible by another number, we perform actual division and see whether the remainder is zero or not. But this method is time consuming. Therefore, the test of divisibility explains whether or not the given number is divisible by the other number without actual division.
2. How to check if a number is divisible by 2?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 2 if its ones digit is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.
For example:
8672, 8888, 1900, 45664, 147896 etc., are divisible by 2.
In 8672, 8888, 1900, 45664, 147896 the ones digits are 2, 8, 0, 4, 6 respectively.
Thus the above numbers are divisible by 2.
Note: The number divisible by 2 are called even numbers.
3. How to check if a number is divisible by 3?
Answer:
A number is divisible 3, if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
For example:
60891, 15924 etc. are divisible by 3.
In 60891: 6 + 0 + 8 + 9 + 1 = 24, which is divisible by 3.
In 15924: 1 + 5 + 9 + 2 +4 = 21, which is divisible by 3.
4. What is the divisibility rules of 4?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 4, if the number formed by the two right-most digits (ones & tens) is a multiple of 4 (or divisible by 4), or both digits are 0.
For example:
93812, 199416, 31520 10028, 2500 etc. are divisible by 4
In 93812: 12 is divisible by 4.
In 99416: 16 is divisible by 4.
In 31520: 20 is divisible by 4.
In 10028: 28 is divisible by 4.
In 2500: 00 i.e., 0 is divisible by 4.
Note: A number which is divisible by 4 is also divisible by 2.
5. How to check if a number is divisible by 5?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 5, if the digit at its ones place is either 5 or 0.
For example:
5120, 9965, 89920, 350090 etc. are divisible by 5.
6. How to check if a number is divisible by 6?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 6, if the number is even and sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
For example:
5922, 6060, 7182 etc. are divisible by 6.
In 5922: 5922 is even and the sum of its digits = 5 + 9 + 9 + 2 + 2 = 27, which is divisible by 3.
Therefore, the number 5922 is divisible by 6.
In 6060: 6060 is even and the sum of its digits = 6 + 0 + 6 + 0 = 12, which is divisible by 3.
Therefore, the number 6060 is divisible by 6.
In 7182: 7182 is even and the sum of its digits = 7 + 1 + 8 + 2 = 18, which is divisible by 3.
Therefore, the number 7182 is divisible by 6.
Note: A number divisible by 6 is also divisible by 2 and 3.
7. How to check if a number is divisible by 7?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 7, if the difference between twice the last digit and the number formed by other digits is either 0 or a multiple by 7.
For example:
889, 2975, 1617, 392 etc are divisible by 7.
In 889: Last digit = 9
Twice the last digit = 18
Difference between 88 and 18 = 70, which is divisible by 7.
Hence, 889 is divisible by 7.
In 2975: Last digit = 5
Twice the last digit = 10
Difference between 297 and 10 = 287, which is divisible by 7.
Hence, 2975 is divisible by 7.
In 1617: Last digit = 7
Twice the last digit = 14
Difference between 161 and 14 = 147, which is divisible by 7.
Hence, 1617 is divisible by 7.
In 392: Last digit = 2
Twice the last digit = 4
Difference between 39 and 4 = 35, which is divisible by 7.
Hence, 392 is divisible by 7.
8. How to check if a number is divisible by 8?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 8, if the number formed by its right-most three digits (ones, tens, hundreds) is divisible by 8.
For example:
564108, 100024, 987048, etc are divisible by 8.
In 564108, the number formed by its right-most three digits i.e., 108 is divisible by 8.
So, the number 564108 is divisible by 8.
In 100024, the number 024 or 24 is divisible by 8.
Therefore, the number 100024 is divisible by 8.
In 987048, the number 048 or 48 is divisible by 8.
Therefore, the number 987048 is divisible by 8.
Note: A number divisible by 8 is also divisible by 2 and 4.
9. What is the divisibility rule of 9?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 9, if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
For example:
1899, 666666, 5886 etc are divisible by 9.
In 1899: The sum of the digits = 1 + 8 + 9 + 9 = 27, which is divisible by 9.
Hence, the number 1899 is divisible by 9.
In 666666: The sum of the digits = 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 36, which is divisible by 9.
Hence, the number 666666 is divisible by 9.
In 5886: The sum of the digits = 5 + 8 + 8 + 6 = 27, which is divisible by 9.
Hence, the number 5886 is divisible by 9.
Note: A number divisible by 9 is also divisible by 3.
10. How to check if a number is divisible by 10?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 10 if the digit at the ones place of the number is 0.
For example:
1000, 9950, 39280, etc. are divisible by 10.
All the above numbers ones place is zero (0)
Thus, 1000, 9950, 39280 are divisible by 10.
Note: A number which is divisible by 10 is also divisible by 2 and 5.
11. What is the divisibility rule of 11?
Answer:
A number is divisible by 11, if the difference between the sums of alternate digits is either 0 or a multiple of 11.
For example:
53856, 6446, 764852, etc. are divisible by 11.
In 53856; the sum of digits of odd places from the left = 6 + 8 + 5 = 19. and the sum of digits at even places from the left = 5 + 3 = 8.
The difference between the sum of digits at odd and even place = 19 – 8 = 11, which is divisible by 11.
Therefore, 53856 is divisible by 11.
In 6446: the sum of digits of odd places from the left = 6 + 4 = 10. and the sum of digits at even places from the left = 4 + 4 = 10.
The difference between the sum of digits at odd and even place = 10 – 10 = 0, which is divisible by 11.
Therefore, 6446 is divisible by 11.
In 764852; the sum of digits of odd places from the left = 2 + 8 + 6 = 16. and the sum of digits at even places from the left = 5 + 4 + 7 = 16.
The difference between the sum of digits at odd and even place = 16 – 16 = 0, which is divisible by 11.
Therefore, 764852 is divisible by 11.
Worksheet on Divisibility Rules:
1. Write of the following numbers are divisible by 2?
(i) 3,276
(ii) 4,285
(iii) 9,292
(iv) 4,280
(v) 9,287
(vi) 2,222
(vii) 8,523
(viii) 1,010
2. Write the following numbers are divisible by 3?
(i) 3,603
(ii) 1,110
(iii) 8,521
(iv) 3,232
(v) 5,505
(vi) 3,006
(vii) 1,732
(viii) 4,013
3. Which of the following number are divisible by 9?
(i) 3,051
(ii) 9,132
(iii) 9,181
(iv) 3,033
(v) 4,236
(vi) 7,002
(vii) 5,409
(viii) 2,151
4. Write of the following numbers are divisible by 10?
(i) 1,010
(ii) 1,855
(iii) 4,320
(iv) 1.000
(v) 3,500
(vi) 6,055
(vii) 9,205
(viii) 8,530
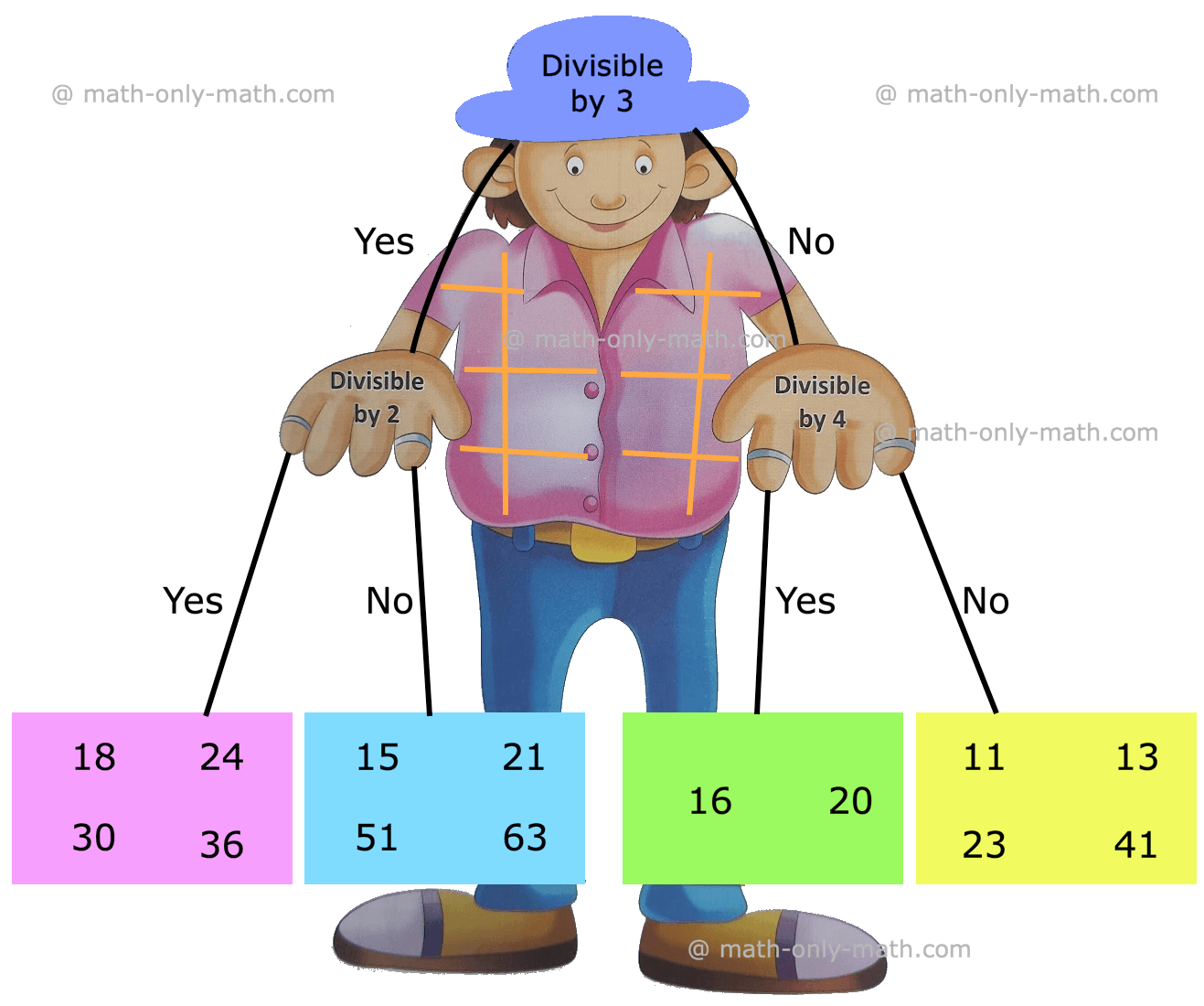
5. Look at the following numbers and write them in the correct boxes.
15, 23, 63, 36, 30, 16, 20, 11, 18, 21, 51, 41, 24, 13
(i) Numbers going into the pink box are divisible by _____ and _____.
(ii) Numbers divisible by 3 and not by 2 go to the _____ box.
(iii) Numbers going into the green box are divisible by _____ and _____.
(iv) Numbers going into the yellow box are not divisible by _____ and _____.
Answer:
1. (i) Yes
(ii) No
(iii) Yes
(iv) Yes
(v) No
(vi) Yes
(vii) No
(viii) Yes
2. (i) Yes
(ii) Yes
(iii) No
(iv) No
(v) Yes
(vi) Yes
(vii) No
(viii) No
3. (i) Yes
(ii) No
(iii) No
(iv) Yes
(v) NO
(vi) Yes
(vii) Yes
(viii) Yes
4. (i) Yes
(ii) No
(iii) Yes
(iv) Yes
(v) Yes
(vi) No
(vii) No
(viii) Yes
5.
(i) Numbers going into the pink box are divisible by 2 and 3.
(ii) Numbers divisible by 3 and not by 2 go to the Blue box.
(iii) Numbers going into the green box are divisible by 2 and 4.
(iv) Numbers going into the yellow box are not divisible by 3 and 4.
Problems on Divisibility Rules
Worksheet on Divisibility Rules
5th Grade Math Problems
From Divisibility Rules to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
Jul 11, 25 02:14 PM
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circl… -
Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Jul 09, 25 01:29 AM
Construction of a Circle when the length of its Radius is given. Working Rules | Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be… -
Combination of Addition and Subtraction | Mixed Addition & Subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:32 PM
We will discuss here about the combination of addition and subtraction. The rules which can be used to solve the sums involving addition (+) and subtraction (-) together are: I: First add -
Addition & Subtraction Together |Combination of addition & subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:23 PM
We will solve the different types of problems involving addition and subtraction together. To show the problem involving both addition and subtraction, we first group all the numbers with ‘+’ and… -
5th Grade Circle | Radius, Interior and Exterior of a Circle|Worksheet
Jul 08, 25 09:55 AM
A circle is the set of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is known












New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.