Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry
Simple math formula on trigonometry is given in such an order that students can easily get the formula.
Trigonometry
● Measurement of Trigonometrical Angles:
(i) The angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle is called a radian.
(ii) A radian is a constant angle.
One radian = (2/π) rt. angle = 57°17’44.8” (approx.)
(iii) 1 rt. angle = 90° ; 1° = 60’ ; 1‘ = 60”.
(iv) 1 rt. angle = 100ᵍ ; 1ᵍ = 100’ ; 1‵ = 100‶.
(v) πᶜ 180° = 200ᵍ.
(vi) The circumference of a circle of radius r is 2πr where π is a constant; approximate value of π is ²²/₇; more accurate value of π is 3.14159 (approx.).
(vii) If Θ be the radian measure of an angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius r by an arc of length s then Θ = ˢ/₀ or, s = rΘ.
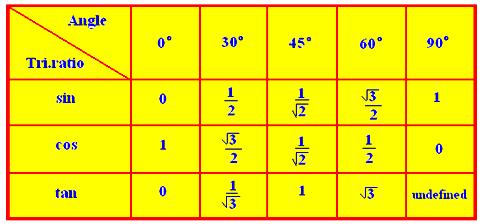
● Trigonometrical Ratios of some Standard Angles:
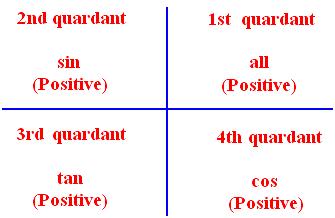
● Trigonometrical Ratios for Associated Angles:
(ii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an even integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = tan Θ or, (- tan Θ).
(iii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an odd integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cot ф or (- cot Θ).
● Compound Angles:
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B.
(ii) sin ( A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B.
(iii) cos (A + B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(iv) cos (A - B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(v) sin (A + B) sin (A - B) = sin² A - sin² B = cos² B - cos² A.
(vi) cos (A + B) cos (A - B) = cos² A - sin² B = cos² B - sin² A.
(vii) tan (A+ B) = (tan A + tan B)/(1 - tan A tan B).
(viii) tan (A - B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1 + tan A tan B).
(ix) cot (A + B) = (cot A cot B - 1)/(cot B + cot A).
(x) cot (A - B) = (cot A cot B + 1)/(cot B - cot A).
(xi) tan (A + B + C) = {(tan A + tan B + tan C) - (tan A tan B tan C)}/(1 - tan A tan B - tan B tan C - tan C tan A).
(xii) 2 sin A cos B = sin (A + B) + sin(A - B).
(xiii) 2 cos A sin B = sin (A + B ) - sin (A - B).
(xiv) 2 cos A cos B = cos (A + B ) + cos (A - B).
(xv) 2 sin A sin B = cos (A - B) - cos (A + B).
(xvii) sin C - sin D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
(xviii) cos C + cos D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 cos (C - D)/2.
(xix) cos C - cos D = 2 sin (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
● Multiple Angles:
(i) sin 2Θ = 2 sin Θ cos Θ.
(ii) cos 2Θ = cos² Θ - sin² Θ.
(iii) cos 2 Θ = 2 cos² Θ - 1.
(iv) cos 2Θ = 1 - 2 sin² Θ.
(v) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 cos² Θ.
(vi) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 sin² Θ.
(vii) tan² Θ = (1 - cos 2Θ)/(1 + cos 2Θ).
(viii) sin 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ)
(ix) cos 2Θ = (1 - tan² Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ).
(x) tan 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 - tan² Θ).
(xi) sin 3Θ = 3 sin Θ - 4 sin³ Θ.
(xii) cos 3ф = 4 cos³ Θ - 3 cos Θ.
(xiii) tan 3Θ = (3 tan Θ - tan³ Θ)/(1 - 3 tan² Θ).
● Submultiple Angles:
(i) sin Θ = 2 sin (Θ/2) cos (Θ/2).
(i) a/(sin A) = b/(sin B) = c/(sin C) = 2R. (xiii) r = ∆/s. ● Formula
11 and 12 Grade Math Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information
about Math Only Math.
Use this Google Search to find what you need.
(ii) cos Θ = cos² (Θ/2) - sin² (Θ/2).
(iii) cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2) - 1.
(iv) cos ф = 1 - 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(v) 1 + cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2).
(vi) 1 - cos Θ = 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(vii) tan² (Θ/2) = (1 - cos Θ)/(1 + cos Θ).
(viii) sin Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(ix) cos Θ = [1 - tan² (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(x) tan Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 - tan² (Θ/2)].
(xi) sin Θ = 3 sin (Θ/3) - 4 sin³ (Θ/3).
(xii) cos Θ = 4 cos³ (Θ/3) - 3 cos (Θ/2).
(xiii) (a) sin 15° = cos 75° = (√3 - 1)/(2√2).
(b) cos 15° = sin 75° = (√3 + 1)/(2√2).
(c) tan 15° = 2 - √3.
(d) sin 22 ½° = √(2 - √2).
(e) cos 22 ½° = ½ [√(2 + √2)].
(f) tan 22 ½° = √2 - 1.
(g) sin 18 ° = (√5 - 1)/4 = cos 72°.
(h) cos 36° = cos 72° = (√5 + 1)/4.
(i) cos 18° = sin 72° = ¼ [√(10 + 2√5)].
(j) sin 36° = cos 54° = ¼ [√(10 - 2√5)].
● General Solutions:
(i) (a) If sin Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If sin Θ = 1 then, Θ = (4n + 1)(π/2).
(c) If sin ф = -1 then, Θ = (4n - 1)(π/2).
(d) If sin Θ = sin α then, Θ = nπ + (-1)ⁿ α.
(ii) (a) If cos Θ = 0 then, Θ = (2n + 1)(π/2).
(b) If cos Θ = 1 then, Θ = 2nπ.
(c) If cos Θ = -1 then, Θ = (2n + 1)π.
(d) If cos Θ = cos α then, Θ = 2nπ ± α.
(ii) (a) If tan Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If tan Θ = tan α then, Θ = 2nπ + α where, n = 0 or any integer.
● Inverse Circular Functions:
(i) sin (sin-1 x) = x ; cos (cos-1 x) = x ; tan (tan-1 x) = x.
(ii) sin-1 (sin Θ) = Θ ; cos-1 (cos Θ) = Θ ; tan-1 (tan Θ) = Θ.
(iii) sin-1 x = cosec-1 (1/x) = cos-1 [√(1 - x2)] = sec-1 [1/√(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [x/√(1 - x2)] = cot-1 [√(1 - x2)/x].
(iv) sin-1 x + cos-1 x = π/2 ; sec-1 x + cosec-1 x = π/2 ;
tan-1 x + cot-1 x = π/2.
(v) (a) tan-1 x + tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x + y)/(1 - xy)]
(b) tan-1 x - tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x - y)/(1 + xy)]
(vi) (a) sin-1 x + sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2) + y√(1 - x2)}
(b) sin-1 x - sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2 ) - y√(1 - x2)}
(vii) (a) cos-1 x + cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy - √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}
(b) cos-1 x - cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy + √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}.
(viii) 2 tan-1 x = sin-1 [2x/(1 + x2)] = cos-1 [(1 - x2)/(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [2x/(1 - x2)].
(ix) tan-1 x + tan-1 y + tan-1 z = tan-1 [(x + y + z - xyz)/(1 - xy - yz - zx)]
(x) sin-1 x and cos-1 x are defined when -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 ; sec-1 x and cosec-1 x are defined when Ι x Ι ≥ 1 ; tan-1 x and cot-1 x are defined
when - ∞ < x < ∞.
(xi) If principal values of sin-1 x, cos-1 x and tan-1 x be α, β and γ respectively, then -π/2 ≤ α ≤ π/2, 0 ≤ β ≤ π and -π/2 ≤ γ ≤ π/2.
● Properties of Triangle:
(ii) a = b cos C + c cos B ; b = c cos A + a cos C ; c = a cos B + b cos A.
(iii) cos A = (b² + c² - a²)/2bc ; cos B = (c² + a² - b²)/2ca ;
cos C = (a² + b² - c²)/2ab
(iv) tan A = [(abc)/R] ∙[ 1/(b² + c² - a²)]
tan B = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(c² + a² - b²)]
tan C = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(a² + b² - c²)].
(v) sin (A/2) = √[(s - b) (s - c)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/(ca)].
sin C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/(ab)].
cos A/2 = √[s (s - a)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[s (s - b)/(ca)].
cos C/2 = √[s (s - c)/(ab)].
tan A/2 = √[(s - b) (s - c)/{s(s - c)}].
tan B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/{s(s - b)}].
tan C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/{s(s - c)}].
(vi) tan [(B - C)/2] = [(b - c)/(b + c)] cot (A/2).
tan [(C - A)/2] = [(c - a)/(c + a)] cot (B/2).
tan [(A - B)/2] = [(a - b)/(a + b)] cot (C/2).
(vii) ∆ = ½ [bc sin A] = ½ [ca sin B] = ½ [ab sin C].
(viii) ∆ = √{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}.
(ix) R = ᵃᵇᶜ/₄₀.
(x) tan (A/2) = {(s - b)(s - c)}/∆.
tan (B/2) = {(s - c)(s - a)}/∆.
tan (C/2) = {(s - a)(s - b)}/∆
(xi) cot A/2 = {s(s - a)}/∆.
cot (B/2) = {s(s - b)}/∆.
cot (C/2) = {s(s - c)}/∆.
(xiv) r = 4R sin (A/2) sin (B/2) sin (C/2).
(xv) r = (s - a) tan (A/2) = (s - b) tan (B/2) = (s - c) tan (C/2).
(xvi) r₁ = ∆/(s - a) ; r₂ = ∆/(s - b); r₃ = ∆/(s - c) .
(xvii) r₁ = 4 R sin (A/2) cos (B/2) cos (C/2).
(xviii) r₂ = 4R sin (B/2) cos (C/2) cos (A/2).
(xix) r₃ = 4 R sin (C/2) cos (A/2) cos (B/2).
(xx) r₁ = s tan (A/2) ; r₂ = s tan (B/2) ; r₃ = s tan (C/2).
From Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry to HOME PAGE


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.