Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
How to Solve Linear Equations?
How to solve linear equations?
Step-by-step instructions are given in the examples of solving linear equations. We will learn how to solve one variable linear equations using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Examples on solving linear equations:
1. Solve the equation 2x - 1 = 14 - x and represent the solution graphically.
Solution:
2x - 1 = 14 - x
⇒ 2x + x = 14 + 1
(Transfer -x from right hand side to the left hand side, then negative x changes to positive x. Similarly again transfer -1 from left hand side to the right hand side, then negative 1 change to positive 1.
Therefore, we arranged the variables in one side and the numbers in the other side.)
⇒ 3x = 15
⇒ 3x/3 = 15/3 (Divide both sides by 3)
⇒ x = 5
Therefore, x = 5 is the solution of the given equation.
The solution may be represented graphically on the number line by graphing linear equations.
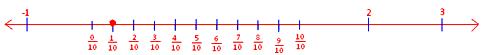
2. Solve the equation 10x = 5x + 1/2 and represent the solution graphically.
Solution:
10x = 5x + 1/2
⇒ 10x – 5x = 1/2
(Transfer 5x from right hand side to the left hand side, then positive 5x changes to negative 5x).
⇒ 5x = 1/2
⇒ 5x/5 = 1/2 ÷ 5 (Divide both sides by 5)
⇒ x = 1/2 × 1/5
⇒ x = 1/10
Therefore, x = 1/10 is the solution of the given equation.
The solution may be represented graphically on the number line.
3. Solve the equation 6(3x + 2) + 5(7x - 6) - 12x = 5(6x - 1) + 6(x - 3) and verify your answer
Solution:
6(3x + 2) + 5(7x - 6) - 12x = 5(6x - 1) + 6(x - 3)
⇒ 18x + 12 + 35x - 30 - 12x = 30x - 5 + 6x - 18
⇒ 18x + 35x - 12x + 12 - 30 = 30x + 6x - 5 - 18
⇒ 41x - 18 = 36x - 23
⇒ 41x - 36x = - 23 + 18
⇒ 5x = -5
⇒ x = -5/5
⇒ x = -1
Therefore, x = -1 is the solution of the given equation.
Now we will verify both the sides of the equation,
6(3x + 2) + 5(7x - 6) - 12x = 5(6x - 1) + 6(x - 3) are equal to each other;
Verification:
L.H.S. = 6(3x + 2) + 5(7x - 6) - 12x
Plug the value of x = -1 we get;
= 6[3 × (-1) + 2] + 5 [7 × (-1) - 6] - 12 × (-1)
= 6[-3 + 2] + 5[-7 - 6] + 12
= 6 × (-1) + 5 (-13) + 12
= - 6 - 65 + 12
= -71 + 12
= -59
Verification:
R.H.S. = 5(6x - 1) + 6(x - 3)
Plug the value of x = - 1, we get
= 5[6 × (-1) - 1] + 6[(-1) - 3]
= 5(-6 - 1) + 6(-1 -3)
= 5 × (-7) + 6 × (-4)
= - 35 - 24
= - 59
Since, L.H.S. = R.H.S. hence verified.
What is cross multiplication?
The process of multiplying the numerator on the left hand side with the denominator on the right hand side and multiplying the denominator on left hand side with the numerator on right hand side is called cross multiplication.
And then equating both the products we get the linear equation.
On solving it we get the value of variable for which L.H.S. = R.H.S. Then, it is an equation of the form.
(mx + n)/(ox + p) = q/r where m, n, o, p, q, r are numbers and ox + p ≠ 0
⇒ r(mx + n) = q(ox + p)
It’s an equation in one variable x but it is not a linear equation as L.H.S. is not a linear polynomial.
We convert this into linear equation by the method of cross multiplication and further solve it step-by-step.
Examples on cross multiplication while solving linear equations:
1. (3x + 4)/5 = (2x - 3)/3
Solution:
(3x + 4)/5 = (2x - 3)/3
On cross multiplication, we get;
⇒ 3(3x + 4) = 5(2x - 3)
⇒ 9x + 12 = 10x - 15
⇒ 9x - 10x = -15 - 12
⇒ -x = -27
⇒ x = 27
Verification:
L.H.S. = (3x + 4)/5
Plug x = 27, we get;
(3 × 27 + 4)/5
= 81 + 4/5
= 85/5
= 17
Verification:
R.H.S. = (2x - 3)/3
Plug x = 27, we get;
(2 × 27 - 3)/3
= 54 - 3/3
= 51/3
= 17
Since, L.H.S. = R.H.S. hence verified.
2. Solve 0.8 - 0.28x = 1.16 - 0.6x
Solution:
0.8 - 0.28x = 1.16 - 0.6x
⇒ 0.6x - 0.28x = 1.16 - 0.8
⇒ 0.32x = 0.36
⇒ x = 0.36/0.32
⇒ x = 36/32
⇒ x = 9/8
Therefore, 9/8 is the required solution.
Verification:
L.H.S. = 0.8 - 0.28x
Plug x = 9/8, we get;
= 0.8 - 0.28 × 9/8
= 8/10 - 2̶8̶/100 × 9/8̶
= 8/10 - 63/200
= (160 - 63)/200
= 97/200
Verification:
R.H.S. = 1.16 - 0.6x
= 1.16 - 0.6 × 9/8
= 116/100 - 6̶/10 × 9/8̶
= 116/100 - 27/40
= (232 - 135)/200
= 97/200
Since, L.H.S. = R.H.S. hence verified.
● Equations
How to Solve Linear Equations?
Problems on Linear Equations in One Variable
Word Problems on Linear Equations in One Variable
Practice Test on Linear Equations
Practice Test on Word Problems on Linear Equations
● Equations - Worksheets
Worksheet on Word Problems on Linear Equation
8th Grade Math Practice
From How to Solve Linear Equations? to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.