Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Polynomial
An expression of the form a0xn + a1xn−1 + a2xn−2 + a3xn−3 + ..... + an where a0, a1, a2, a3, ....., an are given numbers (real or complex), n is a non-negative integer and x is a variable is called a polynomial in x.
a0, a1, a2, a3, etc., are called the coefficients of xn, xn−1, xn−2, xn−3, etc., respectively.
a0xn, a1xn−1, a2xn−2, a3xn−3, ....., an are called the terms of the polynomial.
an is called the constant term. Clearly, it is also the coefficient of x0.
If a0 ≠ 0, the polynomial is said to be of degree n and the term a0xn is called the leading term.
The general form of a polynomial of degree 1 is a0x + a1where a0 ≠ 0.
The general form of a polynomial of degree 2 is a0x2 + a1x + a2 where a0 ≠ 0.
A non-zero constant a0 itself is said to be a polynomial of degree 0 while a polynomial all of whose coefficients are zero is said to be a zero polynomial and is denoted by 0 and no degree is assigned to it.
Since a polynomial is an expression containing the variable x, it is denoted by f(x), p(x) or g(x) etc.
The value of a polynomial f(x) for x = a where a is real
number or a complex number is denoted by f(a).
In particular, if the coefficients a0, a1, a2,
a3, .... of a polynomial f(x) be all real numbers, the polynomial f(x)
is said to be a real polynomial.
Examples of polynomial:
(i) 7x2 + 5x - 3 is a polynomial in x of degree 2 or a quadratic polynomial in x.
(ii) 4x3 + 9x2 - 4x + 2 is a polynomial in x
of degree 3 or a cubic polynomial in x.
(iii) 5 - 2x53 + 9x2 is an expression but not a polynomial, since it contains a term containing x53 , where 53 is not a non-negative integer.
● Factorization
- Polynomial
- Polynomial Equation and its Roots
- Division Algorithm
- Remainder Theorem
- Problems on Remainder Theorem
- Factors of a Polynomial
- Worksheet on Remainder Theorem
- Factor Theorem
- Application of Factor Theorem
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
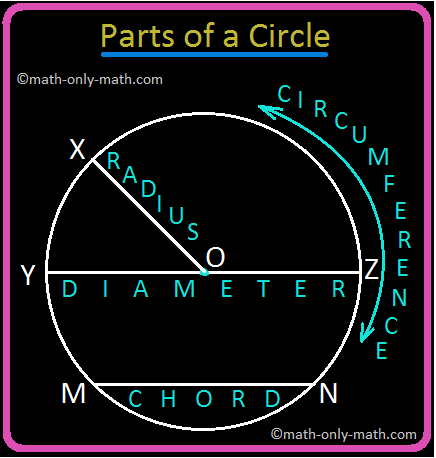
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
Jul 11, 25 02:14 PM
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circl… -
Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Jul 09, 25 01:29 AM
Construction of a Circle when the length of its Radius is given. Working Rules | Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be… -
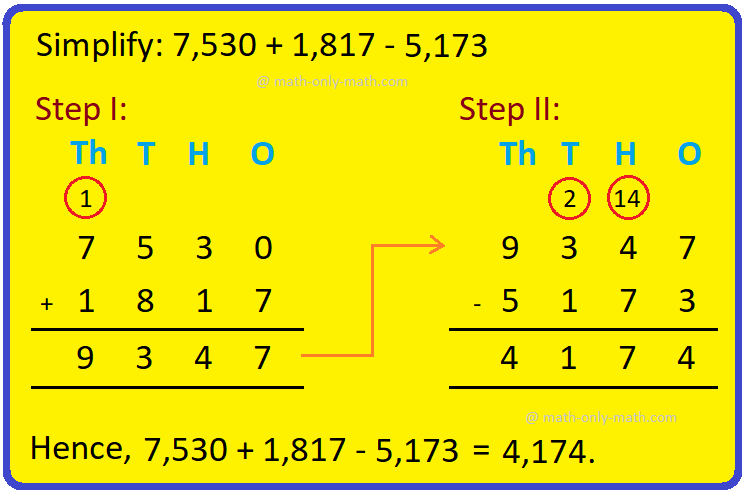
Combination of Addition and Subtraction | Mixed Addition & Subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:32 PM
We will discuss here about the combination of addition and subtraction. The rules which can be used to solve the sums involving addition (+) and subtraction (-) together are: I: First add -
Addition & Subtraction Together |Combination of addition & subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:23 PM
We will solve the different types of problems involving addition and subtraction together. To show the problem involving both addition and subtraction, we first group all the numbers with ‘+’ and… -
5th Grade Circle | Radius, Interior and Exterior of a Circle|Worksheet
Jul 08, 25 09:55 AM
A circle is the set of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is known

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.