Conditional Trigonometric Identities
In conditional trigonometric identities we will discuss certain relationship exists among the angles involved. We know some of the trigonometric identities which were true for all values of the angles involved. These identities hold for all values of the angles which satisfy the given conditions among them and hence they are called conditional trigonometric identities.
Such identities involving different trigonometrical ratios of three or more angles can be deduced when these angles are connected by some given relation. Suppose, if the sum of three angles be equal to two right angles then we can establish many important identities involving trigonometrical ratios of those angles. To establish such identities we require to use the properties of supplementary and complementary angles.
If A, B and C denote the angles of a triangle ABC, then the relation A + B + C = π enables us to establish many important identities involving trigonometric ratios of these angles The following results are useful to obtain the said identities.
If A + B + C = π, then the sum of any two angles
is supplementary to the third i.e.,
(i) B + C = π - A or, C + A = π - B or A + B = π - C.
(ii) If A + B + C = π then sin (A + B) =
sin (π - C) = sin C
sin (B + C) = sin (π - A) =
sin A
sin (C + A) = sin (π - B) = sin B
(iii) If A + B + C = π then cos (A + B) = cos (π - C) = - cos C
cos (B + C) = cos (π - A) = - cos A
cos (C + A) = cos (π - B) = - cos B
(iv) If A + B + C = π then tan (A + B) = tan (π - C)
= - tan C
tan (B
+ C) = tan (π - A) = - tan A
tan (C + A) = tan (π - B) = - tan B
(v) If A + B + C = π then \(\frac{A}{2}\) + \(\frac{B}{2}\) + \(\frac{C}{2}\) = \(\frac{π}{2}\)
Hence, it is evident that the sum of any two of the three angles \(\frac{C}{2}\),
\(\frac{B}{2}\), \(\frac{C}{2}\) is
complementary to the third.
i.e., \(\frac{A + B}{2}\) = \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{C}{2}\),
\(\frac{B + C}{2}\) = \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{A}{2}\)
\(\frac{C + A}{2}\) = \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{B}{2}\)
Therefore,
sin (\(\frac{A}{2}\) + \(\frac{B}{2}\)) = sin \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{C}{2}\) = cos \(\frac{C}{2}\)
sin (\(\frac{B}{2}\) + \(\frac{C}{2}\)) = sin \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{A}{2}\) = cos \(\frac{A}{2}\)
sin (\(\frac{C}{2}\) + \(\frac{A}{2}\)) = sin \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{B}{2}\) = cos \(\frac{B}{2}\)
cos (\(\frac{A}{2}\) + \(\frac{B}{2}\)) = cos \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{C}{2}\) = sin \(\frac{C}{2}\)
sin (\(\frac{B}{2}\) + \(\frac{C}{2}\)) = cos \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{A}{2}\) = sin \(\frac{A}{2}\)
sin (\(\frac{C}{2}\) + \(\frac{A}{2}\)) = cos \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{B}{2}\) = sin \(\frac{B}{2}\)
tan (\(\frac{A}{2}\) + \(\frac{B}{2}\)) = tan \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{C}{2}\) = cot \(\frac{C}{2}\)
tan (\(\frac{B}{2}\) + \(\frac{C}{2}\)) = tan \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{A}{2}\) = cot \(\frac{A}{2}\)
tan (\(\frac{C}{2}\) + \(\frac{A}{2}\)) = tan \(\frac{π}{2}\) - \(\frac{B}{2}\) = cot \(\frac{B}{2}\)
● Conditional Trigonometric Identities
- Identities Involving Sines and Cosines
- Sines and Cosines of Multiples or Submultiples
- Identities Involving Squares of Sines and Cosines
- Square of Identities Involving Squares of Sines and Cosines
- Identities Involving Tangents and Cotangents
- Tangents and Cotangents of Multiples or Submultiples
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Conditional Trigonometric Identities to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Adding 1-Digit Number | Understand the Concept one Digit Number
Apr 26, 24 01:55 PM
Understand the concept of adding 1-digit number with the help of objects as well as numbers. -
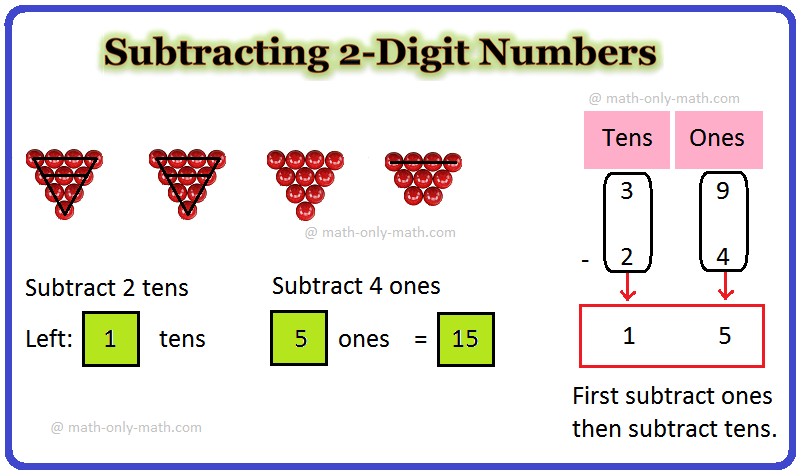
Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers | How to Subtract Two Digit Numbers?
Apr 26, 24 12:36 PM
In subtracting 2-digit numbers we will subtract or minus a two-digit number from another two-digit number. To find the difference between the two numbers we need to ‘ones from ones’ and ‘tens from -
1st Grade Word Problems on Subtraction | Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers
Apr 26, 24 12:06 PM
In 1st grade word problems on subtraction students can practice the questions on word problems based on subtraction. This exercise sheet on subtraction can be practiced by the students to get more ide… -
Subtracting 1-Digit Number | Subtract or Minus Two One-Digit Number
Apr 26, 24 11:21 AM
In subtracting 1-digit number we will subtract or minus one-digit number from one-digit number or one-digit number from 2-digit number and find the difference between them. We know that subtraction me… -
Perimeter of a Square | How to Find the Perimeter of Square? |Examples
Apr 25, 24 05:34 PM
We will discuss here how to find the perimeter of a square. Perimeter of a square is the total length (distance) of the boundary of a square. We know that all the sides of a square are equal. Perimete…