Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Ordering Integers
In ordering integers we will learn how to order the integers on a number line.
All integers can be represented on a number line. The convention followed to compare two integers represented on the number line is similar to that followed for the whole numbers marked on the number line. So the integer occurring on the right is greater than that on the left and the integer on the left is smaller than that on its right.
An integer on a number line is always greater than every integer on its left. Thus, 3 is greater than 2, 2 > 1, 1 > 0, 0 > -1, -1 > -2 and so on.
Similarly, an integer on a number line is always lesser than every integer on its right. Thus, -3 is less than -2, -2 < -1, -1 < 0, 0 < 1, 1 < 2 and so on.
Thus, we have the following examples:
(i) 3 > 2, since 3 is to the right of 2
(ii) 2 > 0, since 2 is to the right of 0
(iii) 0 > -2, since 0 is to the right of -2
(iv) -1 > -2, since -1 is to the right of -2
Integers obey the same Rule of Whole Numbers in their Ordering:
Rule I: Every positive integer is greater than every negative integer.
i.e., Since every positive integer is to the right of every negative integer, therefore, every positive integer is greater than every negative integer.
Rule II: Zero is less than every positive integer and is greater than every negative integer.
i.e., Since zero is to the left of every positive integer, therefore, zero is smaller than every positive integer.
Again, since zero is to the right of every negative integer, therefore, zero is greater than every negative integer.
Rule III: The greater the number, the lesser is its opposite.
i.e., The farther a number is from zero on its right, the larger is its value
For Example:
8 is greater than 5, but -8 is less than -5; similarly, -9 > -15 or, 9 < 15 and so on
Rule IV: The lesser the number, the greater is its opposite.
i.e., The farther a number is from zero on its left, the smaller is its value.
For Example:
6 is less than 7, but -6 is greater than -7; similarly, -8 < -5 or 8 > 5 and so on.
Rule V: The greater a number is the smaller is its opposite.
In general, if x and y are two integers such that
x > y, then -x < - y , and if x < y, then -x > - y
For Example:
(i) 6 > 4 and -6 < -4
(ii) 18 > 13 and -18 < -13.
Note: The symbol (-) is used to denote a negative integer as well as for subtraction.
(i) The temperature at an Everest is -10°C. Here the symbol (-) indicates the negative integer (-10) and no subtraction is involved.
(ii) On the other hand, 23 - 7 indicates the subtraction of 7 from 23.
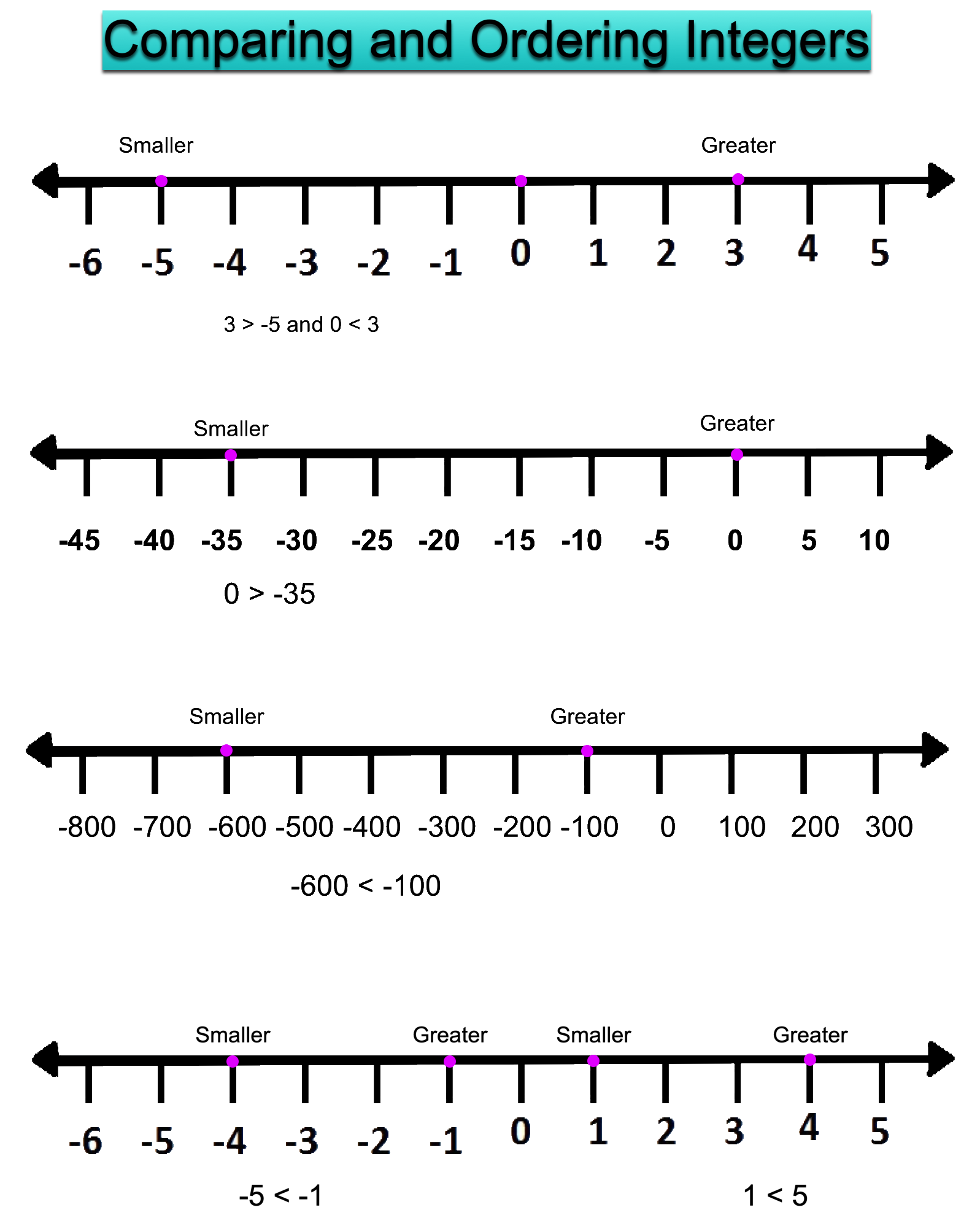
Comparing and Ordering Integers:
A number line can be used to compare and order integers.
Integers to the right on number line are always greater than integers on its left and integers to the left on number line are always smaller than those on its right.
Any two integers can be compared using one of the three symbols: '=' is equal to, '>' is greater than, '<' is less than
From the above figures, we conclude:
Every positive integer is greater than any negative integer.
Zero is less than every positive integer.
Zero is greater than every negative integer.
If 1 < 5, we find -1 > -5.
Solved Examples on Ordering Integers:
1. Arrange the integers from greater to lesser:
(i) 9, -2, 3, 0, -5, -7, 7, -1
(ii) -11, 17, -2, 2, -6, -15, 0, 1
(iii) 12, -21, -18, 14, -5, -1, 1, 10
Solution:
1. (i) 9, 7, 3, 0, -1, -2, -5, -7
(ii) 17, 2, 1, 0, -2, -6, -11, -15
(iii) 14, 12, 10, 1, -1, -5, -18, -21
2. Arrange the following integers in decreasing order.
(i) -3, 12, 7, 0, -8, 6
(ii) 0, -9, -15, 15, 9, -6, - 18, 29
(iii) -25, 0, -1, 8, - 6, - 13, 24, 6
(iv) -706, 409, 170, 109, -75, -555
Solution:
2. (i) 12, 7, 6, 0, -3, -8
(ii) 29, 15, 9, 0, -6, -9, -15, -18
(iii) 24, 8, 6, 0, -1, -6, -13, -25
(iv) 409, 170, 109, -75, -555, -706
3. Arrange the integers from lesser to greater:
(i) 0, 4, -4, 9, -10, -7, 12, -13
(ii) -14, 7, -25, -17, 20, 5, -9, -3
(iii) -6, 4, -18, 21, 29, -8, -16, 19
Solution:
3. (i) -13, -10, -7, -4, 0, 4, 9, 12
(ii) -25, -17, -14, -9, -3, 5, 7, 20
(iii) -18, -16, -8, -6, 4, 19, 21, 29
4. Arrange the following integers in increasing order.
(i) -3, 8, 6, 0, -7, 10
(ii) -17, 0, 9, 6, 10, -5, 8, -7
(iii) 0, -8, 6, -19, 65, -3, 38
(iv) -805, 508, -170, 108, 170, -85, -515
Solution:
4. (i) -7, -3, 0, 6, 8, 10
(ii) -17, -7, -5, 0, 6, 8, 9, 10
(iii) -19, -8, -3, 0, 6, 38, 65
(iv) -805, -515, -170, -85, 108, 170, 508
5. Use the number line to compare:
(i) -7 and -1.
(ii) 4 and -5.
Solution:
(i) -7 is to the left of -1. So - 7 < - 1 or - 1 > - 7
(ii) 4 is to the right of -5. So 4 > - 5 or - 5 < 4
6. Replace ✸ with < or > to make the statement true:
(i) -56 ✸ 0
(ii) 0 ✸ - 7
(iii) - 19 ✸ - 22
Solution:
(i) - 56 < 0
(ii) 0 > - 7
(iii) - 19 > - 22
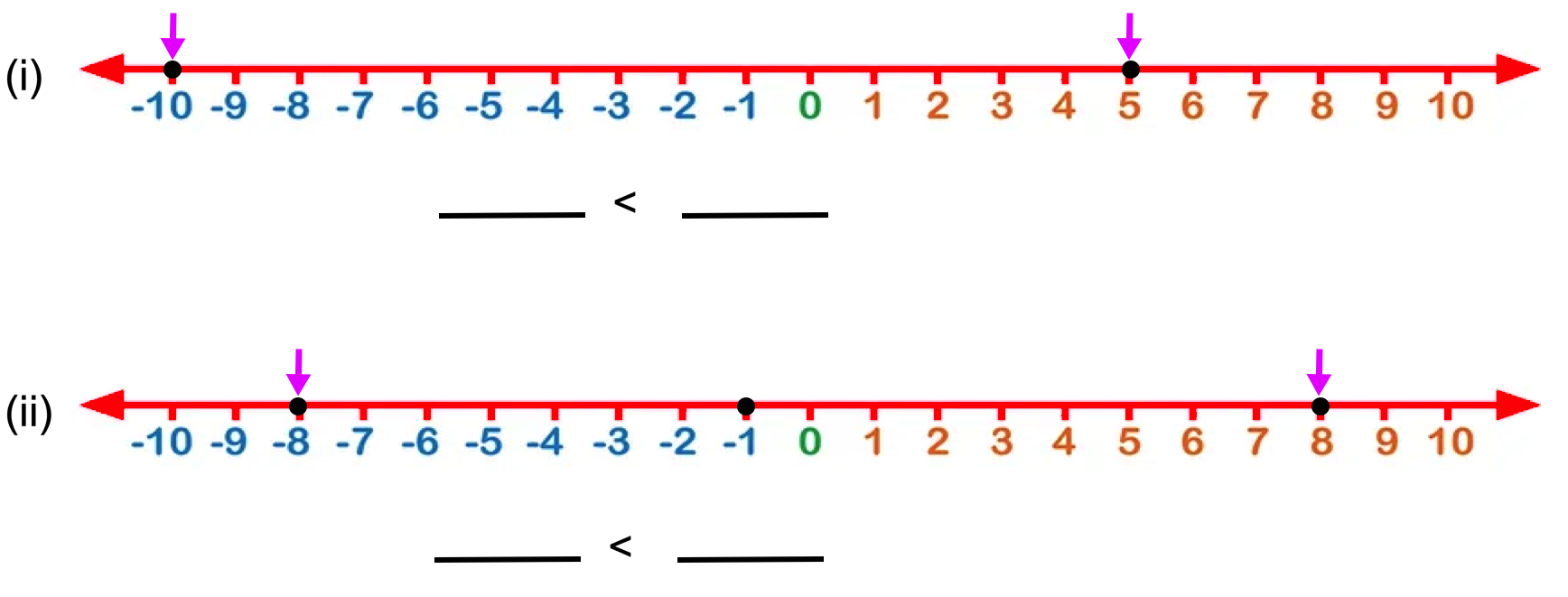
7. Look at the numbers marked by dots '•'and fill in the blanks.
Solution:
(i) - 10 < 5
(ii) - 8 < 8
From Ordering Integers to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.