Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Numerator and Denominator of a Fraction
What are the numerator and denominator of a fraction?
We have already learnt that a fraction is written with two numbers arranged one over the other and separated by a line. The number under the line shows in how many equal parts the whole has been divided into. It is called denominator of the fraction. The number above the line shows how many parts of the whole have been taken. It is called numerator of the fraction. So in \(\frac{2}{3}\), 2 is the numerator and 3 is the denominator.
Numerator and Denominator of a Fraction:
We can see that a fraction has two parts.
The number above the division line and the number below the division line. The number below the division line tells us into how many equal parts single or collection of object has been divided. We call it the Denominator. The number above the division line tells us how many of these equal parts have been taken from the whole. We call it the Numerator.
Read as 2 over 5 or two by five.
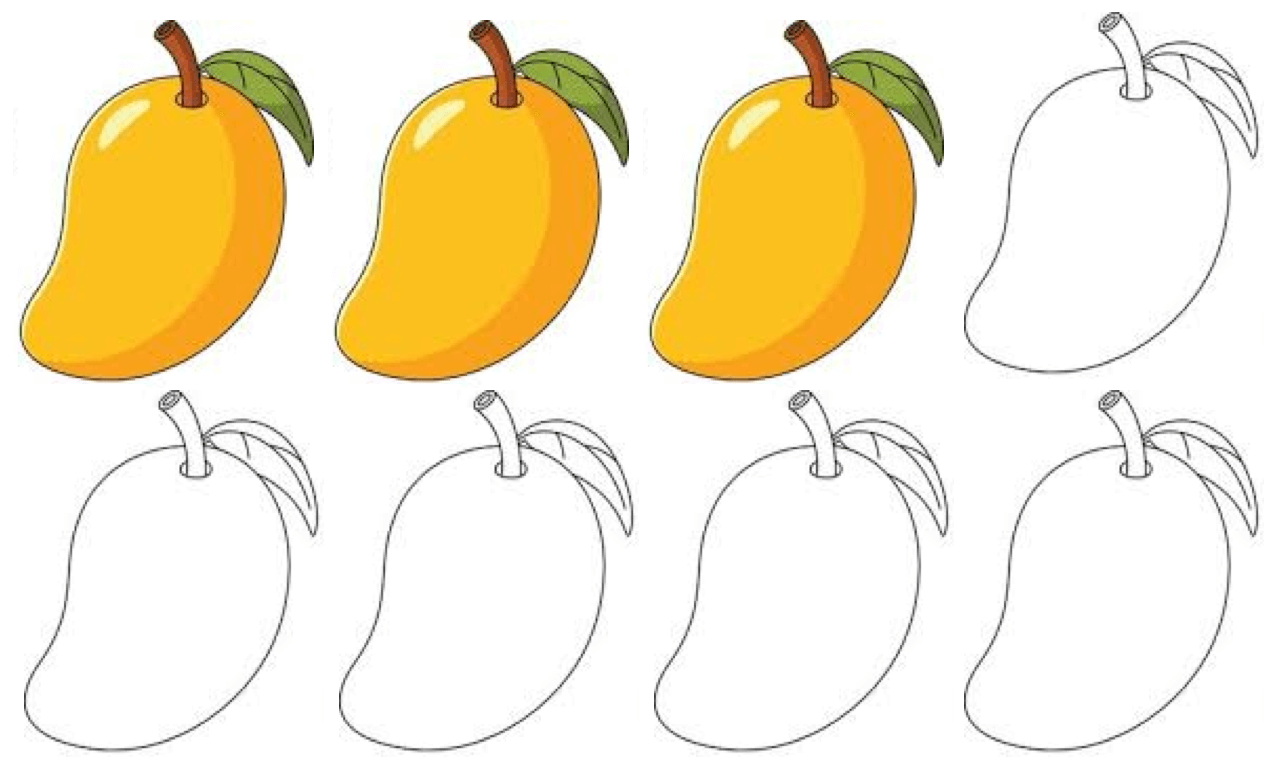
Fraction mean part of a region or part of a collection.
\(\frac{3}{8}\) \(\frac{\textrm{coloured mangoes}}{\textrm{mangoes in all}}\)
\(\frac{3}{8}\) \(\frac{→}{→}\) \(\frac{\textrm{Numerator}}{\textrm{Denominator}}\)
Worksheet on Numerator and Denominator of a Fraction:
Questions on Numerator and Denominator of a Fraction:
I. Write the denominators and numerators-
|
Fraction |
Numerator |
Denominator | |
|
(i) |
\(\frac{5}{8}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
|
(ii) |
\(\frac{1}{4}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
|
(iii) |
\(\frac{6}{2}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
|
(iv) |
\(\frac{2}{7}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
|
(v) |
\(\frac{4}{6}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
|
(vi) |
\(\frac{2}{3}\) |
_____ |
_____ |
Answer:
I. (i) Numerator = 5 and Denominator 8
(ii) Numerator = 1 and Denominator 4
(iii) Numerator = 6 and Denominator 2
(iv) Numerator = 2 and Denominator 7
(v) Numerator = 4 and Denominator 6
(vi) Numerator = 2 and Denominator 3
II. Write the fractions-
|
Fraction |
Numerator |
Denominator | |
|
(i) |
_____ |
2 |
3 |
|
(ii) |
_____ |
8 |
9 |
|
(iii) |
_____ |
5 |
8 |
|
(iv) |
_____ |
1 |
6 |
|
(v) |
_____ |
7 |
15 |
|
(vi) |
_____ |
6 |
11 |
Answer:
II. (i) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{8}{9}\)
(iii) \(\frac{5}{8}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{6}\)
(v) \(\frac{7}{15}\)
(vi) \(\frac{6}{11}\)
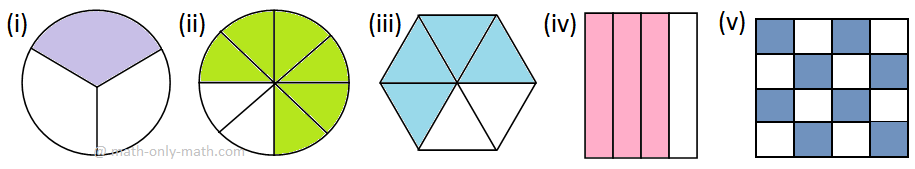
III. Fill in the table -
|
Figure |
(i) |
(ii) |
(iii) |
(iv) |
(v) |
|
Shaded parts (Numerator) |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
|
Number of parts (Denominator) |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
|
Fraction of shaded parts |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
___ |
Answer:
III. (i) Shaded parts (Numerator) = 1
Number of parts (Denominator) = 3
Fraction of shaded parts = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) Shaded parts (Numerator) = 6
Number of parts (Denominator) = 8
Fraction of shaded parts = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
(iii) Shaded parts (Numerator) = 4
Number of parts (Denominator) = 6
Fraction of shaded parts = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
(iv) Shaded parts (Numerator) = 3
Number of parts (Denominator) = 4
Fraction of shaded parts = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(v) Shaded parts (Numerator) = 8
Number of parts (Denominator) = 16
Fraction of shaded parts = \(\frac{8}{16}\)
IV. Fill in the blanks _
(i) In \(\frac{10}{2}\) the numerator is _____ and the denominator is _____.
(ii) In \(\frac{9}{3}\) the denominator is _____ .
(iii) In \(\frac{10}{2}\) the numerator is _____ .
Answer:
IV. (i) 10; 2
(ii) 3
(iii) 10
V. How many fractions have the numerator '6'?
\(\frac{6}{2}\), \(\frac{16}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{5}\), \(\frac{9}{3}\), \(\frac{6}{1}\)
Answer:
V. 2 fractions
VI. Write in fraction form -
|
(i) Numerator 30 and Denominator 5 |
.... ____ .... |
|
(ii) Numerator 9 and Denominator 54 |
.... ____ .... |
|
(iii) Numerator 15 and Denominator 30 |
.... ____ .... |
Answer:
VII. (i) \(\frac{30}{5}\)
(ii) \(\frac{9}{54}\)
(iii) \(\frac{15}{30}\)
VII. Write the fraction with:
|
(i) Numerator 2, Denominator 5 (ii) Numerator 4, Denominator 10 (iii) Numerator 3, Denominator 7 (iv) Numerator 1, Denominator 6 (v) Numerator 4, Denominator 8 |
_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ |
Answer:
VIII. (i) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(ii) \(\frac{4}{10}\)
(iii) \(\frac{3}{7}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{6}\)
(v) \(\frac{4}{8}\)
The number above the line is called the 'numerator' of the fraction and the number below the line is called the 'denominator' of the fraction.
For example, in fraction \(\frac{7}{12}\), 7 is the numerator and 12 is the denominator.
Also, in fraction \(\frac{3}{8}\), 3 is the numerator 8 is the denominator.
Fractional Numbers
From Numerator and Denominator to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
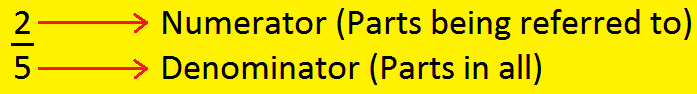
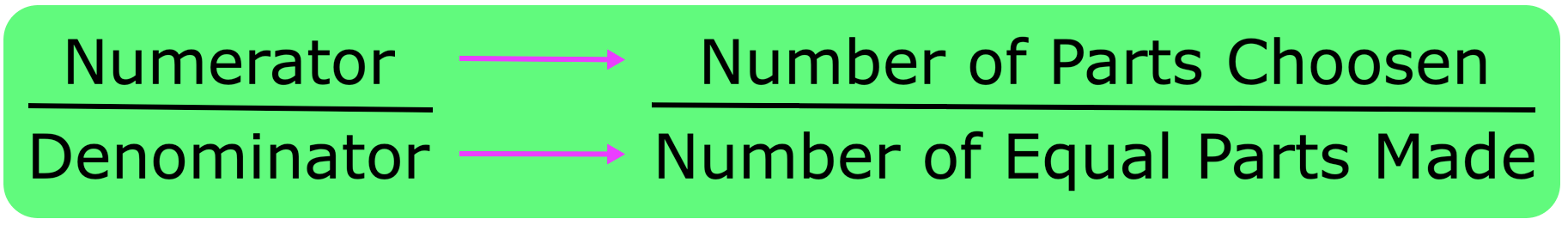


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.