Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Units of Measurement
In metric system of measurement the metre is the basic unit of length, gram is the basic unit of mass and litre is the basic unit of capacity.
In units of measurement of length we use centimeter (cm) to measure. We
can use this unit for measuring the length of a pencil, the width of a
book etc. but this unit is too big to measure the thicken of a pencil.
So we use another unit called millimeter (mm).
Also, centimeter and millimeters are very small units to measure the length of the classroom. We use another unit called meters. Even meter is too small unit when we state the distances between two cities, there we need kilometers (km).
These units are connected with each other by the following relation :
1 kilometer (km) = 1000 meter (m)
1 meter (m) = 100 centimeter (cm)
1 centimeter (cm) = 10 millimeter (mm).
Also,
1 meter (m) = 100 centimeter (cm) = 100 × 10 millimeter (mm) = 1000 millimeter (mm)
1 kilometer (km) = 1000 meter (m) = 1000 × 100 centimeter (cm) = 100,000 centimeter (cm)
1 kilometer (km) = 100,000 centimeter (cm) = 100,000 × 10 millimeter (mm) = 1,000,000 millimeter (mm)
When we go to market to buy sugar, wheat etc, we buy these items in kilograms (kg).
But, items like ginger, chilies etc. are measured in grams (gm).
In order to measure the weight of compound or chemicals in medicines, we use smaller unit called milligrams (mg).
Following are the relations between these three units of measurement of weight.
1 kilograms (kg) = 1000 grams (gm)
1 grams (gm) = 1000 milligrams (mg)
1 kilograms (kg) = 1000 × 1000 milligrams (mg) = 1,000,000 milligrams (mg)
We buy milk in liters whereas liquid medicines etc. are measured in milliliters (ml).
Following is the relation between these two units.
1 liter (l) = 1000 milliliters (ml).
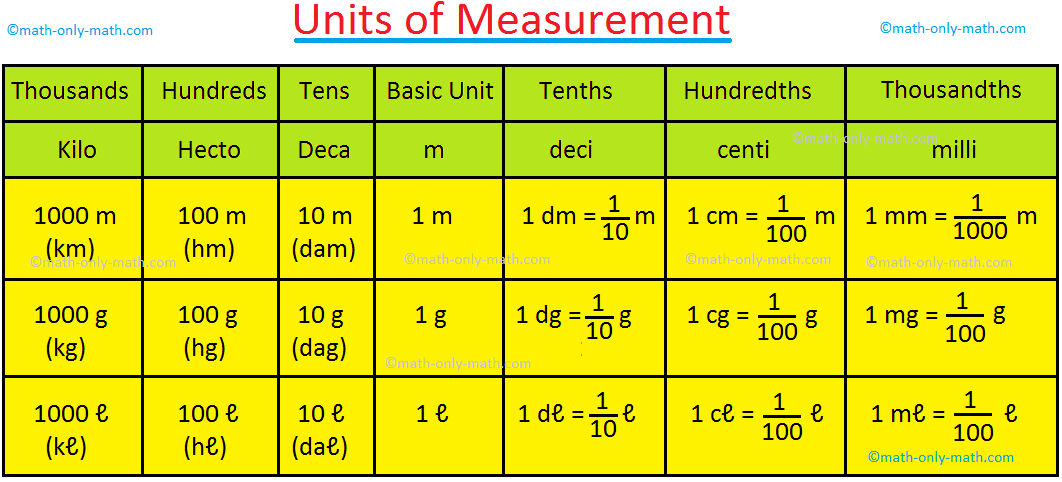
Following prefixes are used to understand easily the relationship between higher units and lower units.
Kilo – thousand, hector – hundred, deca – ten, deci – tenth, centi – hundredth and milli – thousandth
We can write the place-value chart using all above prefixes for each place explaining the relationship to the basic unit. In the following place-value chart each place is ten times greater than the one to its right, and ten times smaller than the one to its left.
We shall express measures now using the decimal rotation.
Note:
In units of measurement, all the units mentioned above have some common words like kilo, milli and centi. It should be noted that kilo is the largest and milli is the smallest. Similarly, centi shows 100 times smaller.
6th Grade Page
From Units of Measurement to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.