Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Solved Examples on the Basic Properties of Tangents
The solved examples on the basic properties of tangents will help us to understand how to solve different type problems on properties of triangle.
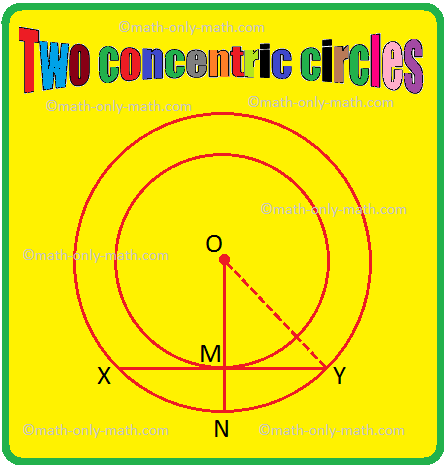
1. Two concentric circles have their centres at O. OM = 4 cm and ON = 5 cm. XY is a chord of the outer circle and a tangent to the inner circle at M. Find the length of XY.
Solution:
Radius OM ⊥ tangent XY. Therefore, OM bisects XY, as ⊥ from centre bisects a chord. So, XY = 2MY. OY = ON = 5 cm. In ∆OMY,
MY^2 = OY^2 – OM^2 = 5^2 cm^2 – 4^2 cm^2 = 25 cm^2 – 16 cm^2 = 9 cm^2.
Therefore, MY = 3 cm. Thus, XY = 6 cm.
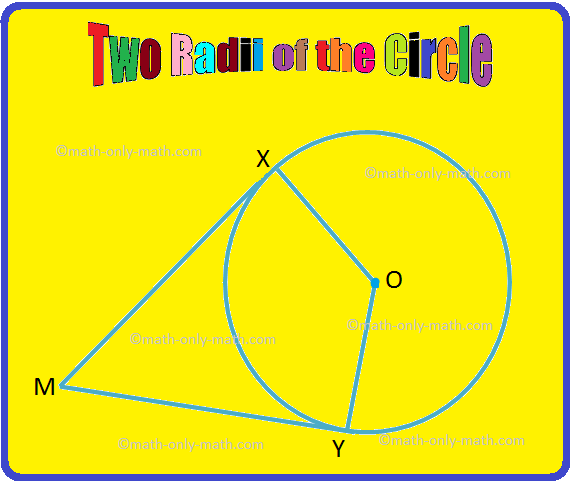
2. In the given figure, OX and OY are two radii of the circle. If MX and MY are tangents to the circle at X and Y respectively, prove that ∠XOY and ∠XMY are supplementary angles.
Solution:
Given: OX and OY are radii and MX and MY are tangents.
To prove: ∠XOY + ∠XMY = 180°.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. ∠OXM = 90° |
1. A tangent is perpendicular to the radius drawn through the point of contact. |
|
2. ∠OYM = 90° |
2. As in 1. |
|
3. ∠OXM + ∠XMY + ∠OYM + ∠XOY = 360° ⟹ 90° + ∠XMY + 90° + ∠XOY = 360° ⟹ ∠XMY + ∠XOY = 360° – 180° ⟹ ∠XOY + ∠XMY = 360° – 180° |
3. The sum of the four angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. From statements 1 and 2. |
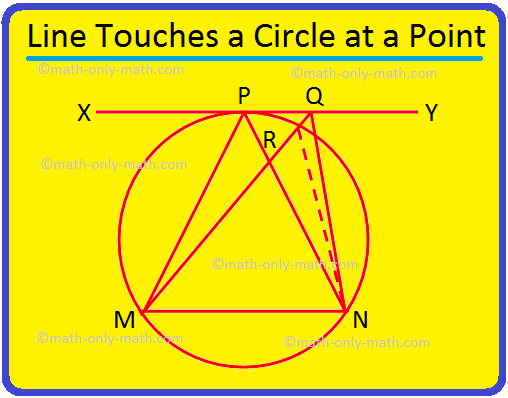
3. If a line XY touches a circle at P and MN is a chord of the circle then prove that ∠MPN > ∠MQN, where Q is any point on XY other than P.
Solution:
Given: MN is a chord of a circle and tyhe tangent at the point P is the line XY. Q is any other point on XY.
To prove: ∠MPN > ∠MQN.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. MQ will cut the circle at a point R. Join R to N. |
1. XY is tangent at P and so all points of XY except P are outside the circle. |
|
2. ∠MPN = ∠MRN. |
2. Angles in the same segment are equal. |
|
3. ∠MRN > ∠RQN |
3. Exterior angle is greater than interior opposite angle in a triangle. |
|
4. ∠MPN > ∠RQN = ∠MQN. |
4. By statements 2 and 3. |
From Solved Examples on the Basic Properties of Tangents to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.