Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Pythagoras’ Theorem
The lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle have a special relationship between them. This relation is widely used in many branches of mathematics, such as mensuration and trigonometry.
Pythagoras’ Theorem: In a right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
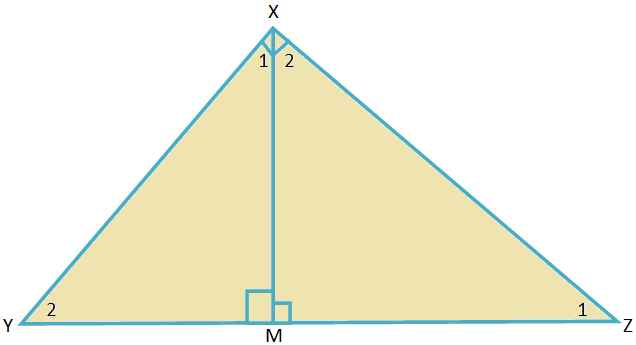
Given: Let XYZ be a triangle in which ∠YXZ = 90°.
YZ is the hypotenuse.
To prove: XY2 + XZ2 = YZ2.
Construction: Draw XM ⊥YZ.
Therefore, ∠XMY = ∠XMZ = 90°.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. In ∆XYM and ∆XYZ, (i) ∠XMY = ∠YXZ = 90° (ii) ∠XYM = ∠XYZ |
1. (i) Given and by construction (ii) Common angle |
|
2. Therefore, ∆XYM ∼ ∆ZYX |
2. BY AA criterion of similarity |
|
3. Therefore, \(\frac{XY}{YZ}\) = \(\frac{YM}{XY}\) |
3. Corresponding sides of similar triangle are proportional |
|
4. Therefore, XY\(^{2}\) = YZ ∙ YM |
4. By cross multiplication in statement 3. |
|
5. In ∆XMZ and ∆XYZ, (i) ∠XMY = ∠YXZ = 90° (ii) ∠XZM = ∠XZY |
5. (i) Given and by construction (ii) Common angle |
|
6. Therefore, ∆XMZ ∼ ∆YXZ. |
6. BY AA criterion of similarity |
|
7. Therefore, \(\frac{XZ}{YZ}\) = \(\frac{MZ}{XZ}\) |
7. Corresponding sides of similar triangle are proportional |
|
8. Therefore, XZ\(^{2}\) = YZ ∙ MZ |
8. By cross multiplication in statement 7. |
|
9. Therefore, XY\(^{2}\) + XZ\(^{2}\) = YZ ∙ YM + YZ ∙ MZ ⟹ XY\(^{2}\) + XZ\(^{2}\) = YZ(YM+ MZ) ⟹ XY\(^{2}\) + XZ\(^{2}\) = YZ ∙ YZ ⟹ XY\(^{2}\) + XZ\(^{2}\) = YZ\(^{2}\) |
9. By adding statements 4 and 8 |
Problems on Pythagoras’ Theorem:
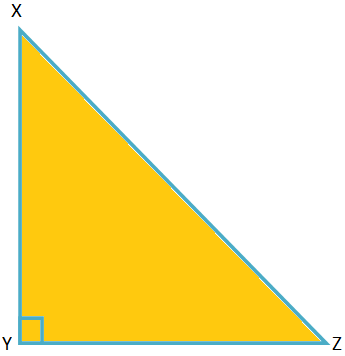
1. In ∆XYZ, ∠Y = 90°. If XY = 3 cm and YZ = 4 cm, find XZ.
Solution:
By Pythagoras, theorem,
XZ\(^{2}\) = XY\(^{2}\) + YZ\(^{2}\)
= (3\(^{2}\) + 4\(^{2}\)) cm\(^{2}\)
= (9 + 16) cm\(^{2}\)
= 25 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, XZ = \(\sqrt{25 cm^{2}}\)
Therefore, XZ = 5 cm
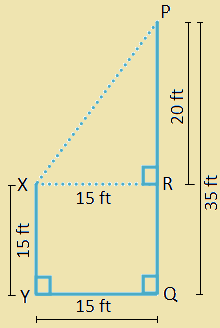
2. Two poles, 15 feet and 35 feet high, are 15 feet apart. Find distance between the tops of the poles.
Solution:
Let the first pole XY = 15 ft
The second pole PQ = 35 ft.
The distance between two poles YQ = 15 ft.
Draw XR ⊥ PQ.
Now, we have,
PR = PQ - RQ = PQ - XY = (35 - 15) ft = 20 ft.
Also, XR = YQ = 15 ft.
Therefore, distance between tops of the poles = XP
= \(\sqrt{XR^{2} + RP^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{15^{2} + 20^{2}}\) ft
= \(\sqrt{225 + 400}\) ft
= \(\sqrt{625}\) ft
= 25 ft
From Pythagoras’ Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.