Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problems on Frequency Polygon
We will discuss here some of the problems on frequency polygon.
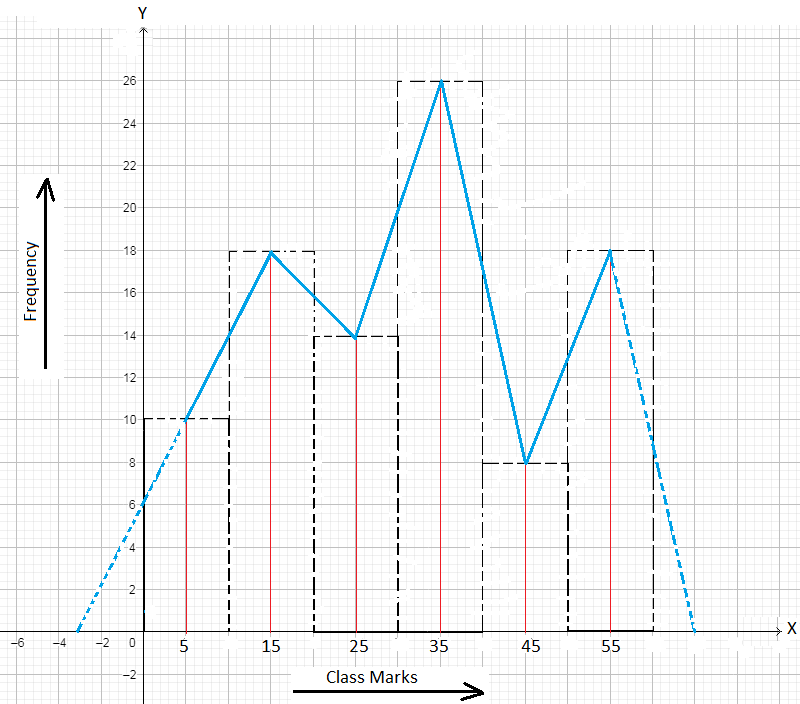
1. The frequency polygon of a frequency distribution is shown below.
Answer the following about the distribution from the histogram.
(i) What is the frequency of the class interval whose class mark is 15?
(ii) What is the class interval whose class mark is 45?
(iii) Construct a frequency table for the distribution.
Solution:
(i) 18
(ii) 40 – 50
(iii) As the class marks of consecutive overlapping class intervals are 5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55 we find the class intervals are 0 – 10, 10 – 20, 20 – 30, 30 – 40, 40 – 50, 50 – 60. Therefore, the frequency table is constructed as below.
|
Class Interval 0 - 10 10 - 20 20 - 30 30 - 40 40 - 50 50 - 60 |
Frequency 10 18 14 26 8 18 |
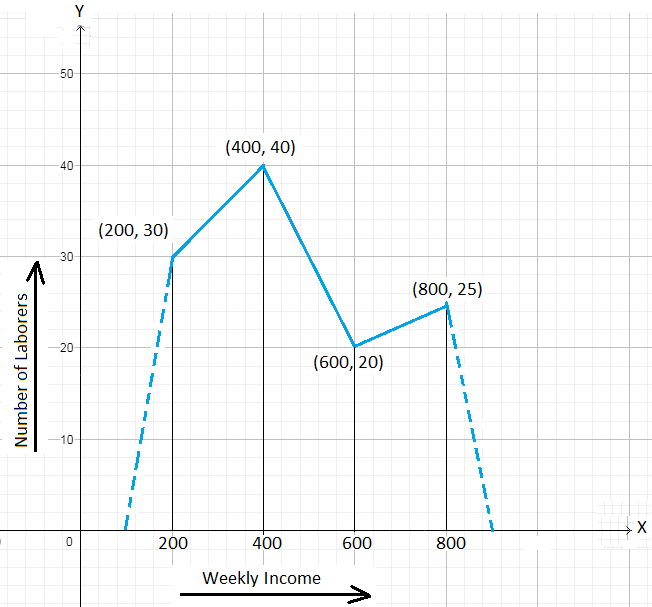
2. The following frequency polygon displays the weekly incomes of laborers of a factory.
Answer the following.
(i) Find the class interval whose frequency is 25.
(ii) How many labourers have a weekly income of at least $ 500 but not more than $ 700?
(iii) What is the range of weekly income of the largest number of labourers?
(iv) Prepare the frequency distribution table.
Solution:
(i) The frequency 25 corresponds to the class mark 800.
The common width of class intervals = 400 - 200 = 200
So, the class interval is (800 - \(\frac{200}{2}\)) – (800 + \(\frac{200}{2}\)), i.e., 700 – 900
(ii) The number of labourers has to fall in the class interval 500 – 700 whose class mark is 600. The frequency corresponding to the class mark 600 is 20. Hence, the required number of labourers is 20.
(iii) The largest number of labourers belong to the class interval whose class mark is 400. The corresponding class interval is (400 - \(\frac{200}{2}\)) – (400 + \(\frac{200}{2}\)), i.e., (300 – 500). So, the largest numbers of labourers have a weekly income of at least $ 300 but less than $ 500.
(iv)
Weekly Income (in $)
100 - 300
300 - 500
500 - 700
700 - 900
Number of labourers
30
40
20
25
From Problems on Frequency Polygon
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.