Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Perimeter and Area of Irregular Figures
Here we will get the ideas how to solve the problems on finding the perimeter and area of irregular figures.
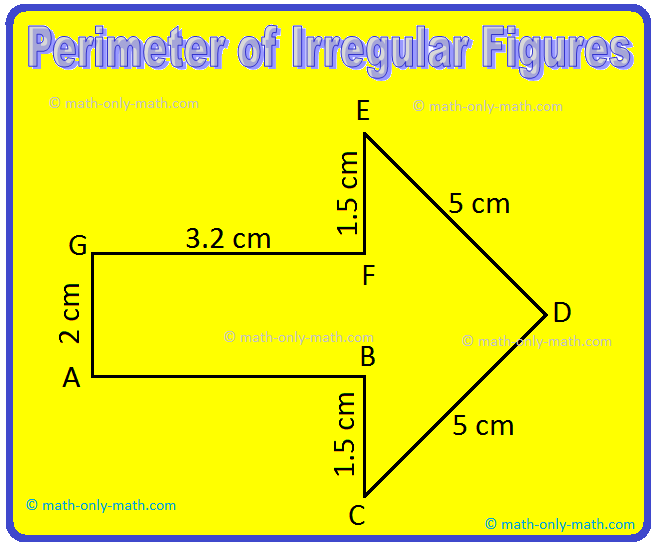
1. Find the perimeter of the given figure.
Solution:
Perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DE + EF + FG + GA
= 3.2 cm + 1.5 cm + 5 cm + 5 cm + 1.5 cm + 3.2 cm + 2 cm
= 21.4 cm
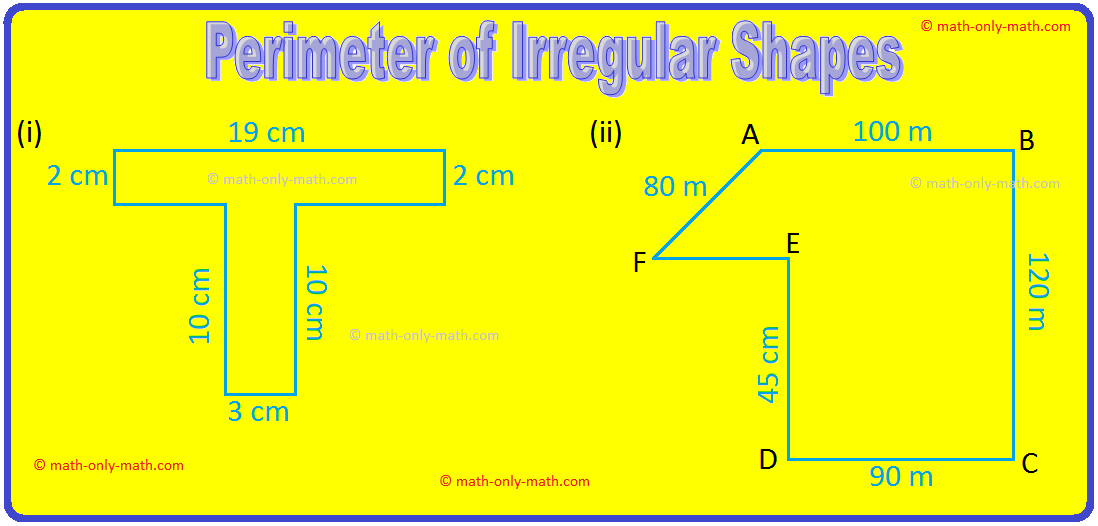
2. Find the perimeter of each of the following figures:
(i) Perimeter of the region = (2 + 19 + 2 + 9 + 10 + 3 + 10 + 7) cm
= 62 cm.
(ii) Perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DE + EF + AF
= (100 + 120 + 90 + 45 + 60 + 80) m
= 495 m .
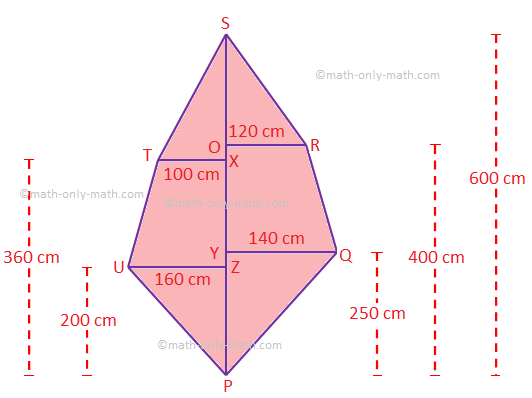
3. The figure PQRSTU is a hexagon.
PS is a diagonal and QY, RO, TX and UZ are the respective distances of the points Q, R, T and U from PS. If PS = 600 cm, QY = 140 cm, RO = 120 cm, TX = 100 cm, UZ = 160 cm, PZ = 200 cm, PY = 250 cm, PX = 360 cm and PO = 400 cm. Find the area of the hexagon PQRSTU.
Solution:
Area of the hexagon PQRSTU = area of ∆PZU + area of
trapezium TUZX + area of ∆TXS + area of ∆PYQ + area of trapezium QROY + area of
∆ROS
= {\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 200 × 160 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (100 + 160)(360 – 200) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (600 – 360) × 100 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 250 × 140 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (120 + 140) (400 – 250) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (600 – 400) × 120} cm\(^{2}\)
= (16000 + 130 × 160 + 120 × 100 + 125 × 140 + 130 × 150 + 100 × 120) cm\(^{2}\)
= (16000 + 20800 + 12000 + 17500 + 19500 + 12000) cm\(^{2}\)
= 97800 cm\(^{2}\)
= 9.78 m\(^{2}\)
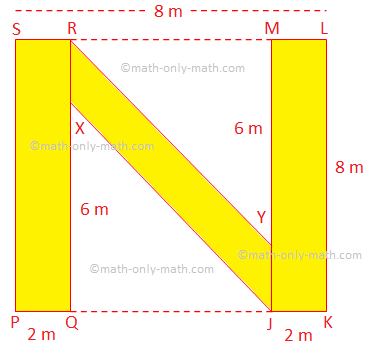
4. In a square lawn of side 8 m, an N-shaped path is made, as shown in the figure. Find the area of the path.
Solution:
Required area = area of the rectangle PQRS + area of the parallelogram XRYJ + area of the rectangle JKLM
= (2 × 8 + PC × BE + 2 × 8) m\(^{2}\)
= (16 + 2 × 4 + 16) cm\(^{2}\)
= 40 m\(^{2}\)
We can solve this problem using another method:
Required area = Area of the square PSLK – Area of the ∆RYM – Area of the ∆XQJ
= [8 × 8 - \(\frac{1}{2}\){8 – (2 + 2)} × 6 - \(\frac{1}{2}\){8 – (2 + 2)} × 6] m\(^{2}\)
= (64 – 12 – 12) m\(^{2}\)
= 40 m\(^{2}\)
From Perimeter and Area of Irregular Figures to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.