Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Perimeter and Area of a Triangle
Here we will discuss about the perimeter and area of a triangle and some of its geometrical properties.
Perimeter, Area and Altitude of a Triangle:
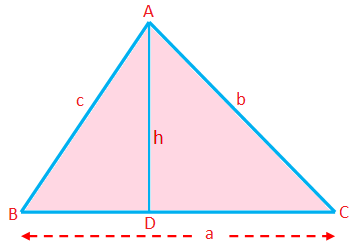
Perimeter of a triangle (P) = Sum of the sides = a + b + c
Semiperimeter of a triangle (s) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(a + b + c)
Area of a triangle (A) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × base × altitude = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ah
Here any side can be taken as base; the length of the perpendicular from the corresponding vertex to this side is the altitude.
Area = \(\sqrt{\textrm{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}}\) (Heron’s formula)
Altitude (h) = \(\frac{\textrm{area}}{\frac{1}{2} \times \textrm{base}}\) = \(\frac{2\triangle}{a}\)
Solved Example on Finding the Perimeter, Semiperimeter and Area
of a Triangle:
The sides of a triangle are 4 cm, 5 cm and 7 cm. Find its perimeter, semiperimeter and area.
Solution:
Perimeter of a triangle (P) = Sum of the sides
= a + b + c
= 4 cm + 5 cm + 7 cm
= (4 + 5 + 7) cm
= 16 cm
Semiperimeter of a triangle (s) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(a + b + c)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4 cm + 5 cm + 7 cm)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4 + 5 + 7) cm
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 16 cm
= 8 cm
Area of a triangle = \(\sqrt{\textrm{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\textrm{8(8 - 4)(8 - 5)(8 - 7)}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\textrm{8 × 4 × 3 × 1}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{96}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{16 × 6}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 4\(\sqrt{6}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 4 × 2.45 cm\(^{2}\)
= 9.8 cm\(^{2}\)
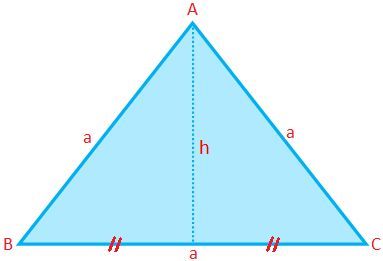
Perimeter, Area and Altitude of an Equilateral Triangle:
Perimeter of an equilateral triangle (P) = 3 × side = 3a
Area of an equilateral triangle (A) = \(\frac{√3}{4}\) × (side)\(^{2}\) = \(\frac{√3}{4}\) a\(^{2}\)
Altitude of an equilateral triangle (h) = \(\frac{√3}{4}\) a
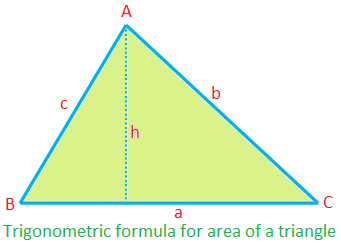
Trigonometric formula for area of a triangle:
Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × ca sin B
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × ab sin C
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × bc sin A
(since, ∆ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ah = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ca ∙ \(\frac{h}{c}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ca sin B, etc.)
Solved Example on Finding the Area of a Triangle:
In a ∆ABC, BC = 6 cm, AB = 4 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Find its area.
Solution:
Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ac sin B = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 4 sin 60° cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 4 × \(\frac{√3}{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 6√3 cm\(^{2}\)
= 6 × 1.73 cm\(^{2}\)
= 10.38 cm\(^{2}\)
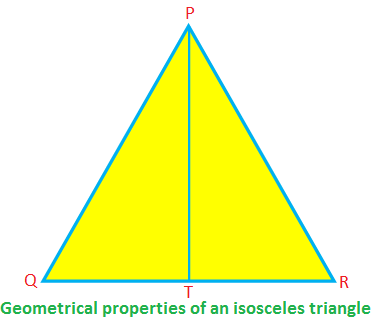
Some geometrical properties of an isosceles triangle:
In the isosceles ∆PQR, PQ = PR, QR is the base, and PT is the altitude.
Then, ∠PTR = 90°, QT = TR, PT\(^{2}\) + TR\(^{2}\) = PR\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ theorem)
∠PQR = ∠PRQ, ∠QPT = ∠RPT.
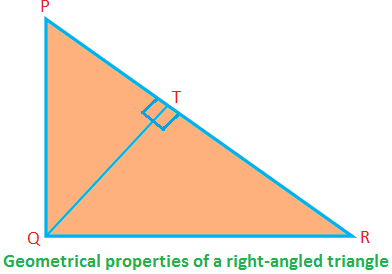
Some geometrical properties of a right-angled triangle:
In the right-angled ∆PQR, ∠PQR = 90°; PQ, QR are the sides (forming the right angle) and PR is the hypotenuse.
Then, PQ ⊥ QR (therefore, if QR is the base, PQ is the altitude).
PQ\(^{2}\) + QR\(^{2}\) = PR\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ theorem)
Area of the ∆PQR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∙ PQ ∙ QR
⟹ PQ ∙ QR = 2 × area of the ∆PQR.
Again, area of the ∆PQR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∙ QT ∙ PR
⟹ QT ∙ PR = 2 × area of the ∆PQR.
Therefore, PQ ∙ QR = QT ∙ PR = 2 × Area of the ∆PQR.
Solved Examples on Perimeter and Area of a Triangle:
1. Find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle whose area is equal to that of a triangle with sides 21 cm, 16 cm and 13 cm.
Solution:
Let a side of the equilateral triangle = x.
Then, its area = \(\frac{√3}{4}\) x\(^{2}\)
Now, the area of the other triangle = \(\sqrt{\textrm{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}}\)
Here, s = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (a + b + c)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (21 + 16 + 13) cm
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) 50 cm
= 25 cm
Therefore, area of the other triangle = \(\sqrt{\textrm{25(25 - 21)(25 - 16)(25 - 13)}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\textrm{25 ∙ 4 ∙ 9 ∙ 12}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 60\(\sqrt{\textrm{3}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
According to the question, \(\frac{√3}{4}\) x\(^{2}\) = 60\(\sqrt{\textrm{3}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
⟹ x\(^{2}\) = 240 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, x = 4√15 cm
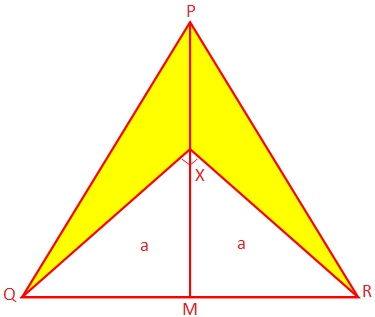
2. PQR is an isosceles triangle whose equal sides PQ and PR are 10 cm each, and the base QR measures 8 cm. PM is the perpendicular from P to QR and X is a point on PM such that ∠QXR = 90°. Find the area of the shaded portion.
Solution:
Since PQR is an isosceles triangle and PM ⊥ QR, QR is bisected at M.
Therefore, QM = MR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) QR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 cm = 4 cm
Now, PQ\(^{2}\) = PM\(^{2}\) + QM\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ theorem)
Therefore, 10\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) = PM\(^{2}\) + 4\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
or, PM\(^{2}\) = 10\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) - 4\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 100 cm\(^{2}\) - 16 cm\(^{2}\)
= (100 - 16) cm\(^{2}\)
= 84 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, PM\(^{2}\) = 2√21 cm
Therefore, area of the ∆PQR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × base × altitude
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × QR × PM
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 × 2√21) cm\(^{2}\)
= 8√21) cm\(^{2}\)
From geometry, ∆XMQ ≅ ∆XMR (SAS criterion)
We get, XQ =XR = a (say)
Therefore, from the right-angled ∆QXR, a\(^{2}\) + a\(^{2}\) = QR\(^{2}\)
or, 2a\(^{2}\) = 8\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
or, 2a\(^{2}\) = 64 cm\(^{2}\)
or, a\(^{2}\) = 32 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, a = 4√2 cm
Again, area of the ∆XQR = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × XQ × XR
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × a × a
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 4√2 cm × 4√2 cm
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (4√2)\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 32 cm\(^{2}\)
= 16 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, area of the shaded portion = area of the ∆PQR - area of the ∆XQR
= (8√21) cm\(^{2}\) - 16 cm\(^{2}\)
= (8√21 - 16) cm\(^{2}\)
= 8(√21 - 2) cm\(^{2}\)
= 8 × 2.58 cm\(^{2}\)
= 20.64 cm\(^{2}\)
From Perimeter and Area of a Triangle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.