Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Midpoint Theorem on Right-angled Triangle
Here we will prove that in a right-angled triangle the median drawn to the hypotenuse is half the hypotenuse in length.
Solution:
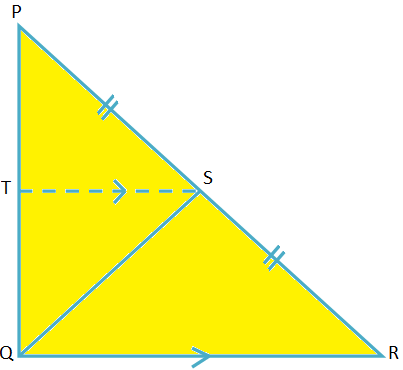
Given: In ∆PQR, ∠Q = 90°. QD is the median drawn to hypotenuse PR.
To prove: QS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)PR.
Construction: Draw ST ∥ QR such that ST cuts PQ at T.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. In ∆PQR, PS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)PR. |
1. S is the midpoint of PR. |
|
2. In ∆PQR, (i) S is the midpoint of PR (ii) ST ∥ QR |
2. (i) Given. (ii) By construction. |
|
3. Therefore, T is the midpoint of PQ. |
3. By converse of the Midpoint Theorem. |
|
4. TS ⊥ PQ. |
4. TS ∥ QR and QR ⊥ PQ |
|
5. In ∆PTS and ∆QTS , (i) PT = TQ (ii) TS = TS (iii) ∠PTS = ∠QTS = 90°. |
5. (i) From the statement 3. (ii) Common side. (iii) From the statement 4. |
|
6. Therefore, ∆PTS ≅ ∆QTS. |
6. By SAS criterion of congruency. |
|
7. PS = QS. |
7. CPCTC |
|
8. Therefore, QS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)PR. |
8. Using statement 7 in statement 1. |
From Midpoint Theorem on Right-angled Triangle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.