Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Methods of Solving Simultaneous Linear Equations
There are different methods for solving simultaneous linear Equations:
I. Elimination of a variable
II. Substitution
III. Cross-multiplication
IV. Evaluation of proportional value of variables
This topic is purely based upon numerical examples. So, let us solve some examples based upon solving linear equations in two variables.
I: Solved example on simultaneous linear Equations using elimination method:
Solve for ‘x’ and ‘y’:
3x + 2y = 18.
4x + 5y = 25.
Solution:
3x + 2y = 18 ............. (i)
4x + 5y = 25 ............. (ii)
Let us multiply equation (i) by 4 on both sides and equation (ii) by 3 on both sides, so as to make coefficients of ‘x’ equal.
On multiplying, we get;
4(3x + 2y) = 4 ∙ 18
or, 12x + 8y = 72 ............. (iii)
and
3(4x + 5y) = 3 ∙ 25
or, 12x + 15y = 75 ............. (iv)
Subtracting (iii) from (iv), we get;
12x + 15y - (12x + 8y) = 75 - 72
or, 12x + 15y - 12x - 8y = 3
or, 7y = 3
or, y = \(\frac{3}{7}\).
Substituting value of ‘y’ in equation (i), we get;
3x + 2(\(\frac{3}{7}\)) = 18.
or, 3x + \(\frac{6}{7}\) = 18
or, 3x = 18 – \(\frac{6}{7}\)
or, 3x = \(\frac{120}{7}\).
or, x = \(\frac{120}{21}\).
or, x = \(\frac{40}{7}\).
Hence, x = \(\frac{40}{7}\) and y = \(\frac{3}{7}\).
II: Solved examples on simultaneous linear Equations using substitution method:
1. Solve for ‘x’ and ‘y’:
x + 3y = 9
3x + 4y = 20
Solution:
x + 3y = 9 ............. (i)
3x + 4y = 20 ............. (ii)
Taking first equation in reference, i.e,
x + 3y = 9
x = 9 - 3y ............. (iii)
Substituting this value of ‘x’ from previous equation in 2nd equation, we get;
3x + 4y = 20.
or, 3(9 - 3y) + 4y = 20
or, 27 - 9y + 4y = 20
or, -5y = 20 - 27
or, -5y = -7
or, 5y = 7
or, y = \(\frac{7}{5}\)
Substituting this value of y into equation of x in (iii), we get;
x = 9 - 3y
or, x = 9 - 3\(\frac{7}{5}\)
or, x = 9 – \(\frac{21}{5}\)
or, x = \(\frac{247}{5}\).
Hence, x = \(\frac{247}{5}\) and y = \(\frac{7}{5}\).
2. Solve for ‘x’ and ‘y’;
x + y = 5
4x + y = 10
Solution:
x + y = 5 ............. (i)
4x + y = 10 ............. (ii)
From equation (i), we get value of y as:
y = 5 - x
substituting this value of y in equation (ii), weget
4x + (5 - x) = 10
or, 4x + 5 - x = 10
or, 3x = 10 - 5
or, 3x = 5
x = \(\frac{5}{3}\).
Substituting this value of x as \(\frac{5}{3}\) in equation y = 5 - x , we get;
y = 5 - \(\frac{5}{3}\)
or, y = \(\frac{10}{3}\).
Hence, x = \(\frac{5}{3}\) and y = \(\frac{10}{3}\).
III. Solved example on simultaneous linear Equations using Cross-multiplication method:
Solve for ‘x’ and ‘y’;
3x + 5y - 25 = 0.
5x + 3y – 35 = 0.
Solution:
Assume two linear equations be
A1 x + B1y + C1 = 0, and
A2x + B2y + C2 = 0.
The coefficients of x are: A1 and A2.
The coefficients of y are: B1 and B2.
The constant terms are: C1 and C2.
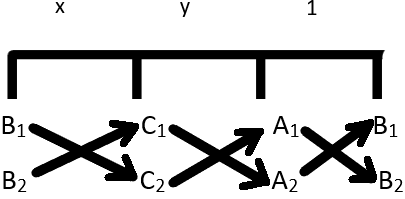
To solve the equations in a simplified way, we use following table:
\(\frac{x}{B_{1}C_{2} - B_{2}C_{1}} = \frac{y}{C_{1}A_{2} - C_{2}A_{1}} = \frac{1}{A_{1}B_{2} - A_{2}B_{1}}\)
In the given equations,
The coefficients of x are 3 and 5.
The coefficients of y are 5 and 3.
The constant terms are -25 and -35.
On substituting the respective values, we get
\(\frac{x}{5 × (-35) - 3 × (-25)} = \frac{y}{(-25) × 5 - (-35) × 3} = \frac{1}{3 × 3 - 5 × 5}\).
or, \(\frac{x}{- 175 + 75} = \frac{y}{-125 + 105} = \frac{1}{9 - 25}\).
or, \(\frac{x}{-100} = \frac{y}{-20} = \frac{1}{-16}\).
On equating x term with constant term, we get;
x = \(\frac{25}{4}\).
On equating y term with constant term, we get;
y = \(\frac{5}{4}\).
IV: Solved example on simultaneous linear Equations using evaluation method:
Solve for x and y:
2x + 3y = 4; 3x - 5y = -2
Solution:
The given equations are
2x + 3y = 4 .......... (1)
3x - 5y = -2.......... (2)
Multiplying equation (2) by 2, we get
6x - 10y = -4.......... (3)
Now we add equations (1) and (3) we get
8x - 7y = 0
or, 8x = 7y
or, \(\frac{x}{7}\) = \(\frac{y}{8}\) (= k)
Substituting x = 7k and y = 8k in equation (1) we get
2 ∙ 7k + 3 ∙ 8k = 4
or, 14k + 24k = 4
or, 38k = 4
or, K = \(\frac{4}{38}\)
or, k = \(\frac{2}{19}\)
Therefore, x = 7 ∙ \(\frac{2}{19}\) and y = 8 ∙ \(\frac{2}{19}\)
Thus, x = \(\frac{14}{19}\) and y = \(\frac{16}{19}\)
From Methods of Solving Simultaneous Linear Equations to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.