Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Laws of Exponents
The laws of exponents are explained here along with their examples.
1. Multiplying Powers with same Base
For example: x² × x³, 2³ × 2⁵, (-3)² × (-3)⁴
In multiplication of exponents if the bases are same then we need to add the exponents.
Consider the following:
1. 2³ × 2² = (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2) = 2\(^{3 + 2}\) = 2⁵
2. 3⁴ × 3² = (3 × 3 × 3 × 3) × (3 × 3) = 3\(^{4 + 2}\) = 3⁶
3. (-3)³ × (-3)⁴ = [(-3) × (-3) × (-3)] × [(-3) × (-3) × (-3) × (-3)]
= (-3)\(^{3 + 4}\)
= (-3)⁷
4. m⁵ × m³ = (m × m × m × m × m) × (m × m × m)
= m\(^{5 + 3}\)
= m⁸
From the above examples, we can generalize that during multiplication when the bases are same then the exponents are added.
aᵐ × aⁿ = a\(^{m + n}\)
In other words, if ‘a’ is a non-zero integer or a non-zero rational number and m and n are positive integers, then
aᵐ × aⁿ = a\(^{m + n}\)
Similarly, (\(\frac{a}{b}\))ᵐ × (\(\frac{a}{b}\))ⁿ = (\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{m + n}\)
\[(\frac{a}{b})^{m} \times (\frac{a}{b})^{n} = (\frac{a}{b})^{m + n}\]
Note:
(i) Exponents can be added only when the bases are same.
(ii) Exponents cannot be added if the bases are not same like
m⁵ × n⁷, 2³ × 3⁴
For example:
1. 5³ ×5⁶
= (5 × 5 × 5) × (5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5)
= 5\(^{3 + 6}\), [here the exponents are added]
= 5⁹
2. (-7)\(^{10}\) × (-7)¹²
= [(-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7)] × [( -7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7) × (-7)].
= (-7)\(^{10 + 12}\), [Exponents are added]
= (-7)²²
3. \((\frac{1}{2})^{4}\) × \((\frac{1}{2})^{3}\)
=[(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (\(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (\(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (\(\frac{1}{2}\))] × [(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (\(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (\(\frac{1}{2}\))]
=(\(\frac{1}{2}\))\(^{4 + 3}\)
=(\(\frac{1}{2}\))⁷
4. 3² × 3⁵
= 3\(^{2 + 5}\)
= 3⁷
5. (-2)⁷ × (-2)³
= (-2)\(^{7 + 3}\)
= (-2)\(^{10}\)
6. (\(\frac{4}{9}\))³ × (\(\frac{4}{9}\))²
= (\(\frac{4}{9}\))\(^{3 + 2}\)
= (\(\frac{4}{9}\))⁵
We observe that the two numbers with the same base are
multiplied; the product is obtained by adding the exponent.
2. Dividing Powers with the same Base
For example:
3⁵ ÷ 3¹, 2² ÷ 2¹, 5(²) ÷ 5³
In division if the bases are same then we need to subtract the exponents.
Consider the following:
2⁷ ÷ 2⁴ = \(\frac{2^{7}}{2^{4}}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2}{2 × 2 × 2 × 2}\)
= 2\(^{7 - 4}\)
= 2³
5⁶ ÷ 5² = \(\frac{5^{6}}{5^{2}}\)
= = \(\frac{5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5}{5 × 5}\)
= 5\(^{6 - 2}\)
= 5⁴
10⁵ ÷ 10³ = \(\frac{10^{5}}{10^{3}}\)
= \(\frac{10 × 10 × 10 × 10 × 10}{10 × 10 × 10}\)
= 10\(^{5 - 3}\)
= 10²
7⁴ ÷ 7⁵ = \(\frac{7^{4}}{7^{5}}\)
= \(\frac{7 × 7 × 7 × 7}{7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7}\)
= 7\(^{4 - 5}\)
= 7\(^{-1}\)
Let a be a non zero number, then
a⁵ ÷ a³ = \(\frac{a^{5}}{a^{3}}\)
= \(\frac{a × a × a × a × a}{a × a × a}\)
= a\(^{5 - 3}\)
= a²
again, a³ ÷ a⁵ = \(\frac{a^{3}}{a^{5}}\)
= \(\frac{a × a × a}{a × a × a × a × a}\)
= a\(^{-(5 - 3)}\)
= a\(^{-2}\)
Thus, in general, for any non-zero integer a,
aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = \(\frac{a^{m}}{a^{n}}\) = a\(^{m - n}\)
Note 1:
Where m and n are whole numbers and m > n;
aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = \(\frac{a^{m}}{a^{n}}\) = a\(^{-(n - m)}\)
Note 2:
Where m and n are whole numbers and m < n;
We can generalize that if ‘a’ is a non-zero integer or a non-zero rational number and m and n are positive integers, such that m > n, then
aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = a\(^{m - n}\) if m < n, then aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = \(\frac{1}{a^{n - m}}\)
Similarly, \((\frac{a}{b})^{m}\) ÷ \((\frac{a}{b})^{n}\) = \(\frac{a}{b}\) \(^{m - n}\)
For example:
1. 7\(^{10}\) ÷ 7⁸ = \(\frac{7^{10}}{7^{8}}\)
= \(\frac{7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7}{7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7}\)
= 7\(^{10 - 8}\), [here exponents are subtracted]
= 7²
2. p⁶ ÷ p¹ = \(\frac{p^{6}}{p^{1}}\)
= \(\frac{p × p × p × p × p × p}{p}\)
= p\(^{6 - 1}\), [here exponents are subtracted]
= p⁵
3. 4⁴ ÷ 4² = \(\frac{4^{4}}{4^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 4 × 4 × 4}{4 × 4}\)
= 4\(^{4 - 2}\), [here exponents are subtracted]
= 4²
4. 10² ÷ 10⁴ = \(\frac{10^{2}}{10^{4}}\)
= \(\frac{10 × 10}{10 × 10 × 10 × 10}\)
= 10\(^{-(4 - 2)}\), [See note (2)]
= 10\(^{-2}\)
5. 5³ ÷ 5¹
= 5\(^{3 - 1}\)
= 5²
6. \(\frac{(3)^{5}}{(3)^{2}}\)
= 3\(^{5 - 2}\)
= 3³
7. \(\frac{(-5)^{9}}{(-5)^{6}}\)
= (-5)\(^{9 - 6}\)
= (-5)³
8. (\(\frac{7}{2}\))⁸ ÷ (\(\frac{7}{2}\))⁵
= (\(\frac{7}{2}\))\(^{8 - 5}\)
= (\(\frac{7}{2}\))³
3. Power of a Power
For example: (2³)², (5²)⁶, (3² )\(^{-3}\)
In power of a power you need multiply the powers.
Consider the following
(i) (2³)⁴
Now, (2³)⁴ means 2³ is multiplied four times
i.e. (2³)⁴ = 2³ × 2³ × 2³ × 2³
=2\(^{3 + 3 + 3 + 3}\)
=2¹²
Note: by law (l), since aᵐ × aⁿ = a\(^{m + n}\).
(ii) (2³)²
Similarly, now (2³)² means 2³ is multiplied two times
i.e. (2³)² = 2³ × 2³
= 2\(^{3 + 3}\), [since aᵐ × aⁿ = a\(^{m + n}\)]
= 2⁶
Note: Here, we see that 6 is the product of 3 and 2 i.e,
(2³)² = 2\(^{3 × 2}\)= 2⁶
(iii) (4\(^{- 2}\))³
Similarly, now (4\(^{-2}\))³ means 4\(^{-2}\)
is multiplied three times
i.e. (4\(^{-2}\))³ =4\(^{-2}\) × 4\(^{-2}\) × 4\(^{-2}\)
= 4\(^{-2 + (-2) + (-2)}\)
= 4\(^{-2 - 2 - 2}\)
= 4\(^{-6}\)
Note: Here, we see that -6 is the product of -2 and 3 i.e,
(4\(^{-2}\))³ = 4\(^{-2 × 3}\) = 4\(^{-6}\)
For example:
1.(3²)⁴ = 3\(^{2 × 4}\) = 3⁸
2. (5³)⁶ = 5\(^{3 × 6}\) = 5¹⁸
3. (4³)⁸ = 4\(^{3 × 8}\) = 4²⁴
4. (aᵐ)⁴ = a\(^{m × 4}\) = a⁴ᵐ
5. (2³)⁶ = 2\(^{3 × 6}\) = 2¹⁸
6. (xᵐ)\(^{-n}\) = x\(^{m × -(n)}\) = x\(^{-mn}\)
7. (5²)⁷ = 5\(^{2 × 7}\) = 5¹⁴
8. [(-3)⁴]² = (-3)\(^{4 × 2}\) = (-3)⁸
In general, for any non-integer a, (aᵐ)ⁿ= a\(^{m × n}\) = a\(^{mn}\)
Thus where m and n are whole numbers.
If ‘a’ is a non-zero rational number and m and n are positive integers, then {(\(\frac{a}{b}\))ᵐ}ⁿ = (\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{mn}\)
For example:
[(\(\frac{-2}{5}\))³]²
= (\(\frac{-2}{5}\))\(^{3 × 2}\)
= (\(\frac{-2}{5}\))⁶
4. Multiplying Powers with the same Exponents
For example: 3² × 2², 5³ × 7³
We consider the product of 4² and 3², which have different bases, but the same exponents.
(i) 4² × 3² [here the powers are same and the bases are different]
= (4 × 4) × (3 × 3)
= (4 × 3) × (4 × 3)
= 12 × 12
= 12²
Here, we observe that in 12², the base is the product of bases 4 and 3.
We consider,
(ii) 4³ × 2³
= (4 × 4 × 4) × (2 × 2 × 2)
= (4 × 2)× ( 4 × 2) × (4 × 2)
= 8 × 8 × 8
= 8³
(iii) We also have, 2³ × a³
= (2 × 2 × 2) × (a × a × a)
= (2 × a) × (2 × a) × (2 × a)
= (2 × a)³
= (2a)³ [Here 2 × a = 2a]
(iv) Similarly, we have, a³ × b³
= (a × a × a) × (b × b × b)
= (a × b) × (a × b) × (a × b)
= (a × b)³
= (ab)³ [Here a × b = ab]
Note: In general, for any non-zero integer a, b.
aᵐ × bᵐ
= (a × b)ᵐ
= (ab)ᵐ [Here a × b = ab]
aᵐ × bᵐ = (ab)ᵐ
Note: Where m is any whole number.
(-a)³ × (-b)³
= [(-a) × (-a) × (-a)] × [(-b) × (-b) × (-b)]
= [(-a) × (-b)] × [(-a) × (-b)] × [(-a) × (-b)]
= [(-a) × (-b)]³
= (ab)³, [Here a × b = ab and two negative become positive, (-) × (-) = +]
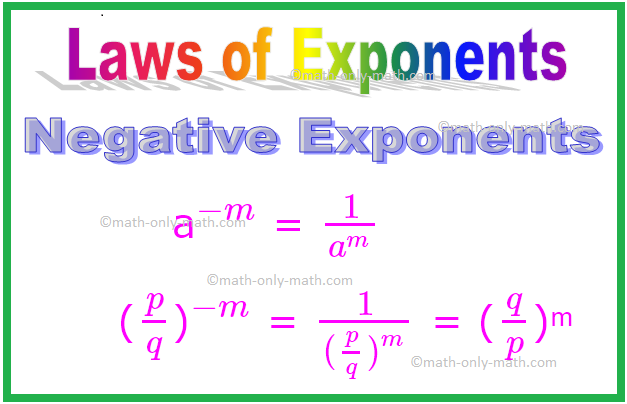
5. Negative Exponents
If the exponent is negative we need to change it into positive exponent by writing the same in the denominator and 1 in the numerator.
If ‘a’ is a non-zero integer or a non-zero rational number and m is a positive integers, then
a\(^{-m}\) is the reciprocal of aᵐ, i.e.,
a\(^{-m}\) = \(\frac{1}{a^{m}}\), if we take ‘a’ as \(\frac{p}{q}\) then (\(\frac{p}{q}\))\(^{-m}\) = \(\frac{1}{(\frac{p}{q})^{m}}\) = (\(\frac{q}{p}\))ᵐ
again, \(\frac{1}{a^{-m}}\) = aᵐ
Similarly, (\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{-n}\) = (\(\frac{b}{a}\))ⁿ, where n is a positive integer
Consider the following
2\(^{-1}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
2\(^{-2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2^{2}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
2\(^{-3}\) = \(\frac{1}{2^{3}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{8}\)
2\(^{-4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2^{4}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{16}\)
2\(^{-5}\) = \(\frac{1}{2^{5}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{32}\)
[So in negative exponent we need to write 1 in the numerator and in the denominator 2 multiplied to itself five times as 2\(^{-5}\). In other words negative exponent is the reciprocal of positive exponent]
For example:
1. 10\(^{-3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{10^{3}}\), [here we can see that 1 is in the numerator and in the denominator 10³ as we know that negative exponent is the reciprocal]
= \(\frac{1}{10}\) × \(\frac{1}{10}\) × \(\frac{1}{10}\), [Here 10 is multiplied to itself 3 times]
= \(\frac{1}{1000}\)
2. (-2)\(^{-4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{(-2)^{4}}\) [Here we can see that 1 is in the numerator and in the denominator (-2)⁴]
= (- \(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (- \(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (- \(\frac{1}{2}\)) × (- \(\frac{1}{2}\))
= \(\frac{1}{16}\)
3. 2\(^{-5}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2^{5}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
4. \(\frac{1}{3^{-4}}\)
= 3⁴
= 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 81
5. (-7)\(^{-3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{(-7)^{3}}\)
6. (\(\frac{3}{5}\))\(^{-3}\)
= (\(\frac{5}{3}\))³
7. (-\(\frac{7}{2}\))\(^{-2}\)
= (-\(\frac{2}{7}\))²
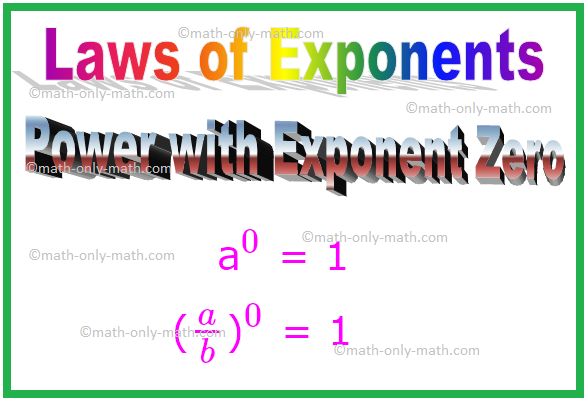
6. Power with Exponent Zero
If the exponent is 0 then you get the result 1 whatever the base is.
For example: 8\(^{0}\), (\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{0}\), m\(^{0}\)…....
If ‘a’ is a non-zero integer or a non-zero rational number then,
a\(^{0}\) = 1
Similarly, (\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{0}\) = 1
Consider the following
a\(^{0}\) = 1 [anything to the power 0 is 1]
(\(\frac{a}{b}\))\(^{0}\) = 1
(\(\frac{-2}{3}\))\(^{0}\) = 1
(-3)\(^{0}\) = 1
For example:
1. (\(\frac{2}{3}\))³ × (\(\frac{2}{3}\))\(^{-3}\)
= (\(\frac{2}{3}\))\(^{3 + (-3)}\), [Here we know that aᵐ × aⁿ = a\(^{m + n}\)]
= (\(\frac{2}{3}\))\(^{3 - 3}\)
= (\(\frac{2}{3}\))\(^{0}\)
= 1
2. 2⁵ ÷ 2⁵
= \(\frac{2^{5}}{2^{5}}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2}{2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2}\)
= 2\(^{5 - 5}\), [Here by the law aᵐ ÷ aⁿ =a\(^{m - n}\)]
= 2
= 1
3. 4\(^{0}\) × 3\(^{0}\)
= 1 × 1, [Here as we know anything to the power 0 is 1]
= 1
4. aᵐ × a\(^{-m}\)
= a\(^{m - m}\)
= a\(^{0}\)
= 1
5. 5\(^{0}\) = 1
6. (\(\frac{-4}{9}\))\(^{0}\) = 1
7. (-41)\(^{0}\) = 1
8. (\(\frac{3}{7}\))\(^{0}\) = 1
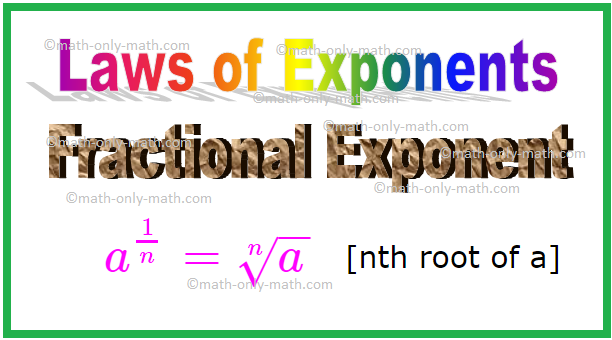
7. Fractional Exponent
In fractional exponent we observe that the exponent is in fraction form.
a\(^{\frac{1}{n}}\), [Here a is called the base and \(\frac{1}{n}\) is called the exponent or power]
= \(\sqrt[n]{a}\), [nth root of a]
\[a^{\frac{1}{n}} = \sqrt[n]{a}\]
Consider the following:
2\(^{\frac{1}{1}}\) = 2 (it will remain 2).
2\(^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = √2 (square root of 2).
2\(^{\frac{1}{3}}\) = ∛2 (cube root of 2).
2\(^{\frac{1}{4}}\) = ∜2 (fourth root of 2).
2\(^{\frac{1}{5}}\) = \(\sqrt[5]{2}\) (fifth root of 2).
For example:
1. 2\(^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = √2 (square root of 2).
2. 3\(^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = √3 [square root of 3]
3. 5\(^{\frac{1}{3}}\) = ∛5 [cube root of 5]
4. 10\(^{\frac{1}{3}}\) = ∛10 [cube root of 10]
5. 21\(^{\frac{1}{7}}\) = \(\sqrt[7]{21}\) [Seventh root of 21]
● Exponents
Integral Exponents of a Rational Numbers
● Exponents - Worksheets
8th Grade Math Practice
From Laws of Exponents to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
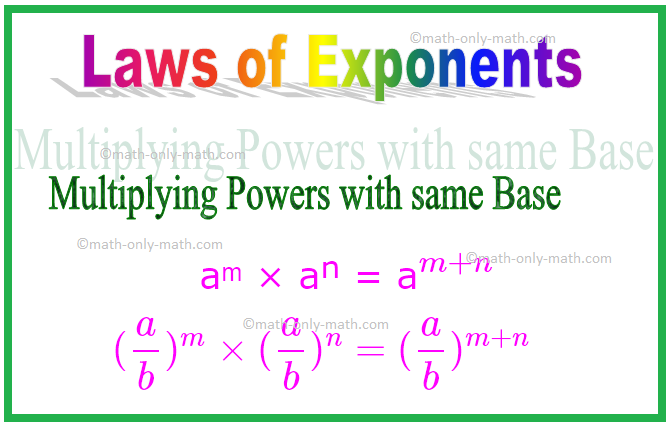
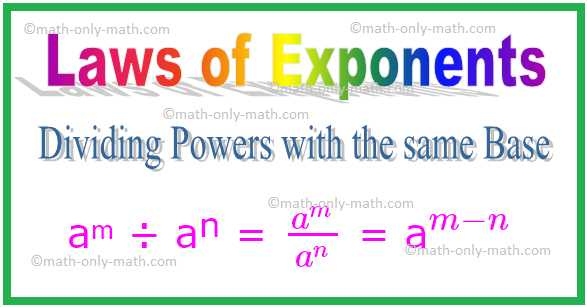

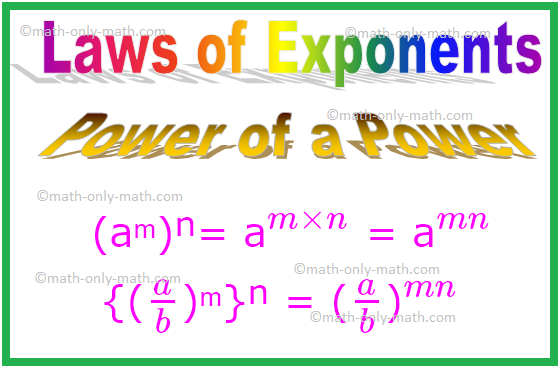
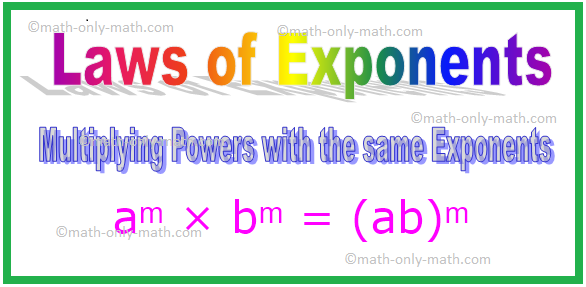


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.