Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Finding sin Value from Trigonometric Table
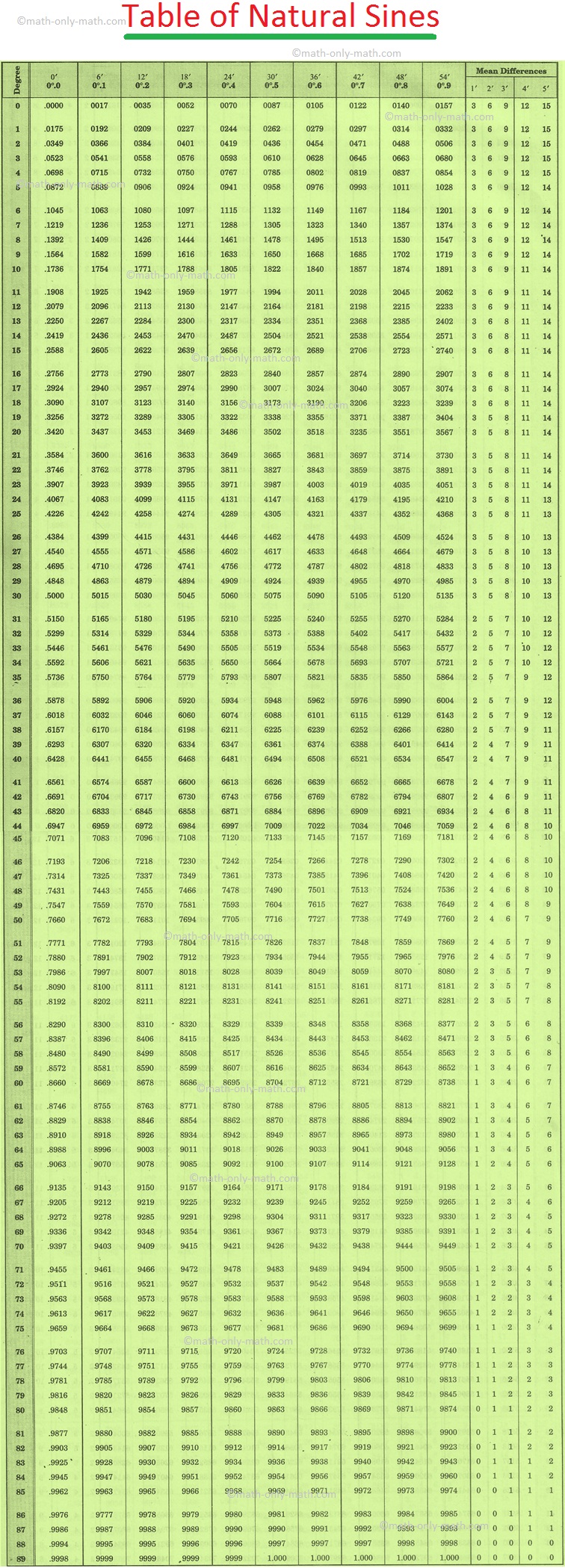
We know the values of the trigonometric ratios of some standard angles, viz, 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°. While applying the concept of trigonometric ratios in solving the problems of heights and distances, we may also require to use the values of trigonometric ratios of nonstandard angles, for example, sin 54°, sin 63° 45′, cos 72°, cos 46° 45′ and tan 48°. The approximate values, correct up to 4 decimal places, of natural sines, natural cosines and natural tangents of all angles lying between 0° and 90°, are available in trigonometric tables.
Reading Trigonometric Tables
Trigonometric tables consist of three parts.
(i) On the extreme left, there is a column containing 0 to 90 (in degrees).
(ii) The degree column is followed by ten columns with the headings
0′, 6′, 12′, 18′, 24′, 30′, 36′, 42′, 48′ and 54′ or
0.0°, 0.1°, 0.2°, 0.3°, 0.4°, 0.5°, 0.6°, 0.7°, 0.8° and 0.9°
(iii) After that, on the right, there are five columns known as mean difference columns with the headings 1′, 2′, 3′, 4′ and 5′.
Note: 60′ = 60 minutes = 1°.
1. Reading the values of sin 55°
To locate the value of sin 55°, look at the extreme left column. Start from the top and move downwards till you reach 55.
We want the value of sin 55°, i.e., sin 55° 0′. Now, move to the right in the row of 55 and reach the column of 0′.
We find 0.8192.
Therefore, sin 55° = 0.8192.
2. Reading the values of sin 55° 36′
To locate the value of sin 55° 36′, look at the extreme left column. Start from the top and move downwards till you reach 55.
Now, move to the right in the row of 55 and reach the column of 36′.
We find 8251i.e., 0.8251
Therefore, sin 55° 36′ = 0.8251.
3. Reading the values of sin 55° 20′
To locate the value of sin 55° 20′, look at the extreme left column. Start from the top and move downwards till you reach 55.
Now, move to the right in the row of 55 and reach the column of 18′.
We find 8221 i.e., 0.8221
So, sin 55° 20′ = 0.8221 + mean difference for 2′
= 0.8221
+ 3 [Addition, because sin 55° 20′ > sin 55° 18′]
0.8224
Therefore, sin 55° 20′ = 0.8224.
Conversely, if sin θ = 0.9298 then θ = sin 68° 24′ because in the table, the value 0.9298 corresponds to the column of 24′ in the row of 68, i.e., 68°.
From Finding sin Value from Trigonometric Table to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.