Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Divide by 2-digit Divisors
We will learn step-by-step how to divide by 2-digit divisors.
Let us consider some examples of division by two-digit numbers or divisors.
1. Divide 618 by 12.
|
Quotient = 51 Remainder = 6 |
Divisor (12) has two digits. Consider the two digits of the dividend from the left (61). Now, consider the left most digit of the divisor 12 i.e. 1 and the left most digit of the dividend i.e. 6. As, 1 goes into 6, 6 times. So, 6 may be the left most digit of the quotient.
Let us check 12 × 6 = 72, but 72 > 61. Now, consider 5 instead of 6 as left most digit of the quotient. Let us check 12 × 5 = 60, but 60 < 61. Now, write 5 as the left most digit of the quotient and 60 below the 61. Subtract 61 - 60 = 1. Write 1 as remainder. Bring down 8 from the dividend 618 and write it to the right of 1. It makes the remainder 18, which we consider as dividend now. i.e. we have to find 18 ÷ 12. 1 goes into 1, 1 time. So, 1 may be the second digit of the quotient. Let us check. 12 × 1 = 12 and 12 < 18 So, write 1 as quotient next to the 5 and 12 below the 18. Subtract 18 - 12 = 6. Write 6 as remainder. 6 becomes the final remainder as there is no digit left in dividend 618 to bring down and the remainder 6 cannot be divided by the divisor 12. |
2. Divide 8268 by 15.
|
Quotient = 551 Remainder = 3 |
Divisor (15) has two digits. So, we will divide by 2-digit divisors. Consider the two digits of the dividend from the left (82). Now, consider the left most digit of the divisor 15 i.e. 1 and the left most digit of the dividend i.e. 8. As, 1 goes into 8, 8 times. So, 8 may be the left most digit of the quotient.
Let us check 15 × 8 = 120, but 120 > 82. So, consider 7 and check 15 × 7 = 105, but 105 > 82. Now, consider 6 and check 15 × 6 = 90, but 90 > 82. Now, consider 5 and check 15 × 5 = 75, and 75 < 82. Write 5 as the left most digit of the quotient and 75 below the 82. Subtract 82 - 75 = 7. Write 7 as remainder. Bring down 6 from the dividend 8268 and write it to the right of 7. It makes the remainder 76, which we consider as dividend now. i.e. we have to find 76 ÷ 15. Repeat the process of 2nd step till we get a remainder either 0 or a number which is not divisible by divisor (15). |
3. Divide 4573 by 52.
|
Quotient = 87 Remainder = 49 |
Divisor (52) has two digits. So, we will divide by 2-digit divisors. Consider the two left most digits of the dividend (45). Since 45 < 52. Consider 3 left most digits of dividend i.e. 457. Because 1st digit of divisor (5) is greater than 1st digit of dividend (4) so, consider 45. 5 goes into 45, 9 times. So, 9 may be the left most digit of the quotient. Let us check 52 × 9 = 468, but 468 > 457. Consider 8 and check 52 × 8 = 416, but 416 < 457.
Write 8 as quotient and 416 below the 457. Subtract 457 - 416 = 41. Write 41 as remainder. Bring down 3 from the dividend 4573 and write it to the right of 41. Consider 413 as dividend now. i.e. we have to find 413 ÷ 52. Repeat the process of 2nd step till we get a remainder either 0 or a number which is not divisible by divisor (52). |
From Divide by 2-digit Divisors to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
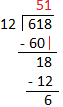
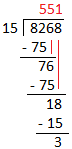
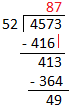


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.