Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Comparing Fractions
In comparing fractions, we may use the following steps:
STEP I
Find the LCM of the denominators of the given fractions.
STEP II
Convert all fractions to its equivalent fraction with denominator equal to the LCM obtained in step I.
STEP III
Arrange all the fractions in ascending or descending order by arranging numerators in ascending or descending order.
To compare two or more fractions, we convert them to like fractions and compare their numerators.
Examples on comparing fractions;
1. Which is bigger ³/₄ or ⁵/₁₂?
Solution:
First find the Least Common Multiple (L.C.M) of 4 and 12.
We have,
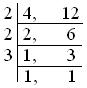
Therefore, LCM Least Common Multiple (L.C.M) of 4 and 12 is 2 × 2 × 3 = 12.
Now we need to convert the given fractions (3/4 and 5/12) to equivalent fractions with denominator 12.
We have,
3/4 = (3 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 9/12
We know that 9 > 5
Therefore, 9/12 > 5/12 ⇒ 3/4 > 5/12
2. Arrange the fractions 7/8, 2/3, 5/6 in ascending order.
Solution:
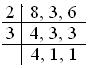
L.C.M. of 8, 3 and 6 = 2 × 3 × 4= 24.
7/8 = (7 × 3)/(8 × 3) = 21/24;
2/3 = (2 × 2 × 4)/(3 × 2 × 4) = 16/24;
5/6 = (5 × 4)/(6 × 4) = 20/24.
As 16 < 20 <21,
16/24 < 20/24 < 21/24 ⇒ 2/3 < 5/6 < 7/8.
Hence, the given fractions in ascending order are 2/3, 5/6, 7/8.
3. Arrange the following fractions in ascending order;
⁵/₈, ⁵/₆, ⁷/₄, ³/₅
Solution:
Let us first find the LCM of the denominators:
We have,
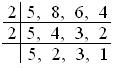
Therefore, LCM = 2 × 2 × 5 × 2 × 3 = 120
Now, we convert each fraction to its equivalent fraction with
denominator 120.
We have,
3/5 = (3 × 24)/(5 × 24) = 72/120 [Since, 120 ÷ 5 = 24]
5/8 = (5 × 15)/(8 × 15) = 75/120 [Since, 120 ÷ 8 = 15]
5/6 = (5 × 20)/(6 × 20) = 100/120 [Since, 120 ÷ 6 = 20]
7/4 = (7 × 30)/(4 × 30) = 210/120 [Since, 120 ÷ 4 = 30]
We know that 72 < 75 < 100 < 210.
⇒ 72/120 < 75/120 < 100/120 < 210/120
⇒ 3/5 < 5/8 < 5/6 < 7/4
Note:
If two fractions have the same numerator but different denominators, the fraction with greater denominator is smaller.
For example; 9/14 < 9/10
Also, 7/25 < 7/18 < 7/11 < 7/10 < 7/8
4. State which of the two fractions 7/12 and 5/21 has higher value.
Solution:
L.C.M. of 12 and 21 is 84.
7/12 = (7 × 7)/(12 × 7) = 49/84
5/21 = (5 × 4)/(21 × 4) = 20/84
Now, 49>20
Therefore, 7/12 > 5/21
5. Arrange the following fractions in descending order:
(i) 2/9, 2/3, 8/21
(ii) 1/5, 3/7, 7/10, 13/28
(i) 2/9, 2/3, 8/21
Solution:
First we convert the given fractions into like fractions i.e., fractions having common denominator. For this, we first find the LCM of the denominator of the given fractions.
Denominators are 9, 3 and 21
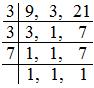
LCM of 9, 3, 21 = 3 × 3 × 7 = 63
Now, we convert each fraction into equivalent fractions with 63 as its denominator.
2/9 = (2 × 7)/(9 × 7) = 14/63 [Since, 63 ÷ 9 = 7]
2/3 = (2 × 21)/(3 × 21) = 42/63 [Since, 63 ÷ 3 = 21]
8/21 = (8 × 3)/(21 × 3) = 24/63 [Since, 63 ÷ 21 = 3]
We know that 42 > 24 > 14
Therefore, 42/63 > 24/63 > 14/63 ⇒ 2/3 > 8/21 > 2/9
(ii) 1/5, 3/7, 7/10, 13/28
Solution:
Denominators of the given fractions are: 5, 7, 10 and 28
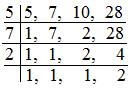
LCM of denominators = 5 × 7 × 2 × 2 = 140
We now convert each fraction into an equivalent fraction with 140 as its denominator.
Therefore, 1/5 = (1 × 28)/(5 × 28) = 28/140 [Since, 140 ÷ 5 = 28]
3/7 = (3 × 20)/(7 × 20) = 60/140 [Since, 140 ÷ 7 = 20]
7/10 = (7 × 14)/(10 × 14) = 98/140 [Since, 140 ÷ 10 = 14]
13/28 = (13 × 5)/(28 × 5) = 65/140 [Since, 140 ÷ 28 = 5]
Therefore,
98/140 > 65/140 > 60/140 > 28/140 ⇒ 7/10 > 13/28 > 3/7 > 1/5
Note:
We can also arrange the given fractions in descending order by making their numerators the same and using the result that the fraction having greater denominator is smaller, provided that they have the same numerator.
7th Grade Math Problems
From Comparing Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.