Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
2 Digit Numbers
The 2 digit numbers begin with 10. After ten, the next two-digit number is 11. Then 12, 13, 14, … etc. are two digit numbers.
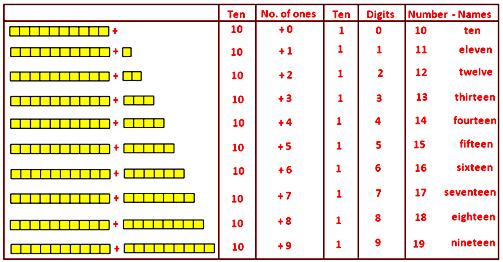
We see, the digits, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 are placed gradually to the right of the digit 1. Thus, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19 are formed. Their number-names are ten, eleven, twelve, thirteen, fourteen, fifteen, sixteen, seventeen, eighteen and nineteen.
These numbers i.e., from 10 to 19 may be demonstrated as follows:
After (19) nineteen, the next number is (20) twenty. In numbers 10 to 19 there is digit 1 of the left side of the number. In each number from 10 to 19, this one represents ten and the right side digit represents digit’s value. As in 17, 1 represents one ten and 7 represents seven. The number one ten and seven is called seventeen.
In number 20, there are two tens. After 20 the numbers are 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28 and 29. In these numbers there is digit 2 towards the left of the numbers. This two represents twenty, i.e., 2 × 10 or two tens, while the right side digits represent their original values.
In every two-digit number there are two places where the concerned digits are placed. One place is called one’s place. It is towards the right side. The other place is called ten’s place. It is towards the left side. The digit place at the right side, i.e., one’s place has its original value. The digit placed at the left side, i.e., ten’s place has its value ten times of its original value.
For example:
17 = 1 × 10 + 7 = 10 + 7
19 = 1 × 10 + 9 = 10 + 9
21 = 2 × 10 + 1 = 20 + 1
25 = 2 × 10 + 5 = 20 + 5
28 = 2 × 10 + 8 = 20 + 8
The two digit numbers have nine groups, i.e., 10 to 19, 20 to 29, 30 to 39, 40 to 49, 50 to 59, 60 to 69, 70 to 79, 80 to 89 and 90 to 99. Each group has 10 numbers. The total number of two digit numbers is 90.
From 1 to 99 there are 99 numbers, out of which there are 9 one-digit numbers, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. If one digit numbers are subtracted from 99 we get 90 two-digit numbers.
2nd Grade Math Practice
From 2 Digit Numbers to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.