Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Symmetric Functions of Roots of a Quadratic Equation
Let α and β be the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, (a ≠ 0), then the expressions of the form α + β, αβ, α2 + β2, α2 - β2, 1/α^2 + 1/β^2 etc. are known as functions of the roots α and β.
If the expression doesn’t change on interchanging α and β, then it is known as symmetric. In other words, an expression in α and β which remains same when α and β are interchanged, is called symmetric function in α and β.
Thus \frac{α^{2}}{β} + \(\frac{β^{2}}{α}\) is a symmetric function while α^{2} - β^{2} is not a symmetric function. The expressions α + β and αβ are called elementary symmetric functions.
We know that for the quadratic equation ax^{2} + bx + c = 0,
(a ≠ 0), the value of α + β = -\frac{b}{a} and αβ = \frac{c}{a}. To evaluate of a symmetric
function of the roots of a quadratic equation in terms of its coefficients; we
always express it in terms of α + β and αβ.
With the above information, the values of other functions of α and β can be determined:
(i) α^{2} + β^{2} = (α + β)^{2} - 2αβ
(ii) (α - β)^{2} = (α + β)^{2} - 4αβ
(iii) α^{2} - β^{2} = (α + β)(α - β) = (α + β) √{(α + β)^2 - 4αβ}
(iv) α^{3} + β^{3} = (α + β)^{3} - 3αβ(α + β)
(v) α^{3} - β^{3} = (α - β)(α^{2} + αβ + β^{2})
(vi) α^{4} + β^{4} = (α^{2} + β^{2})^{2} - 2α^{2}β^{2}
(vii) α^{4} - β^{4} = (α + β)(α - β)(α^{2} + β^{2}) = (α + β)(α - β)[(α + β)^{2} - 2αβ]
Solved example to find the symmetric functions of roots of a quadratic equation:
If α and β are the roots of the quadratic ax^{2} + bx + c = 0, (a ≠ 0), determine the values of the following expressions in terms of a, b and c.
(i) \frac{1}{α} + \frac{1}{β}
(ii) \frac{1}{α^{2}} + \frac{1}{β^{2}}
Solution:
Since, α and β are the roots of ax^{2} + bx + c = 0,
α + β = -\frac{b}{a} and αβ = \frac{c}{a}
(i) \frac{1}{α} + \frac{1}{β}
= \(\frac{α + β}{αβ}\) = -b/a/c/a = -b/c
(ii) \frac{1}{α^{2}} + \frac{1}{β^{2}}
= α^2 + β^2/α^2β^2
= (α + β)^{2} - 2αβ/(αβ)^2
= (-b/a)^2 – 2c/a/(c/a)^2 = b^2 -2ac/c^2
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Symmetric Functions of Roots of a Quadratic Equation to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Worksheet on Area, Perimeter and Volume | Square, Rectangle, Cube,Cubo
Jul 25, 25 12:21 PM
In this worksheet on area perimeter and volume you will get different types of questions on find the perimeter of a rectangle, find the perimeter of a square, find the area of a rectangle, find the ar… -
Worksheet on Volume of a Cube and Cuboid |The Volume of a RectangleBox
Jul 25, 25 03:15 AM
We will practice the questions given in the worksheet on volume of a cube and cuboid. We know the volume of an object is the amount of space occupied by the object.1. Fill in the blanks: -
Volume of a Cuboid | Volume of Cuboid Formula | How to Find the Volume
Jul 24, 25 03:46 PM
Cuboid is a solid box whose every surface is a rectangle of same area or different areas. A cuboid will have a length, breadth and height. Hence we can conclude that volume is 3 dimensional. To measur… -
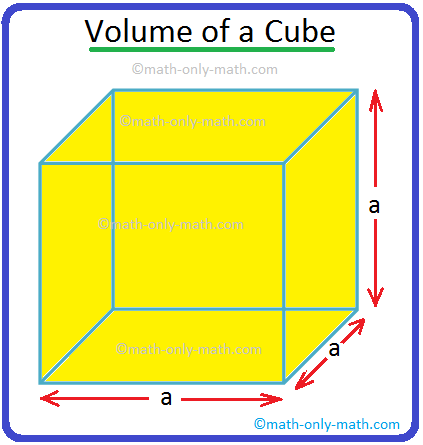
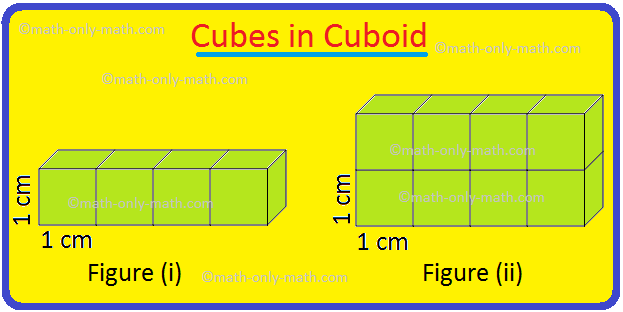
Volume of a Cube | How to Calculate the Volume of a Cube? | Examples
Jul 23, 25 11:37 AM
A cube is a solid box whose every surface is a square of same area. Take an empty box with open top in the shape of a cube whose each edge is 2 cm. Now fit cubes of edges 1 cm in it. From the figure i… -
5th Grade Volume | Units of Volume | Measurement of Volume|Cubic Units
Jul 20, 25 10:22 AM
Volume is the amount of space enclosed by an object or shape, how much 3-dimensional space (length, height, and width) it occupies. A flat shape like triangle, square and rectangle occupies surface on…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.