Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry
Simple math formula on trigonometry is given in such an order that students can easily get the formula.
Trigonometry
● Measurement of Trigonometrical Angles:
(i) The angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle is called a radian.
(ii) A radian is a constant angle.
One radian = (2/π) rt. angle = 57°17’44.8” (approx.)
(iii) 1 rt. angle = 90° ; 1° = 60’ ; 1‘ = 60”.
(iv) 1 rt. angle = 100ᵍ ; 1ᵍ = 100’ ; 1‵ = 100‶.
(v) πᶜ 180° = 200ᵍ.
(vi) The circumference of a circle of radius r is 2πr where π is a constant; approximate value of π is ²²/₇; more accurate value of π is 3.14159 (approx.).
(vii) If Θ be the radian measure of an angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius r by an arc of length s then Θ = ˢ/₀ or, s = rΘ.
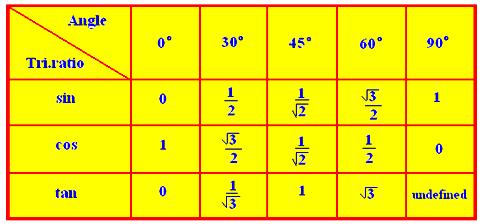
● Trigonometrical Ratios of some Standard Angles:
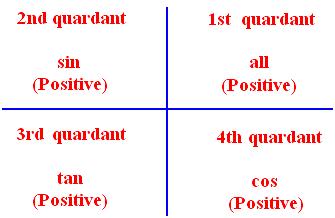
● Trigonometrical Ratios for Associated Angles:
(ii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an even integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = tan Θ or, (- tan Θ).
(iii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an odd integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cot ф or (- cot Θ).
● Compound Angles:
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B.
(ii) sin ( A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B.
(iii) cos (A + B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(iv) cos (A - B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(v) sin (A + B) sin (A - B) = sin² A - sin² B = cos² B - cos² A.
(vi) cos (A + B) cos (A - B) = cos² A - sin² B = cos² B - sin² A.
(vii) tan (A+ B) = (tan A + tan B)/(1 - tan A tan B).
(viii) tan (A - B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1 + tan A tan B).
(ix) cot (A + B) = (cot A cot B - 1)/(cot B + cot A).
(x) cot (A - B) = (cot A cot B + 1)/(cot B - cot A).
(xi) tan (A + B + C) = {(tan A + tan B + tan C) - (tan A tan B tan C)}/(1 - tan A tan B - tan B tan C - tan C tan A).
(xii) 2 sin A cos B = sin (A + B) + sin(A - B).
(xiii) 2 cos A sin B = sin (A + B ) - sin (A - B).
(xiv) 2 cos A cos B = cos (A + B ) + cos (A - B).
(xv) 2 sin A sin B = cos (A - B) - cos (A + B).
(xvii) sin C - sin D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
(xviii) cos C + cos D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 cos (C - D)/2.
(xix) cos C - cos D = 2 sin (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
● Multiple Angles:
(i) sin 2Θ = 2 sin Θ cos Θ.
(ii) cos 2Θ = cos² Θ - sin² Θ.
(iii) cos 2 Θ = 2 cos² Θ - 1.
(iv) cos 2Θ = 1 - 2 sin² Θ.
(v) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 cos² Θ.
(vi) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 sin² Θ.
(vii) tan² Θ = (1 - cos 2Θ)/(1 + cos 2Θ).
(viii) sin 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ)
(ix) cos 2Θ = (1 - tan² Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ).
(x) tan 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 - tan² Θ).
(xi) sin 3Θ = 3 sin Θ - 4 sin³ Θ.
(xii) cos 3ф = 4 cos³ Θ - 3 cos Θ.
(xiii) tan 3Θ = (3 tan Θ - tan³ Θ)/(1 - 3 tan² Θ).
● Submultiple Angles:
(i) sin Θ = 2 sin (Θ/2) cos (Θ/2).
(ii) cos Θ = cos² (Θ/2) - sin² (Θ/2).
(iii) cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2) - 1.
(iv) cos ф = 1 - 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(v) 1 + cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2).
(vi) 1 - cos Θ = 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(vii) tan² (Θ/2) = (1 - cos Θ)/(1 + cos Θ).
(viii) sin Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(ix) cos Θ = [1 - tan² (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(x) tan Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 - tan² (Θ/2)].
(xi) sin Θ = 3 sin (Θ/3) - 4 sin³ (Θ/3).
(xii) cos Θ = 4 cos³ (Θ/3) - 3 cos (Θ/2).
(xiii) (a) sin 15° = cos 75° = (√3 - 1)/(2√2).
(b) cos 15° = sin 75° = (√3 + 1)/(2√2).
(c) tan 15° = 2 - √3.
(d) sin 22 ½° = √(2 - √2).
(e) cos 22 ½° = ½ [√(2 + √2)].
(f) tan 22 ½° = √2 - 1.
(g) sin 18 ° = (√5 - 1)/4 = cos 72°.
(h) cos 36° = cos 72° = (√5 + 1)/4.
(i) cos 18° = sin 72° = ¼ [√(10 + 2√5)].
(j) sin 36° = cos 54° = ¼ [√(10 - 2√5)].
● General Solutions:
(i) (a) If sin Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If sin Θ = 1 then, Θ = (4n + 1)(π/2).
(c) If sin ф = -1 then, Θ = (4n - 1)(π/2).
(d) If sin Θ = sin α then, Θ = nπ + (-1)ⁿ α.
(ii) (a) If cos Θ = 0 then, Θ = (2n + 1)(π/2).
(b) If cos Θ = 1 then, Θ = 2nπ.
(c) If cos Θ = -1 then, Θ = (2n + 1)π.
(d) If cos Θ = cos α then, Θ = 2nπ ± α.
(ii) (a) If tan Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If tan Θ = tan α then, Θ = 2nπ + α where, n = 0 or any integer.
● Inverse Circular Functions:
(i) sin (sin-1 x) = x ; cos (cos-1 x) = x ; tan (tan-1 x) = x.(ii) sin-1 (sin Θ) = Θ ; cos-1 (cos Θ) = Θ ; tan-1 (tan Θ) = Θ.
(iii) sin-1 x = cosec-1 (1/x) = cos-1 [√(1 - x2)] = sec-1 [1/√(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [x/√(1 - x2)] = cot-1 [√(1 - x2)/x].
(iv) sin-1 x + cos-1 x = π/2 ; sec-1 x + cosec-1 x = π/2 ;
tan-1 x + cot-1 x = π/2.
(v) (a) tan-1 x + tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x + y)/(1 - xy)]
(b) tan-1 x - tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x - y)/(1 + xy)]
(vi) (a) sin-1 x + sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2) + y√(1 - x2)}
(b) sin-1 x - sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2 ) - y√(1 - x2)}
(vii) (a) cos-1 x + cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy - √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}
(b) cos-1 x - cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy + √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}.
(viii) 2 tan-1 x = sin-1 [2x/(1 + x2)] = cos-1 [(1 - x2)/(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [2x/(1 - x2)].
(ix) tan-1 x + tan-1 y + tan-1 z = tan-1 [(x + y + z - xyz)/(1 - xy - yz - zx)]
(x) sin-1 x and cos-1 x are defined when -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 ; sec-1 x and cosec-1 x are defined when Ι x Ι ≥ 1 ; tan-1 x and cot-1 x are defined
when - ∞ < x < ∞.
(xi) If principal values of sin-1 x, cos-1 x and tan-1 x be α, β and γ respectively, then -π/2 ≤ α ≤ π/2, 0 ≤ β ≤ π and -π/2 ≤ γ ≤ π/2.
● Properties of Triangle:
(i) a/(sin A) = b/(sin B) = c/(sin C) = 2R.
(ii) a = b cos C + c cos B ; b = c cos A + a cos C ; c = a cos B + b cos A.
(iii) cos A = (b² + c² - a²)/2bc ; cos B = (c² + a² - b²)/2ca ;
cos C = (a² + b² - c²)/2ab
(iv) tan A = [(abc)/R] ∙[ 1/(b² + c² - a²)]
tan B = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(c² + a² - b²)]
tan C = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(a² + b² - c²)].
(v) sin (A/2) = √[(s - b) (s - c)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/(ca)].
sin C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/(ab)].
cos A/2 = √[s (s - a)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[s (s - b)/(ca)].
cos C/2 = √[s (s - c)/(ab)].
tan A/2 = √[(s - b) (s - c)/{s(s - c)}].
tan B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/{s(s - b)}].
tan C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/{s(s - c)}].
(vi) tan [(B - C)/2] = [(b - c)/(b + c)] cot (A/2).
tan [(C - A)/2] = [(c - a)/(c + a)] cot (B/2).
tan [(A - B)/2] = [(a - b)/(a + b)] cot (C/2).
(vii) ∆ = ½ [bc sin A] = ½ [ca sin B] = ½ [ab sin C].
(viii) ∆ = √{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}.
(ix) R = ᵃᵇᶜ/₄₀.
(x) tan (A/2) = {(s - b)(s - c)}/∆.
tan (B/2) = {(s - c)(s - a)}/∆.
tan (C/2) = {(s - a)(s - b)}/∆
(xi) cot A/2 = {s(s - a)}/∆.
cot (B/2) = {s(s - b)}/∆.
cot (C/2) = {s(s - c)}/∆.
(xiii) r = ∆/s.
(xiv) r = 4R sin (A/2) sin (B/2) sin (C/2).
(xv) r = (s - a) tan (A/2) = (s - b) tan (B/2) = (s - c) tan (C/2).
(xvi) r₁ = ∆/(s - a) ; r₂ = ∆/(s - b); r₃ = ∆/(s - c) .
(xvii) r₁ = 4 R sin (A/2) cos (B/2) cos (C/2).
(xviii) r₂ = 4R sin (B/2) cos (C/2) cos (A/2).
(xix) r₃ = 4 R sin (C/2) cos (A/2) cos (B/2).
(xx) r₁ = s tan (A/2) ; r₂ = s tan (B/2) ; r₃ = s tan (C/2).
● Formula
- Basic Math Formulas
- Math Formula Sheet on Co-Ordinate Geometry
- All Math Formula on Mensuration
- Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Quadrilaterals | Four Sided Polygon | Closed Figure | Adjoining Figure
Jul 14, 25 02:55 AM
Quadrilaterals are known as four sided polygon.What is a quadrilateral? A closed figure made of our line segments is called a quadrilateral. For example: -
Formation of Numbers | Smallest and Greatest Number| Number Formation
Jul 14, 25 01:53 AM
In formation of numbers we will learn the numbers having different numbers of digits. We know that: (i) Greatest number of one digit = 9, -
5th Grade Geometry Practice Test | Angle | Triangle | Circle |Free Ans
Jul 14, 25 01:53 AM
In 5th grade geometry practice test you will get different types of practice questions on lines, types of angle, triangles, properties of triangles, classification of triangles, construction of triang… -
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
Jul 11, 25 02:14 PM
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circl… -
Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Jul 09, 25 01:29 AM
Construction of a Circle when the length of its Radius is given. Working Rules | Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be…

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.