Subscribe to our ▶️YouTube channel🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Area of a Polygon
In area of a polygon we will learn about polygon, regular polygon, central point of the polygon, radius of the inscribed circle of the polygon, radius of the circumscribed circle of a polygon and solved problems on area of a polygon.
Polygon: A figure bounded by four or more straight lines is called a polygon.
Regular Polygon: A polygon is said to be regular when all its sides are equal and all its angles are equal.
A polygon is named according to the number of sides it contains.
Given below are the names of some polygons and the number of sides contained by them.
Central Point of a Polygon:
The inscribed and the circumscribed circles of a polygon have the same centre, called the central point of the polygon.
Radius of the Inscribed Circle of a Polygon:
The length of perpendicular from the central point of a polygon upon any one of its sides, is the radius of the inscribed circle of the polygon.
The radius of the inscribed circle of a polygon is denoted by r.
Radius of the Circumscribed Circle of a Polygon:
The line segment joining the central point of a polygon to any vertex is the radius of the circumscribed circle of the polygon. The radius of the circumscribed circle of a polygon is denoted by R.
In the figure given below, ABCDEF is a polygon having central point O and one of its sides a unit. OL ⊥ AB.
Then, OL = r and OB = R
Area of a polygon of n sides
= n × (area ∆OAB) = n × ¹/₂ × AB × OL
= (ⁿ/₂ × a × r)
Now, A = 12 nar ⇔ a = 2Anr ⇔ na = 2Ar
⇔ Perimeter = 2Ar
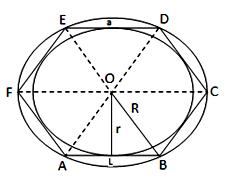
From right ∆OLB, we have:
OL² = OB² - LB² ⇔ r² = {R² - (ᵃ/₂)²}
⇔ r = √(R² - (a²/4)
Therefore, area of the polygon = {n/2 × a × √(R² - a²/4) square units.
In area of a polygon some of the particular cases such as;
(i) Hexagon:
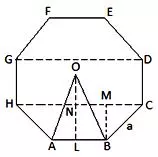
OL² = (OB² - LB²)
= {a² - (a/2)²} = (a² - a²/4) = 3a²/4
⇒ OL = {(√3)/2 × a}
⇒ Area ∆OAB = 1/2 × AB × OL
= {1/2 × a × (√3)/2 × a}
= (√3)a²/4
⇔ area of hexagon ABCDEF = {6 × (√3)a²/4} square units
= {3(√3)a²/2} square units.
Therefore, area of a hexagon = {3(√3)a²/2} square units.
(ii) Octagon:
BM is the side of a square whose diagonal is BC = a.
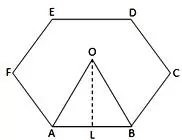
Therefore, BM = a√2
Now, OL = ON + LN
= ON + BM = (a/2 + a/√2)
⇔ Area of given octagon
= 8 × area of ∆OAB = 8 × 1/2 × AB × OL
= 4 × a × (a/2 + a/√2) = 2a² (1 + √2) square units.
Therefore, area of an octagon = 2a² (1 + √2) square units.
We will solve the examples on different names of the area of a polygon.
Area of a Polygon
1. Find the area of a regular hexagon each of whose sides measures 6 cm.
Solution:
Side of the given hexagon = 6 cm.
Area of the hexagon = {3√(3)a²/2} cm²
= (3 × 1.732 × 6 × 6)/2 cm²
= 93.528 cm².
2. Find the area of a regular octagon each of whose sides measures 5 cm.
Solution:
Side of the given octagon = 5 cm.
Area of the octagon = [2a² (1 + √2) square units
= [2 × 5 × 5 × (1 + 1.414)] cm²
= (50 × 2.414) cm²
= 120.7 cm².
3. Find the area of a regular pentagon each of whose sides measures 5 cm and the radius of the inscribed circle is 3.5 cm.
Solution:
Here a = 5 cm, r = 3.5 cm and n = 5.
Area of the pentagon = (n/2 × a × r) square units
= (5/2 × 5 × 7/2) cm²
= 43.75 cm².
4. Each side of a regular pentagon measures 8 cm and the radius of its circumscribed circle is 7 cm. Find the area of the pentagon.
Solution:
Area of the pentagon = {n/2 × a × √(R² - a²/4) square units
= {5/2 × 8 × √(7² - 64/4)} cm²
= {20 × √(49 - 16)} cm²
= (20 × √33) cm²
= (20 × 5.74) cm²
= (114.8) cm².
● Area of a Trapezium
● Area of a Trapezium - Worksheet
Worksheet on Area of a Polygon
8th Grade Math Practice
From Area of a Polygon to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Worksheet on Area of a Square and Rectangle | Area of Squares & Rectan
Jul 19, 25 05:00 AM
We will practice the questions given in the worksheet on area of a square and rectangle. We know the amount of surface that a plane figure covers is called its area. 1. Find the area of the square len… -
Area of Rectangle Square and Triangle | Formulas| Area of Plane Shapes
Jul 18, 25 10:38 AM
Area of a closed plane figure is the amount of surface enclosed within its boundary. Look at the given figures. The shaded region of each figure denotes its area. The standard unit, generally used for… -
What is Area in Maths? | Units to find Area | Conversion Table of Area
Jul 17, 25 01:06 AM
The amount of surface that a plane figure covers is called its area. It’s unit is square centimeters or square meters etc. A rectangle, a square, a triangle and a circle are all examples of closed pla… -
Worksheet on Perimeter | Perimeter of Squares and Rectangle | Answers
Jul 17, 25 12:40 AM
Practice the questions given in the worksheet on perimeter. The questions are based on finding the perimeter of the triangle, perimeter of the square, perimeter of rectangle and word problems. I. Find… -
Formation of Square and Rectangle | Construction of Square & Rectangle
Jul 16, 25 11:46 PM
In formation of square and rectangle we will learn how to construct square and rectangle. Construction of a Square: We follow the method given below. Step I: We draw a line segment AB of the required…

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.