Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Volume and Surface Area of Cube
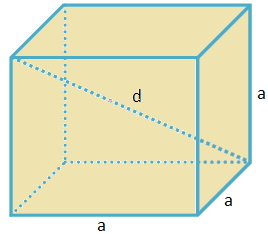
What is Cube?
A cuboid is a cube if its length, breadth and height are equal.
In a cube, all the faces are squares which are equal in area and all the edges are equal. A dice is an example of a cube.
Volume of a Cube (V) = (edge)3 = a3
Total surface Area of a Cube (S) = 6(edge)2 = 6a2
Diagonal a Cube (d) = √3(edge) = √3a
Where a = edge
Problems on Volume and Surface Area of Cube:
1. If the edge of a cube measures 5 cm, find (i) it volume, (ii) its surface area, and (iii) the length of a diagonal.
Solution:
(i) volume = (edge)3
= 53 cm3
= 125 cm3
(ii) Surface area = 6(edge)2
= 6 × 52 cm2
= 6 × 25 cm2
= 150 cm2
(iii) The length of a diagonal = √3(edge)
= √3 × 5 cm.
= 5√3 cm.
2. If the surface area of a cube is 96 cm2, find its volume.
Solution:
Let the edge of the cube be x.
Then, its surface area = 6x2
Therefore, 96 cm2 = 6x2
⟹ x2 = \(\frac{96 cm^{2}}{6}\)
⟹ x2 = 16 cm2
⟹ x = 4 cm.
Therefore, edge = 4 cm.
Therefore, the volume = (edge)3
= 43 cm3
= 64 cm3.
3. A cube of edge 2 cm is divided into cubes of edge 1 cm. How many cubes will be made? Find the total surface area of the smaller cubes.
Solution:
Volume of the bigger cube = (edge)3
= 23 cm3
= 8 cm3.
Volume of each of the smaller cubes = (edge)3
= 13 cm3
= 1 cm3
Therefore, the number of smaller cubes = \(\frac{8 cm^{3}}{1 cm^{3}}\)
= 8
The total surface area of a smaller cube = 6(edge)2
= 6 × 1 cm2
= 6 cm2
Therefore, the total surface area of the eight smaller cubes = 8 × 6 cm2 = 48 cm2.
From Volume and Surface Area of Cube to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.