Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Trigonometric Identities
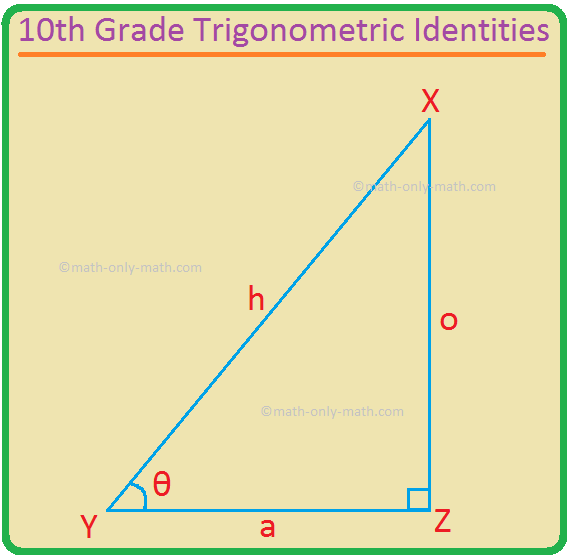
XYZ is a right-angled triangle in which ∠XZY = 90° and ∠XYZ = θ, which in an acute angle.
We know,
sin θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Opposite}}{\textrm{Hypotenuse}}\) = \(\frac{o}{h}\);
cos θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Adjacent}}{\textrm{Hypotenuse}}\) = \(\frac{a}{h}\);
tan θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Opposite}}{\textrm{Adjacent}}\) = \(\frac{o}{a}\);
csc θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Hypotenuse}}{\textrm{Opposite}}\) = \(\frac{h}{o}\);
sec θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Hypotenuse}}{\textrm{Adjacent}}\) = \(\frac{h}{a}\);
cot θ = \(\frac{\textrm{Adjacent}}{\textrm{Opposite}}\) = \(\frac{a}{o}\).
Let’s multiply sin θ and csc θ
sin θ ∙ csc θ = \(\frac{o}{h}\) × \(\frac{h}{o}\) = 1
Therefore, csc θ = \(\frac{1}{sin θ}\)
Now, multiply cos θ and sec θ
cos θ ∙ sec θ = \(\frac{a}{h}\) × \(\frac{h}{a}\) = 1
Therefore, sec θ = \(\frac{1}{cos θ}\)
Again, multiply tan θ and cot θ
tan θ ∙ cot θ = \(\frac{o}{a}\) × \(\frac{a}{a}\) = 1
Therefore, cot θ = \(\frac{1}{tan θ}\)
Let’s divide sin θ by cos θ
sin θ ÷ cos θ = \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\) = \(\frac{\frac{o}{h}}{\frac{a}{h}}\) = \(\frac{o}{a}\) = tan θ.
Therefore, tan θ = \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\).
Similarly, divide cos θ by sin θ
cos θ ÷ sin θ = \(\frac{cos θ}{sin θ}\) = \(\frac{\frac{a}{h}}{\frac{o}{h}}\) = \(\frac{a}{o}\) = cot θ.
Therefore, cot θ = \(\frac{cos θ}{sin θ}\).
If a relation of equality between two expressions involving trigonometric ratios of an angle θ holds true for all values of θ then the equality is called a trigonometric identity. But it holds true only for some values of θ, the equality gives a trigonometric equation. There are a number of fundamental trigonometric identities.
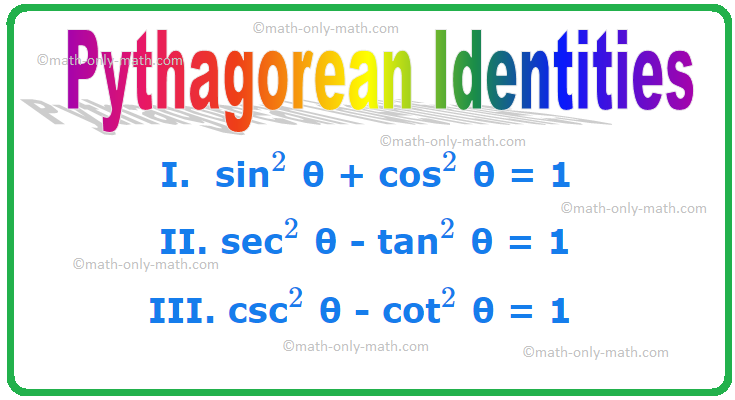
I. sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1
We have, sin θ = \(\frac{o}{h}\) and cos θ = \(\frac{a}{h}\).
Therefore, sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = \(\frac{o^{2}}{h^{2}}\) + \(\frac{a^{2}}{h^{2}}\).
= \(\frac{o^{2} + a^{2}}{h^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{h^{2}}{h^{2}}\); [Since, in the right-angled ∆XYZ, o\(^{2}\) + a\(^{2}\) = h\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ Theorem)]
= 1.
Therefore, sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1.
Consequently, 1 - sin\(^{2}\) θ = cos\(^{2}\) θ and 1 - cos\(^{2}\) θ = sin\(^{2}\) θ.
II. sec\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ = 1
We have, sec θ = \(\frac{h}{a}\) and tan θ = \(\frac{o}{a}\).
Therefore, sec\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ = \(\frac{h^{2}}{a^{2}}\) - \(\frac{o^{2}}{a^{2}}\).
= \(\frac{h^{2} - o^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{a^{2}}{a^{2}}\); [Since, in the right-angled ∆XYZ, o\(^{2}\) + a\(^{2}\) = h\(^{2}\) ⟹ h\(^{2}\) - o\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ Theorem)]
= 1.
Therefore, sec\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ = 1.
Consequently, 1 + tan\(^{2}\) θ = sec\(^{2}\) θ and sec\(^{2}\) θ - 1 = tan\(^{2}\) θ.
III. csc\(^{2}\) θ - cot\(^{2}\) θ = 1
We have, csc θ = \(\frac{h}{o}\) and cot θ = \(\frac{a}{o}\).
Therefore, csc\(^{2}\) θ - cot\(^{2}\) θ = \(\frac{h^{2}}{o^{2}}\) - \(\frac{a^{2}}{o^{2}}\).
= \(\frac{h^{2} - a^{2}}{o^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{o^{2}}{o^{2}}\); [Since, in the right-angled ∆XYZ, o\(^{2}\) + a\(^{2}\) = h\(^{2}\) ⟹ h\(^{2}\) - a\(^{2}\) = o\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ Theorem)]
= 1.
Therefore, csc\(^{2}\) θ - cot\(^{2}\) θ = 1.
Consequently, 1 + cot\(^{2}\) θ = csc\(^{2}\) θ and csc\(^{2}\) θ - 1 = cot\(^{2}\) θ.
These three trigonometric identities are also called Pythagorean identities.
Note: The equalities csc θ = \(\frac{1}{sin θ}\), sec θ = \(\frac{1}{cos θ}\), cot θ = \(\frac{1}{tan θ}\), tan θ = \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\) and cot θ = \(\frac{cos θ}{sin θ}\) are holds for all values of θ. Therefore, these equalities are trigonometric identities.
Thus, we have the following trigonometric identities.
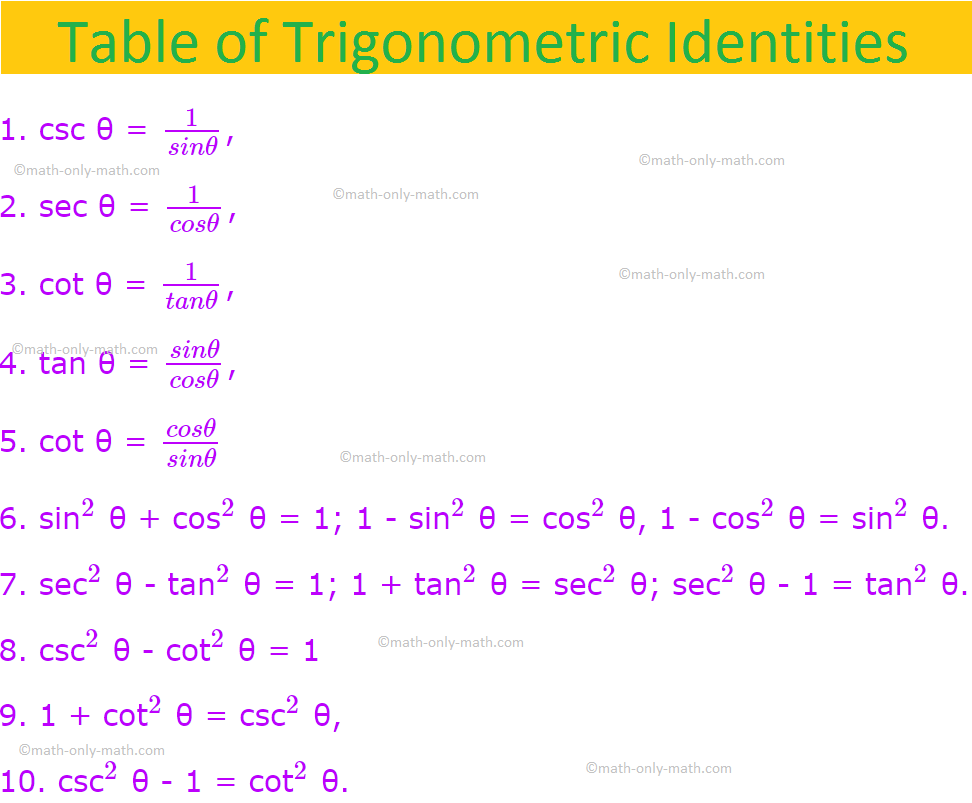
Table of Trigonometric Identities
1. csc θ = \(\frac{1}{sin θ}\),
2. sec θ = \(\frac{1}{cos θ}\),
3. cot θ = \(\frac{1}{tan θ}\),
4. tan θ = \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\),
5. cot θ = \(\frac{cos θ}{sin θ}\)
6. sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1; 1 - sin\(^{2}\) θ = cos\(^{2}\) θ, 1 - cos\(^{2}\) θ = sin\(^{2}\) θ.
7. sec\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ = 1; 1 + tan\(^{2}\) θ = sec\(^{2}\) θ; sec\(^{2}\) θ - 1 = tan\(^{2}\) θ.
8. csc\(^{2}\) θ - cot\(^{2}\) θ = 1
9. 1 + cot\(^{2}\) θ = csc\(^{2}\) θ,
10. csc\(^{2}\) θ - 1 = cot\(^{2}\) θ.
Solved Examples on Trigonometric Identities:
1. Prove that sin\(^{4}\) θ + cos\(^{4}\) θ + 2 sin\(^{2}\) θ ∙ cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1
Solution:
LHS = sin\(^{4}\) θ + cos\(^{4}\) θ + 2 sin\(^{2}\) θ ∙ cos\(^{2}\) θ
= (sin\(^{2}\) θ)\(^{2}\) + (cos\(^{2}\) θ)\(^{2}\) + 2 sin\(^{2}\) θ ∙ cos\(^{2}\) θ
= (sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ)\(^{2}\)
= 1\(^{2}\); [Since, sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1]
= 1 = RHS. (Proved).
How to Solve Trigonometric Identities Proving Problems?
2. Show that sec θ - cos θ = sin θ tan θ
Solution:
LHS = sec θ - cos θ
= \(\frac{1}{cos θ}\) - cos θ
= \(\frac{1 - cos^{2} θ}{cos θ}\)
= \(\frac{sin^{2} θ}{cos θ}\); [Since, sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1]
= sin θ ∙ \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\)
= sin θ ∙ tan θ = RHS. (Proved)
3. Prove that 1 - \(\frac{cos^{2} A}{1 + sin A}\) = sin A
Solution:
LHS = 1 - \(\frac{cos^{2} A}{1 + sin A}\)
= 1 - \(\frac{1 - sin^{2} A}{1 + sin A}\); [cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1 - sin\(^{2}\) θ]
= 1 - \(\frac{(1 + sin A)(1 – sin A)}{1 + sin A}\)
= 1 – (1 – sin A)
= 1 – 1 + sin A
= sin A = RHS. (Proved).
Verifying Trigonometric Identities & Equations
4. Prove that \(\frac{sin A}{1 + cos A}\) + \(\frac{sin A}{1 - cos A}\) = 2 csc A.
Solution:
LHS = \(\frac{sin A}{1 + cos A}\) + \(\frac{sin A}{1 - cos A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A(1 – cos A) + sin A(1 + cos A)}{(1 + cos A)(1 – cos A)}\)
= \(\frac{sin A – sin A ∙ cos A + sin A + sin A ∙ cos A)}{1 - cos^{2} A}\)
= \(\frac{2 sin A}{sin^{2} A}\); [Since, 1 - cos\(^{2}\) A = sin\(^{2}\) A]
= \(\frac{2}{sin A}\)
= 2 ∙ \(\frac{1}{sin A}\); [Since, csc A = \(\frac{1}{sin A}\)]
= RHS. (Proved).
Proving Trigonometric Identities Practice Problems Online
5. Prove that \(\frac{sin A}{1 + cos A}\) = \(\frac{1 – cos A}{sin A}\).
Solution:
LHS = \(\frac{sin A}{1 + cos A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A}{1 + cos A}\) ∙ \(\frac{1 - cos A}{1 - cos A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A(1 - cos A)}{1 - cos^{2} A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A(1 - cos A)}{sin^{2} A}\); [Since 1 - cos\(^{2}\) θ = sin\(^{2}\) θ]
= \(\frac{1 - cos A}{sin A}\) = RHS. (Proved).
Trigonometry Problems and Questions with Solutions
6. Prove that \(\sqrt{\frac{1 + sin θ}{1 - sin θ}}\) = sec θ +tan θ.
Solution:
LHS = \(\sqrt{\frac{1 + sin θ}{1 - sin θ}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{(1 + sin θ) (1 + sin θ)}{(1 - sin θ)(1 + sin θ)}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{(1 + sin θ)^{2}}{1 – sin^{2} θ}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{(1 + sin θ)^{2}}{cos^{2} θ}}\); [Since 1 - sin\(^{2}\) θ = cos\(^{2}\) θ]
= \(\frac{1 + sin θ}{cos θ}\)
= \(\frac{1}{cos θ}\) + \(\frac{sin θ}{cos θ}\)
= secθ + tan θ = RHS. (Proved).
Trigonometric identities problems for class 10
7. Prove that tan\(^{2}\) A – tan\(^{2}\) B = \(\frac{sin^{2} A - sin^{2} B}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\) = sec\(^{2}\) A - sec\(^{2}\) B
Solution:
LHS = tan\(^{2}\) A – tan\(^{2}\) B
= \(\frac{sin^{2} A}{cos^{2} A}\) - \(\frac{ sin^{2} B}{cos^{2} B}\)
= \(\frac{sin^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B - sin^{2} B ∙ cos^{2} A}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\)
= \(\frac{sin^{2} A (1 - sin^{2} B) - sin^{2} B(1 - sin^{2} A)}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\); [Since, cos2 B = 1 - sin2 B and cos2 A = 1 - sin2 A]
= \(\frac{sin^{2} A - sin^{2} A sin^{2} B - sin^{2} B + sin^{2} B sin^{2} A}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\);
= \(\frac{sin^{2} A - sin^{2} B}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\) = MHS
= \(\frac{(1 - cos^{2} A) - (1 - cos^{2} B)}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\); [Since, sin2 A = 1 - cos2 A and sin2 B = 1 - cos2 B]
= \(\frac{cos^{2} B - cos^{2} A}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\)
= \(\frac{cos^{2} B}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\) - \(\frac{cos^{2} A}{cos^{2} A ∙ cos^{2} B}\)
= \(\frac{1}{cos^{2} A}\) - \(\frac{1}{cos^{2} B}\)
= sec\(^{2}\) A – sec\(^{2}\) B = RHS. (Proved)
Again,
LHS = tan\(^{2}\) A – tan\(^{2}\) B
= (sec\(^{2}\) A – 1) – (sec\(^{2}\) B – 1); [Since, tan\(^{2}\) θ = sec\(^{2}\) θ – 1 ]
= sec\(^{2}\) A – 1 – (sec\(^{2}\) B +1
= sec\(^{2}\) A – sec\(^{2}\) B = RHS. (Proved).
Solving Trigonometric Equations using Trigonometric Identities
8. Prove that tan\(^{2}\) θ - sin\(^{2}\) θ = tan\(^{2}\) θ ∙ sin\(^{2}\) θ
Solution:
LHS = tan\(^{2}\) θ - sin\(^{2}\) θ
= tan\(^{2}\) θ - \(\frac{sin^{2} θ}{cos^{2} θ}\) ∙ cos\(^{2}\)
= tan\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ ∙ cos\(^{2}\)
= tan\(^{2}\) θ(1 - cos\(^{2}\))
= tan\(^{2}\) θ ∙ sin\(^{2}\) θ = RHS. (Proved).
List of trigonometric identities Problems
9. Prove that 1 + \(\frac{cot^{2} θ}{1 + csc θ}\) = csc θ
Solution:
LHS = 1 + \(\frac{cot^{2} θ}{1 + csc θ}\)
= 1 + \(\frac{csc^{2} θ - 1}{1 + csc θ}\)
= 1 + \(\frac{(csc θ + 1)(csc θ – 1)}{1 + csc θ}\)
= 1 + (csc θ – 1)
= 1 + csc θ – 1
= csc θ = RHS. (Proved).
Solve the problem using trigonometric identities
10. Prove that \(\frac{sec θ - )}{sec θ + 1}\) = (cot θ – csc θ)\(^{2}\).
Solution:
LHS = \(\frac{sec θ - 1}{sec θ + 1}\)
= \(\frac{sec θ - 1}{sec θ + 1}\) ∙ \(\frac{sec θ - 1}{sec θ - 1}\)
= \(\frac{(sec θ - 1)^{2}}{sec^{2} θ - 1}\)
= \(\frac{(sec θ - 1)^{2}}{tan^{2} θ}\); [Since sec\(^{2}\) θ – 1 = tan\(^{2}\) θ]
= \((\frac{sec θ - 1}{tan θ})^{2}\)
= \((\frac{\frac{1}{cos θ} - 1}{\frac{sin θ }{cos θ} })^{2}\)
= \((\frac{1 – cos θ}{cos θ} ∙ \frac{cos θ}{sin θ})^{2}\)
= \((\frac{1 – cos θ}{sin θ})^{2}\)
= \((\frac{1}{sin θ} - \frac{cos θ}{sin θ})^{2}\)
= (csc θ – cot θ)\(^{2}\)
= (cot θ – csc θ)\(^{2}\) = RHS. (Proved).
Proving Trigonometric Identities
11. Prove that \(\frac{sin A}{cot A + csc A}\) = 2 + \(\frac{sin A}{cot A - csc A }\)
Solution:
LHS = \(\frac{sin A}{cot A + csc A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A(cot A - csc A)}{(cot A + csc A)(cot A - csc A)}\)
= \(\frac{sin A ∙ cot A – sin A ∙ csc A}{cot^{2} A – csc^{2} A}\)
= \(\frac{sin A ∙ \frac{cos A}{sin A} – 1}{-1}\); [since, sin θ csc θ = 1, csc\(^{2}\) θ – cot\(^{2}\) θ = 1]
= \(\frac{cos A - 1}{-1}\)
= 1 – cos A
RHS = 2 + \(\frac{sin A}{cot A - csc A}\)
= 2 + \(\frac{sin A}{ cot A - csc A}\) ∙ \(\frac{(cot A + csc A)}{(cot A + csc A)}\)
= 2 + \(\frac{sin A(cot A + csc A)}{cot^{2} A – csc^{2} A}\)
= 2 + \(\frac{sin A(\frac{cos A}{sin A} + \frac{1}{sin A})}{-1}\)
= 2 + \(\frac{cos A + 1}{-1}\)
= 2 – (cos A + 1)
= 2 – cos A – 1
= 1 – cos A
Therefore, LHS = RHS. (Proved).
Alternative Method
The identity is established if we can prove that
\(\frac{sin A}{cot A + csc A}\) - \(\frac{sin A}{cot A - csc A }\) = 2
Now, here
LHS = \(\frac{sin A}{cot A + csc A}\) - \(\frac{sin A}{cot A - csc A }\)
= \(\frac{sin A(cot A - csc A) – sin A(cot A + csc A)}{( cot A + csc A)(cot A - csc A)}\)
= \(\frac{sin A ∙ cot A – sin A ∙ csc A – sin A ∙ cot A – sin A ∙ csc A}{(cot A + csc A)(cot A - csc A)}\)
= \(\frac{–2 sin A ∙ csc A}{cot^{2} A – csc^{2} A}\)
= \(\frac{–2}{-1 }\); [Since sin θ csc θ = 1, csc\(^{2}\) θ – cot\(^{2}\) θ = 1]
= 2 = RHS. (Proved)
Problems on Evaluation using Trigonometric Identities:
12. If sin θ + csc θ = 2, find the value of sin\(^{10}\) θ + csc\(^{11}\) θ
Solution:
Given that, sin θ + csc θ = 2 ……………. (i)
⟹ sin θ + \(\frac{1}{ sin θ}\) = 2
⟹ \(\frac{ sin^{2} θ + 1}{sin θ }\) = 2
⟹ sin\(^{2}\) θ + 1= 2 sin θ
⟹ sin\(^{2}\) θ - 2 sin θ + 1 = 0
⟹ (sin θ - 1)\(^{2}\) = 0
⟹ sin θ - 1 = 0
⟹ sin θ = 1
⟹ csc θ = \(\frac{1}{ sin θ}\) = \(\frac{1}{ 1}\) = 1
Therefore, csc θ = 1.
Now, sin\(^{10}\) θ + csc\(^{11}\) θ
= 1\(^{10}\) + 1\(^{11}\)
= 1 + 1
= 2.
13. If sec θ – tan θ = \(\frac{1}{3}\), find the value of sec A and tan A.
Solution:
Given, sec θ – tan θ = \(\frac{1}{3}\) ………… (i)
We know that the Pythagorean identity, sec\(^{2}\) θ - tan\(^{2}\) θ = 1.
⟹ (sec θ + tan θ)(sec θ - tan θ) = 1
⟹ (sec θ + tan θ) ∙ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 1, [Given sec θ – tan θ = \(\frac{1}{3}\)]
⟹ sec θ + tan θ = 3 ……….. (ii)
Now adding (i) and (ii) we get
2 sec θ = \(\frac{1}{3}\) + 3
⟹ 2 sec θ = \(\frac{10}{3}\)
⟹ sec θ = \(\frac{10}{3}\) ∙ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
⟹ sec θ = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Therefore, sec θ = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Putting the value of sec θ = \(\frac{5}{3}\) in (ii), we get
\(\frac{5}{3}\) + tan θ = 3
⟹ tan θ = 3 - \(\frac{5}{3}\)
⟹ tan θ = \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Therefore, tan θ = \(\frac{4}{3}\).
14. If tan A + sec A = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\), find the value of sin A
Solution:
Given that, tan A + sec A = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\) ……………….. (i)
We know the Pythagorean trigonometric identity,
sec\(^{2}\) A - tan\(^{2}\) A = 1.
⟹ (sec A + tan A)(sec A – tan A) = 1
⟹ \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\)(sec A – tan A) = 1; [given , tan A + sec A = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\)]
⟹ sec A – tan A = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) ……………….. (ii)
Solving these two equations we get,
2 sec A = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\) + \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
⟹ 2 sec A = \(\frac{4 + 3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
⟹ 2 sec A = \(\frac{7}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
⟹ sec A = \(\frac{7}{4\sqrt{3}}\) ……………….. (iii)
Putting the value of sec A = \(\frac{7}{4\sqrt{3}}\) in (i) we get,
tan A + \(\frac{7}{4\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\)
⟹ tan A = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\frac{7}{4\sqrt{3}}\)
⟹ tan A = \(\frac{8 - 7}{4\sqrt{3}}\)
⟹ tan A = \(\frac{1}{4\sqrt{3}}\)……………….. (iv)
Now dividing (iv) by (iii) we get,
\(\frac{tan A}{sec A}\) = \(\frac{1}{7}\)
⟹ sin A = \(\frac{1}{7}\)
Therefore, sin A = \(\frac{1}{7}\).
Problems on establishing conditional results
15. If cos A + sin A = \(\sqrt{2}\) cos A, prove that cos A - sin A = \(\sqrt{2}\) sin A.
Solution:
Let cos A - sin A = k. Now,
(cos A + sin A)\(^{2}\) + (cos A - sin A)\(^{2}\) = cos\(^{2}\) A + sin\(^{2}\) A + 2 cos A ∙ sin A + cos\(^{2}\) A + sin\(^{2}\) A - 2 cos A ∙ sin A
= 1 + 2 cos A sin A + 1 - 2 cos A sin A
= 2
Therefore, (\(\sqrt{2}\) cos A)\(^{2}\) + k\(^{2}\) = 2
⟹ k\(^{2}\) = 2 - (\(\sqrt{2}\) cos A)\(^{2}\)
⟹ k\(^{2}\) = 2 - 2cos\(^{2}\) A
⟹ k\(^{2}\) = 2(1 - cos\(^{2}\) A)
⟹ k\(^{2}\) = 2sin\(^{2}\) A; [Since, sin\(^{2}\) θ + cos\(^{2}\) θ = 1]
⟹ k = \(\sqrt{2}\) sin A
⟹ cos A - sin A = \(\sqrt{2}\) sin A. (Proved).
From Trigonometric Identities to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.