Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
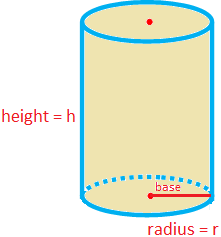
Right Circular Cylinder
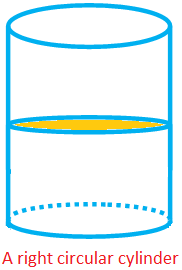
A cylinder, whose uniform cross section perpendicular to its height (or length) is a circle, is called a right circular cylinder.
A right circular cylinder has two plane faces which are circular and curved surface.
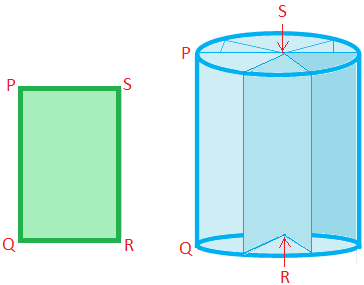
A right circular cylinder is a solid generated by the revolution of a rectangle about one of its sides.
Here, the rectangle PQRS has been revolved about the side SR. The length of the side SR will be the height and the length of the side PS will be the radius of the cross section.
Volume of a Right Circular Cylinder
= (Area of the Cross Section) × Height
= (Area of the Base) × Height
= (Area of the Circle whose Radius is r) × h
= πr2h
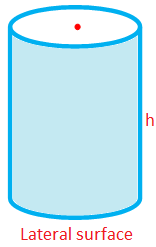
Lateral Surface Area or Curved Surface Area of a Right Circular Cylinder
= (Perimeter of the Cross Section) × Height
= 2πrh
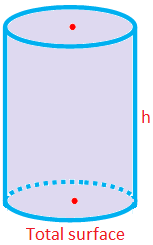
Total Surface Area of a Right Circular Cylinder
= Lateral Surface Area + 2 × (Area of the Cross Section)
= 2πrh + 2πr2
= 2πr(h + r)
Solved Examples on Volume and Surface Area of Right Circular Cylinders:
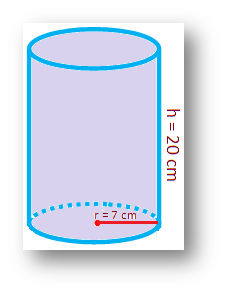
1. The radius of the base of a solid right circular cylinder is 7 cm and its height is 20 cm. Find its (i) volume, (ii) curved surface area, and (iii) total surface area.
Solution:
Here, the radius of the base of a solid right circular cylinder r = 7 cm and height h = 20 cm.
(i) Volume of the right circular cylinder = πr2h
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) ∙ 72 ∙ 20 cm3
= 3,080 cm3.
(ii) Curved surface area of the right circular cylinder
= 2πr × h
= 2 ∙ \(\frac{22}{7}\) ∙ 7 ∙ 20 cm2
= 880 cm2.
(iii) Total surface area of the right circular cylinder
= 2πrh + 2πr2
= 2πr(h + r)
= 2 ∙ \(\frac{22}{7}\) ∙ 7(20 + 7) cm2
= 1,188 cm2.
2. The volume of the right circular cylinder is 308 cm3 and its height is 8 cm. Find (i) the radius of its cross section, and (ii) the area of its curved surface.
Solution:
Let r be the radius of the cross section (or base).
Here h = 8 cm.
Then, the volume of the right circular cylinder = πr2h = πr2 ∙ 8 cm.
Therefore, 308 cm3 = πr2 ∙ 8 cm
⟹ r2 = \(\frac{308 \textrm{cm}^{2}}{π ∙ 8}\)
⟹ r2 = \(\frac{308 \textrm{cm}^{2}}{\frac{22}{7} ∙ 8}\)
⟹ r2 = \(\frac{308 × 7}{22 × 8}\) cm2.
⟹ r2 = \(\frac{49}{4}\) cm2.
Therefore, r = \(\frac{7}{2}\) cm.
Therefore, (i) radius of the cross section of the right circular cylinder
= \(\frac{7}{2}\) cm
= 3.5 cm,
(ii) area of the curved surface of the right circular cylinder
= 2πrh
= 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\) × 8 cm2.
= 176 cm2.
3. The radius of the base of a right circular cylinder is increased by 75% and the height is decreased by 50%. Find the per cent increase or decrease in the (i) volume, and (ii) curved surface area.
Solution:
Let the radius of the right circular cylinder = r,
Height of the right circular cylinder = h,
Volume of the right circular cylinder = V, and
Curved surface area of the right circular cylinder = S.
Therefore, V = πr2h and S = 2πrh.
After the changes, radius = R = r + (75% of r)
= r + ¾ r
= \(\frac{7}{4}\)r;
Height = H = h – (50% of h)
= h – ½ h
= ½ h.
(i) The changed volume V’ = πR2H
= π ∙ \(\left ( \frac{7}{4}r \right )^{2}\) ∙ \(\frac{1}{2}\)h
= \(\frac{49}{32}\) πr2h
= \(\frac{49}{32}\)V.
Therefore, the volume increases by \(\frac{49}{32}\)V – V, i.e., \(\frac{17}{32}\)V.
Therefore, the percent increase in volume = \(\frac{\frac{17}{32}V}{V}\) × 100%
= \(\frac{17 × 100}{32}\)%
= 53\(\frac{1}{8}\)%.
(ii) The changed curved surface area S’ = 2πRH
= 2π ∙ \(\frac{7}{4}\)r ∙ \(\frac{1}{2}\) h
= \(\frac{7}{8}\) ∙ 2πrh
= \(\frac{7}{8}\) S.
Therefore, the curved surface area decreases by S - \(\frac{7}{8}\) S , i.e., \(\frac{1}{8}\) S.
Therefore, the per cent decreases in curved surface area = \(\frac{\frac{1}{8}S}{S}\) × 100%
= 12\(\frac{1}{2}\)%.
From Right Circular Cylinder to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.