Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Mean of Ungrouped Data
The mean of data indicate how the data are distributed around the central part of the distribution. That is why the arithmetic numbers are also known as measures of central tendencies.
Mean Of Raw Data:
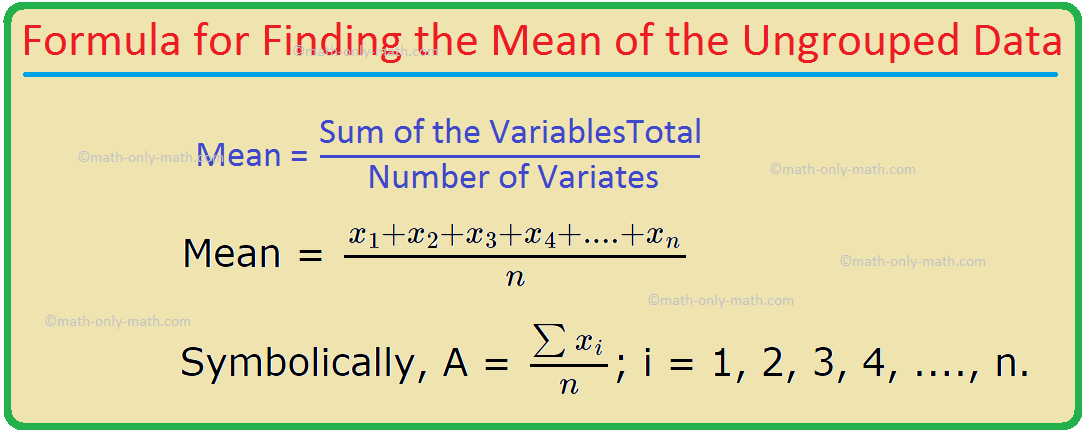
The mean (or arithmetic mean) of n observations (variates) x\(_{1}\), x\(_{2}\), x\(_{3}\), x\(_{4}\), ....., x\(_{n}\) is given by
Mean = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + x_{4} + .... + x_{n}}{n}\)
In words, mean = \(\frac{\textbf{Sum of the Variables}}{\textbf{Total Number of Variates}}\)
Symbolically, A = \(\frac{\sum x_{i}}{n}\); i = 1, 2, 3, 4, ...., n.
Note: \(\sum x_{i}\) = nA, i,e., sum of variates = mean × number of variates.
Solved Examples on Mean of Ungrouped Data or mean of the Arrayed Data:
1. A student scored 80%, 72%, 50%, 64% and 74% marks in five subjects in an examination. Find the mean percentage of marks obtained by him.
Solution:
Here, observations in percentage are
x\(_{1}\) = 80, x\(_{2}\) = 72, x\(_{3}\) = 50, x\(_{4}\) = 64, x\(_{5}\) = 74.
Therefore, their mean A = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + x_{4} + x_{5}}{5}\)
= \(\frac{80 + 72 + 50 + 64 + 74}{5}\)
= \(\frac{340}{5}\)
= 68.
Therefore, mean percentage of marks obtained by the student was 68%.
2. Sachin Tendulkar scores the following runs in six innings of a series.
45, 2, 78, 20, 116, 55.
Find the mean of the runs scored by the batsman in the series.
Solution:
Here, the observations are x1 = 45, x2 = 2, x3 = 78, x4 = 20, x5 = 116, x6 = 55.
Therefore, the required mean = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + x_{4} + x_{5} + x_{6}}{6}\)
= \(\frac{45 + 2 + 78 + 20 + 116 + 55}{6}\)
= \(\frac{316}{6}\)
= 52.7.
Therefore, the mean of the runs scored by Sachin Tendulkar in the series is 52.7.
Note: The mean of the runs scored by the batsman in six innings indicates the batsman's form, and one can expect the batsman to score about 53 runs in his next outing. However, it may so happen that the batsman scores a duck (0) or a century (100) the next time he bats.
3. Find the mean of the first six whole numbers.
Solution:
The first six whole numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Therefore, the mean = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + x_{4} + x_{5} + x_{6}}{6}\)
= \(\frac{0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5}{6}\)
= \(\frac{15}{6}\)
= \(\frac{5}{2}\)
= 2.5.
4. The mean of 6 variates is 8. Five of them are 8, 15, 0, 6, 11. Find the sixth variate.
Solution:
Let the sixth variate be a. Then by definition,
Mean = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + x_{4} + x_{5} + x_{6}}{6}\)
= \(\frac{8 + 15 + 0 + 6 + 11 + a}{6}\)
= \(\frac{40 + a}{6}\)
According to the problem,
\(\frac{40 + a}{6}\) = 8
⟹ 40 + a = 48
⟹ a = 48 - 40
⟹ a = 8
Therefore, the sixth variate = 8.
5. The mean length of ropes in 40 coils is 14 m. A new coil is added in which the length of the rope is 18 m. What is the mean length of the ropes now?
Solution:
For the original 40 coils of rope,
Mean (length) A = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + ...... + x_{40}}{40}\)
⟹ 14 = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + ...... + x_{40}}{40}\)
⟹ x1 + x2 + x3 + ...... + x40 = 560 ................ (i)
For the 41 coils of rope,
A = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + ...... + x_{40} + x_{41}}{41}\)
= \(\frac{560 + 18}{41}\), [From (i)]
= \(\frac{578}{41}\)
= 14.1 (Approx).
Therefore, the required mean length 14.1 m approximately.
6. The mean height of the 10 girls of a class is 1.4 m and the mean height of the 30 boys of the calss is 1.45 m. Find the mean height of the 40 students of the class.
Solution:
The mean height of the girls = \(\frac{\textrm{Sum of the Heights of the Girls}}{\textrm{Number of Girls}}\)
According to the problem,
\(\frac{\textrm{Sum of the Heights of the Girls}}{10}\) = 1.4 m
⟹ Sum of the Heights of the Girls = 1.4 × 10 m = 14 m.
The mean height of the boys = \(\frac{\textrm{Sum of the Heights of the Boys}}{\textrm{Number of Boys}}\)
According to the problem,
\(\frac{\textrm{Sum of the Heights of the Boys}}{30}\) = 1.45 m
⟹ Sum of the Heights of the Boys = 1.45 × 30 m = 43.5 m.
Therefore, the sum of the heights of the 40 students of the class = (14 + 43.5) m = 57.5 m.
Therefore, the mean height of 40 students of the class
= \(\frac{\textrm{The Sum of the Heights of the 40 Students of the Class}}{40}\)
= \(\frac{57.5}{40}\)
= 1.44 m.
7. The mean age of 10 boys is calculated to be 16 yers. Later it was detected that one boy's age was taken 12 years more than the actule and another boy's age was taken 7 years less than the actual. Find the correct mean of the ages of the boys.
Solution:
We have, mean = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + ...... + x_{n}}{n}\)
According to the problem,
\(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3} + ...... + x_{n}}{10}\) = 16
⟹ x1 + x2 + x3 + ...... + x10 = 16 × 10
⟹ x1 + x2 + x3 + ...... + x10 = 160 ............ (i)
Therefore, the actual sum of the ages = 160 - 12 + 7 [Using (i)]
Therefore, the correct mean = \(\frac{\textrm{Correct Sum of the Ages}}{\textrm{Number of Boys}}\)
= \(\frac{155}{10}\)
= 15.5 years.
From Mean of Ungrouped Data to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.