Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Lateral Surface Area of a Cuboid
Here we will learn how to solve the application problems on lateral surface area of a cuboid using the formula.
Formula for finding the lateral surface area of a cuboid
Area of a Rooms is example of cuboids.
Are of the four walls of a room = sum of the four vertical (or lateral) faces
= 2(l + b)h
Where l = Length, b = breadth and h = height.
Therefore, lateral surface area of a cuboid = 2(l + b)h
Problems on Lateral Surface Area of a Cuboid:
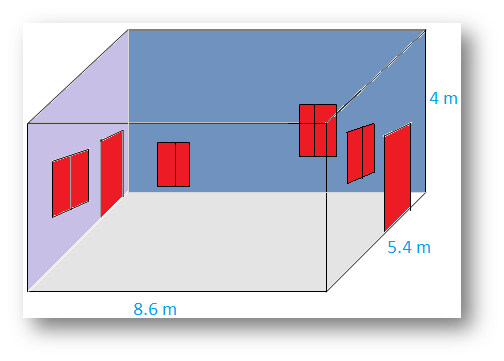
The dimensions of a cubical room are 8.6 m × 5.4 m × 4 m. The room has two doors each measuring 2 m by 1 m and four windows each measuring 1 m by 1 m. What will be the cost of plastering the four walls and the ceiling at RS 65 per m2?
Solution:
The total area of the four walls
= Lateral surface area of the cuboid
= 2(l + b)h
= 2(86 + 5.4) × 4 m2
= 112 m2.
The area of the ceiling = l × b
= 8.6 × 5.4 m2
= 46.44 m2
The sum of the areas of the two doors and the four windows
= 2(2 × 1) m2 + 4(1 × 1) m2
= 8 m2
Therefore, the total area to be plastered = (112 + 46.44 - 8) m2
= 150.44 m2
Therefore, the cost of plastering = 150.44 × Rs. 65
= Rs. 9778.60.
From Lateral Surface Area of a Cuboid to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.