Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Important Properties of Direct Common Tangents
We will discuss here three important properties of direct common tangents.
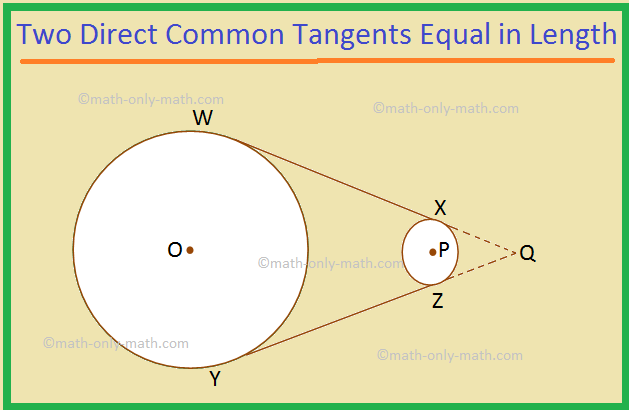
I. The two direct common tangents drawn to two circles are equal in length.
Given: WX and YZ are the two direct common tangents drawn to the two given circles with centres O and P.
To prove: WX = YZ.
Construction: Produce WX and YZ show that they meet at Q.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. WQ = YQ |
1. The two tangents, drawn to a circle from an external point are equal in length. |
|
2. XQ = ZQ |
2. As in statement 1. |
|
3. WQ – XQ = YQ – ZQ ⟹ WX = YZ (Proved). |
3. Subtracting statement 2 from statement 1. |
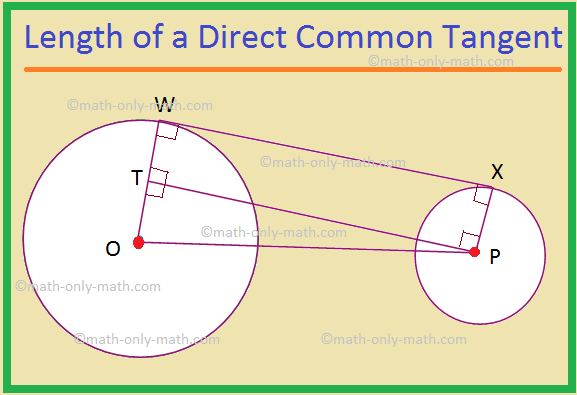
II. The length of a direct common tangent to two circles is \(\sqrt{d^{2} – (r_{1} – r_{2})^{2}}\), where d is the distance between the centres of the circles, and r\(_{1}\) and r\(_{2}\) are the radii of the given circles.
Proof:
Let two circles be given with centres O and P, and radii r\(_{1}\) and r\(_{2}\) respectively. Let WX be a direct common tangent.
Therefore, OW = r\(_{1}\) and PX = r\(_{2}\).
Also, r\(_{1}\) > r\(_{2}\).
Let the distance between the centres of the circles, OP = d.
Draw PT ⊥ OW.
Now, OW ⊥ WX and PX ⊥ WX, because a tangent is perpendicular to the radius drawn through the point of contact
Therefore, WXPT is a rectangle.
So, WT = XP = r\(_{2}\) and WX = PT, and the opposite sides of a rectangle are equal.
OT = OW – WT = r\(_{1}\) - r\(_{2}\).
In the right-angled triangle OPT,
We have, PT2 = OP2 – OT2 [by, Pythagoras Theorem]
⟹ PT2 = d2 – (r\(_{1}\) - r\(_{2}\))\(^{2}\)
⟹ PT = \(\sqrt{d^{2} – (r_{1} – r_{2})^{2}}\)
⟹ WX = \(\sqrt{d^{2} – (r_{1} – r_{2})^{2}}\); [As PT = WX]
Note: This formula remains true even when the circles touch or intersect each other.
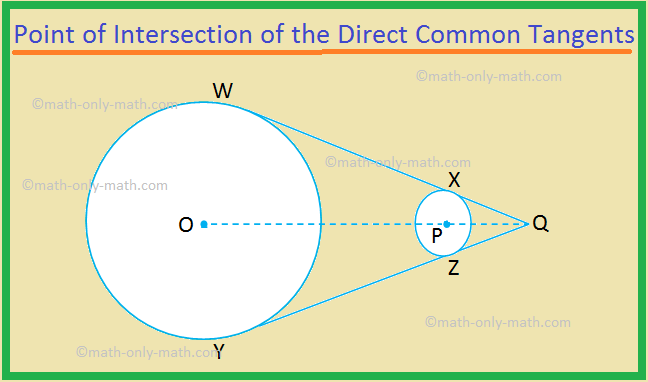
III. The point of intersection of the direct common tangents and the centres of the circles are collinear.
Given: Two circles with centres O and P, and there direct common tangents WX and YZ, which intersect at Q.
To prove: Q, P and O lie on the same straight line.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. PQ bisects ∠XQZ |
1. The tangents drawn to a circle from an external point are equally inclined to the line joining the point to the centre of the circle. |
|
2. OQ bisects ∠WQY |
2. As in statement 1. |
|
3. Therefore, PQ and OQ lie along the same straight line ⟹ Q, P and O are collinear. (Proved). |
3. As ∠XQZ and ∠WQY are the same angle, so their bisectors must be the same straight line. |
From Important Properties of Direct Common Tangents to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.