Subscribe to our ▶️YouTube channel🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Quadratic Equations
In quadratic equations we will learn about ………
● Solving a quadratic equation (factorization method)
● Roots of the quadratic equation.
In polynomials, we studied that a polynomial of degree 1 is called a linear polynomials.
For example: x - 5, 7x, 3 - 2x are linear polynomials which may be monomials or binomials.
A polynomial of degree 2 (two) is called a quadratic polynomial.
For example: 3x², x² + 7 , x² – 3x + 4 are quadratic polynomials which may be monomials, binomials or trinomials.
What is known as quadratic equation?
When these quadratic polynomials are equated to zero, equation is formed and is known as a quadratic equation.
The standard form of quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0. Here a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. The power of x in the equation must be a non-negative integer.
Examples of quadratic equation
(i) 3x² - 6x + 1 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(ii) x + (1/x) = 5 is a quadratic equation.
On solving, we get x × x + (1/x) × x = 5 × x
⇒ x² + 1 = 5x
⇒ x² - 5x + 1 = 0
(iii) √2x² - x - 7 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(iv) 3x² - √x + 1 = 0 is not a quadratic equation, since the power of x must be a positive integer.
(v) x² - (1/x) + 7 = 0 is not a quadratic equation, since on solving it becomes an equation of degree 3.
(vi) x² - 4 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(vii) x² = 0 is a quadratic equation.
Solving a quadratic equation and finding the roots of quadratic equation
● Write the quadratic equation in the standard form, i.e.,
ax² + bx + c = 0.
● Factorize the quadratic equation.
● Express it as the product of two linear factors, say (px + q) and (rx + s), where p, q, r, S are real numbers and p, r are not equal to zero.
Then, ax² + bx + c = 0
(px + q) (rx + s) = 0
● Put each of the linear factors equal to zero
i.e., px + q = 0 and rx + s = 0
⇒ px = - q ⇒ rx = - s
⇒ x = -q/p ⇒ x = -s/r
● Thus, the two values of x are called the roots of the quadratic equation.
● Therefore, the solution set = {-q/p, -s/r}
How to solve quadratic equations?
Worked-out problems on solving quadratic equation will help the students to understand the detailed explanation showing the step-by-step quadratic equation solution.
1. Solve: x² + 6x + 5 = 0
Solution:
x² + 6x + 5 = 0
⇒ x² + 5x + x + 5 = 0
⇒ x(x + 5) + 1(x + 5) = 0
⇒ (x + 1) (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 and x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = -1 and x = -5
Therefore, solution set = {-1, -5}
2. Solve: 8x² = 21 + 22x
Solution:
8x² = 21 + 22x
⇒ 8x² - 21 - 22x = 0
⇒ 8x² - 22x - 21 = 0
⇒ 8x² - 28x + 6x - 21 = 0
⇒ 4x (2x - 7) + 3(2x - 7) = 0
⇒ (4x + 3) (2x - 7) = 0
⇒ 4x + 3 = 0 and 2x - 7 = 0
⇒ 4x = -3 and 2x = 7
⇒ x = -3/₄ and x = ⁷/₂
Therefore, solution set = {-3/₄, ⁷/₂}
3. 1/(x + 4) - 1/(x - 7) = 11/30
Solution:
1/(x + 4) - 1/(x - 7) = 11/30
⇒ [(x - 7) - (x + 4)]/(x + 4) (x - 7) = ¹¹/₃₀
⇒ [x - 7 - x - 4]/(x² - 3x - 28) = ¹¹/₃₀
⇒ - 11/(x² - 3x - 28) = ¹¹/₃₀
⇒ -1/(x² - 3x - 28) = ¹/₃₀
⇒ -30 = x² - 3x - 28
⇒ x² - 3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x² - 2x - x + 2 = 0
⇒ x(x - 2) - 1(x - 2) = 0
⇒ (x - 1) (x - 2) = 0
⇒ x - 1 = 0 and x - 2 = 0
⇒ x = 1 and x = 2
Therefore, Solution set = {1, 2}
4. Solve (2x - 3)/(x + 2) = (3x - 7)/(x + 3)
Solution:
(2x - 3)/(x + 2) = (3x - 7)/(x + 3)
⇒ (2x - 3) (x + 3) = (x + 2) (3x - 7)
⇒ 2x² + 6x - 3x - 9 = 3x² - 7x + 6x - 14
⇒ 2x² + 6x - 3x - 9 - 3x² + 7x - 6x + 14 = 0
⇒ 2x² - 3x² + 6x - 3x + 7x - 6x - 9 + 14 = 0
⇒ -x² - 4x + 5 = 0
⇒ x² + 4x - 5 = 0
⇒ x² + 5x - x - 5 = 0
⇒ x (x + 5) -1 (x + 5) = 0
⇒ (x - 1) (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x - 1 = 0 and x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = 1 and x = -5
Therefore, solution set = {1, -5}
5. Solve x² - 9/5 + x² = -5/₉
Solution:
x² - 9/5 + x² = -5/₉
⇒ 9(x² - 9) = -5 (5 + x²)
⇒ 9x² - 81 = -25 - 5x²
⇒ 9x² + 5 x² = -25 + 81
⇒ 14x² = 56
⇒ x² = 56/14
⇒ x² = 4
⇒ x² - 4 = 0
⇒ x² - 2² = 0
⇒ (x - 2) (x + 2) = 0
⇒ x - 2 = 0 and x + 2 = 0
⇒ x = 2 and x = -2
Therefore, solution set = {2, -2}
These are the above examples on quadratic equations which are explained to show the exact way to solve.
8th Grade Math Practice
From Quadratic Equations to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
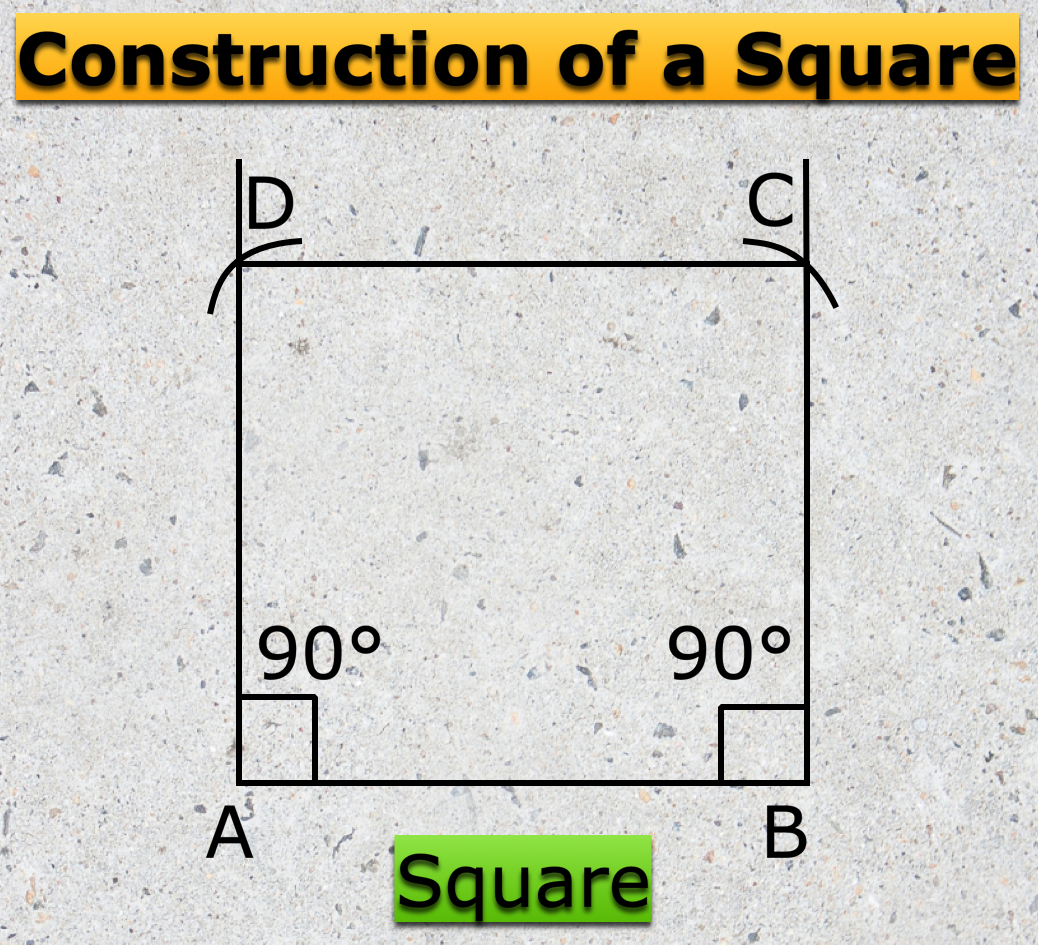
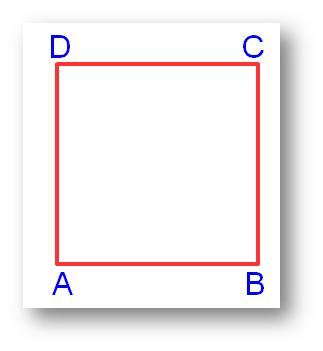
Formation of Square and Rectangle | Construction of Square & Rectangle
Jul 15, 25 02:46 AM
In formation of square and rectangle we will learn how to construct square and rectangle. Construction of a Square: We follow the method given below. Step I: We draw a line segment AB of the required… -
5th Grade Quadrilaterals | Square | Rectangle | Parallelogram |Rhombus
Jul 15, 25 02:01 AM
Quadrilaterals are known as four sided polygon.What is a quadrilateral? A closed figure made of our line segments is called a quadrilateral. For example: -
Formation of Numbers | Smallest and Greatest Number| Number Formation
Jul 14, 25 01:53 AM
In formation of numbers we will learn the numbers having different numbers of digits. We know that: (i) Greatest number of one digit = 9, -
5th Grade Geometry Practice Test | Angle | Triangle | Circle |Free Ans
Jul 14, 25 01:53 AM
In 5th grade geometry practice test you will get different types of practice questions on lines, types of angle, triangles, properties of triangles, classification of triangles, construction of triang… -
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
Jul 11, 25 02:14 PM
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circl…

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.