Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Perimeter and Area of Quadrilateral
Here we will discuss about the perimeter and area of a quadrilateral and some example problems.
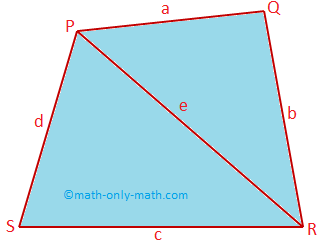
In the quadrilateral PQRS, PR is a diagonal, QM ⊥ PR and SN ⊥ PR.
Then, area (A) of the quadrilateral PQRS = Area of ∆PQR + Area of ∆SPR
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × QM × PR) + (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × SN × PR)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (QM + SN) × PR
Also, area (A) of the quadrilateral PQRS = Area of ∆PQR + Area of ∆SPR
= \(\sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - e)}\) + \(\sqrt{S(S - c)(S - d)(S - e)}\)
where, s = \(\frac{\textrm{a + b + e}}{2}\) and S = \(\frac{\textrm{c + d + e}}{2}\)
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c + d
Solved example problems on finding the perimeter and area of quadrilateral:
1. PQRS is a quadrilateral whose diagonal QS is perpendicular to the side PQ. If PQ = 4.5 cm, PS = 7.5 cm and the distance of R from QS is 1.5 cm, find the area of the quadrilateral.
Solution:
In the right-angled ∆PQS,
PS\(^{2}\) = PQ\(^{2}\) + QS\(^{2}\)
⟹ (7.5)\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) = (4.5)\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) + QS\(^{2}\)
⟹ QS\(^{2}\) = [(7.5)\(^{2}\) – (4.5)\(^{2}\)] cm\(^{2}\)
⟹ QS\(^{2}\) = (7.5 + 4.5)(7.5 - 4.5) cm\(^{2}\)
⟹ QS\(^{2}\) = 12 × 3 cm\(^{2}\)
⟹ QS\(^{2}\) = 36 cm\(^{2}\)
⟹ QS = 6 cm.
Therefore, area of the quadrilateral PQRS = Area of the ∆PQS + Area of the ∆QRS
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) PQ × QS + \(\frac{1}{2}\) RT × QS
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(PQ + RT) × QS
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4.5 + 1.5) × 6 cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6 × 6 cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 36 cm\(^{2}\)
= 18 cm\(^{2}\).
2. PQRS is a quadrilateral in which PQ = 4 cm, QC = 5 cm, RS = 7 cm, SP = 6 cm and the diagonal PR = 8 cm. Find its area.
Solution:
Area of the quadrilateral PQRS = Area of the ∆PQR + Area of the ∆SPR
In the ∆PQR, let a = PQ = 4 cm, b = QR = 5 cm and c = RP = 8 cm.
Therefore, s = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(a + b + c)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4 + 5 + 8) cm
= \(\frac{17}{2}\) cm.
Area of the ∆PQR = \(\sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{17}{2}(\frac{17}{2} - 4)(\frac{17}{2} - 5)(\frac{17}{2} - 8)}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{17}{2} ∙ \frac{9}{2} ∙ \frac{7}{2} ∙ \frac{1}{2}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{17 ∙ 9 ∙ 7 ∙ 1}{16}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{119}\) cm\(^{2}\).
In the ∆SPR, let a = PS = 6 cm, b = RS = 7 cm and c = RP = 8 cm.
Therefore, S = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(a + b + c)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(6 + 7 + 8) cm
= = \(\frac{21}{2}\) cm.
Area of the ∆SPR = \(\sqrt{S(S - a)(S - b)(S - c)}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{21}{2}(\frac{21}{2} - 6)(\frac{21}{2} - 7)(\frac{21}{2} - 8)}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{21}{2} ∙ \frac{9}{2} ∙ \frac{7}{2} ∙ \frac{5}{2}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{21 ∙ 9 ∙ 7 ∙ 5}{16}}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{735}\) cm\(^{2}\).
Therefore, area of the quadrilateral PQRS = (\(\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{119}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{735}\)) cm\(^{2}\).
= \(\frac{3}{4}\)(10.9 + 27.1) cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) × 38 cm\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{57}{2}\) cm\(^{2}\)
= 28.5 cm\(^{2}\)
From Perimeter and Area of Quadrilateral to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.