Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Perimeter and Area of Mixed Figures
Here we will discuss about the Perimeter and area of mixed figures.
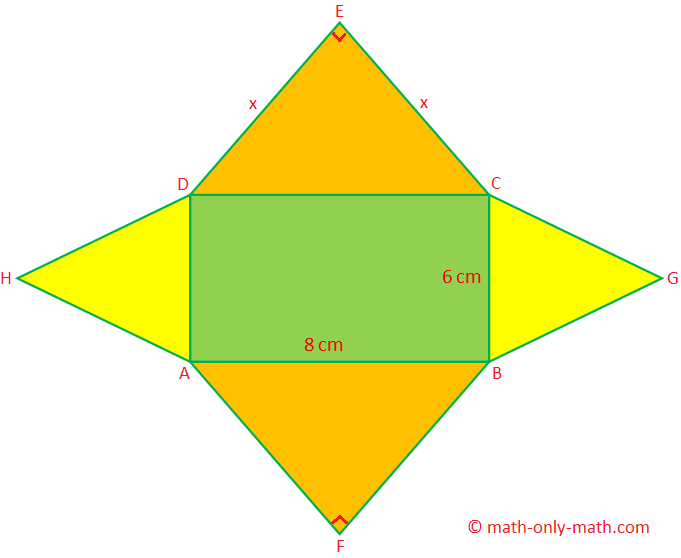
1. The length and breadth of a rectangular field is 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. On the shorter sides of the rectangular field two equilateral triangles are constructed outside. Two right-angled isosceles triangles are constructed outside the rectangular field, with the longer sides as the hypotenuses. Find the total area and perimeter of the figure.
Solution:
The figure consists of the following.
(i) The rectangular field ABCD, whose area = 8 × 6 cm\(^{2}\) = 48 cm\(^{2}\)
(ii) Two equilateral triangles BCG and ADH. For each, area = \(\frac{√3}{4}\) × 6\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) = 9√3 cm\(^{2}\)
(iii) Two isosceles right-angled triangles CDE and ABF, whose areas are equal.
IF CE = ED = x then x\(^{2}\) + x\(^{2}\) = 8\(^{2}\) cm\(^{2}\) (by Pythagoras’ theorem)
or, 2x\(^{2}\) = 64 cm\(^{2}\)
or, x\(^{2}\) = 32 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, x = 4√2 cm
Therefore, area of the ∆CDE = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CE × DE
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x\(^{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (4√2)\(^{2}\) cm2
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) 32 cm\(^{2}\)
= 16 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, area of the figure = area of the rectangular field ABCD + 2 × area of the ∆BCG + 2 × area of the ∆CDE
= (48 + 2 × 9√3 + 2 × 16) cm\(^{2}\)
= (80 + 18√3) cm\(^{2}\)
= (80 + 18 × 1.73) cm\(^{2}\)
= (80 + 31.14) cm\(^{2}\)
= 111.14 cm\(^{2}\)
Perimeter of the figure = length of the boundary of the figure
= AF + FB + BG + GC + CE + ED + DH + HA
= 4 × CE + 4 × BG
= (4 × 4√2 + 4 × 6) cm
= 8(3 + 2√2) cm
= 8(3 + 2 × 1.41) cm
= 8 × 5.82 cm
= 46.56 cm
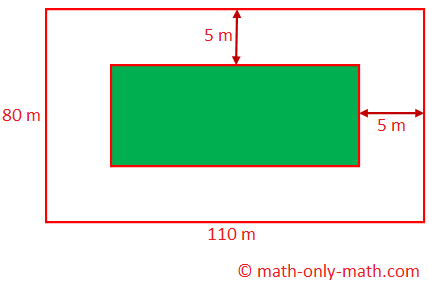
2. The dimension of a field are 110 m × 80 m. The field is to be converted into a garden, leaving a path 5 m broad around the garden. Find the total cost of making the garden if the cost per square metre is Rs 12.
Solution:
For the garden, length = (110 – 2 × 5) m = 100 m, and
Breadth = (80 – 2 × 5) m = 70 m
Therefore, area of the garden = 100 × 70 m\(^{2}\) = 7000 m\(^{2}\)
Therefore, total cost of making the garden = 7000 × Rs 12 = Rs 84000
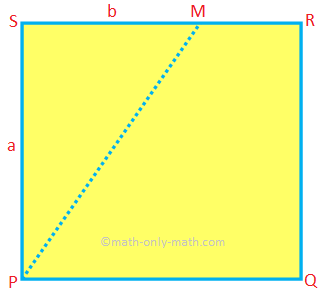
3. A square-shaped piece of paper is cut into two pieces along a line joining a corner and a point on an opposite edge. If the ratio of the areas of the two pieces be 3:1, find the ratio of the perimeters of the smaller piece and the original piece of paper.
Solution:
Let PQRS be the square-shaped piece of paper. Let its side measure a units.
It is cut along PM. Let SM = b units
Area of the ∆MSP = \(\frac{1}{2}\) PS × SM = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ab square units.
Area of the square PQRS = a\(^{2}\) square units.
According to the question,
\(\frac{\textrm{area of the quadrilateral PQRM}}{\textrm{area of the ∆MSP}}\) = \(\frac{3}{1}\)
⟹ \(\frac{\textrm{area of the quadrilateral PQRM}}{\textrm{area of the ∆MSP}}\) + 1 = 4
⟹ \(\frac{\textrm{area of the quadrilateral PQRM + area of the ∆MSP}}{\textrm{area of the ∆MSP}}\) = 4
⟹ \(\frac{\textrm{area of the square PQRS}}{\textrm{area of the ∆MSP}}\) = 4
⟹ \(\frac{a^{2}}{\frac{\textrm{1}}{2} ab} = 4\)
⟹\(\frac{2a}{b}\) = 4
⟹ a = 2b
⟹ b = \(\frac{1}{2}\)a
Now, PM2 = PS2 + SM2; (by Pythagoras’ theorem)
Therefore, PM2 = a2 + b2
= a2 + (\(\frac{1}{2}\)a )2
= a2 + \(\frac{1}{4}\)a2
= \(\frac{5}{4}\)a2.
Therefore, PM2 = \(\frac{√5}{2}\)a.
Now, \(\frac{\textrm{perimeter of the ∆MSP}}{\textrm{perimeter of the square PQRS}}\) = \(\frac{\textrm{MS + PS + PM}}{\textrm{4a}}\)
= \(\frac{\frac{1}{2}a + a +\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}a}{4a}\)
= \(\frac{(\frac{3 + \sqrt{5}}{2})a}{4a}\)
= \(\frac{3 + √5}{8}\)
= (3 + √5) : 8.
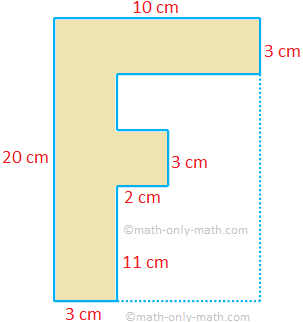
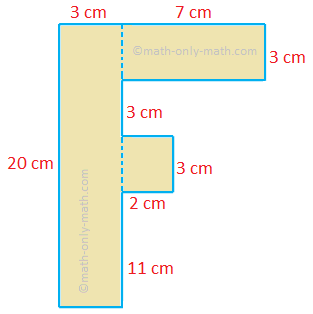
4. From a 20 cm × 10 cm plywood board an F-shaped block is cut out, as shown in the figure. What is the area of a face of the remaining board? Also find the length of the boundary of the block.
Solution:
Clearly, the block is a combination of three rectangular blocks, as shown in the below figure.
Therefore, area of a face of the block = 20 × 3 cm\(^{2}\) + 3 × 2 cm\(^{2}\) + 7 × 3 cm\(^{2}\)
= 60 cm\(^{2}\) + 6 cm\(^{2}\) + 21 cm\(^{2}\)
= 87 cm\(^{2}\)
Area of a face of the uncut board = 20 × 10 cm\(^{2}\)
= 200 cm\(^{2}\)
Therefore, area of a face of the remaining board = 200 cm\(^{2}\) - 87 cm\(^{2}\)
= 113 cm\(^{2}\)
Required length of the boundary = (20 + 3 + 11 + 2 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 7 + 3 + 10) cm
= 64 cm
From Perimeter and Area of Mixed Figures to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.