Transverse and Conjugate Axis of the Hyperbola
We will discuss about the transverse and conjugate axis of the hyperbola along with the examples.
Definition of the transverse axis of the hyperbola:
The transverse axis is the axis of a hyperbola that passes through the two foci.
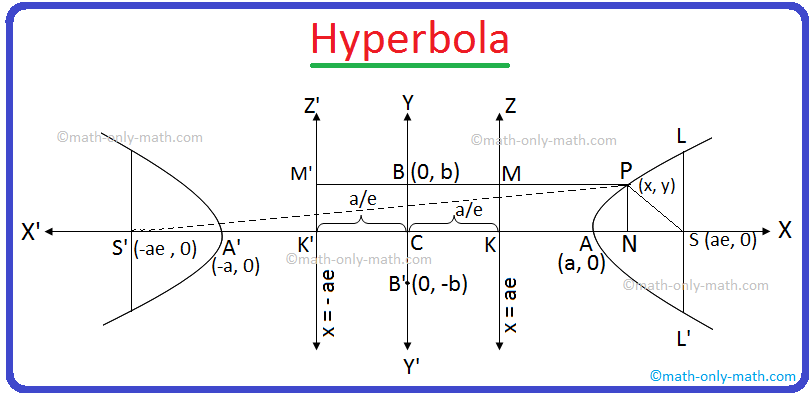
The straight line joining the vertices A and A’ is called the transverse axis of the hyperbola.
AA' i.e., the line segment joining the vertices of a hyperbola is called its Transverse Axis. The transverse axis of the hyperbola \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) - \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1 is along the x-axis and its length is 2a.
The straight line through the centre which is perpendicular to the transverse axis does not meet the hyperbola in real points.
Definition of the conjugate axis of the hyperbola:
If two points B and B' are on the y-axis such that CB = CB’ = b, then the line segment BB’ is called the conjugate axis of the hyperbola. Therefore, the length of conjugate axis = 2b.
Solved examples to find the transverse and conjugate axes of an hyperbola:
1. Find the lengths of transverse and conjugate axis of the hyperbola 16x\(^{2}\) - 9y\(^{2}\) = 144.
Solution:
The given equation of the hyperbola is 16x\(^{2}\) - 9y\(^{2}\) = 144.
The equation of the hyperbola 16x\(^{2}\) - 9y\(^{2}\) = 144 can be written as
\(\frac{x^{2}}{9}\) - \(\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1 ……………… (i)
The above equation (i) is of the form \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) - \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1, where a\(^{2}\) = 9 and b\(^{2}\) = 16.
Therefore, the length of the transverse axis is 2a = 2 ∙ 3 = 6 and the length of the conjugate axis is 2b = 2 ∙ 4 = 8.
2. Find the lengths of transverse and conjugate axis of the hyperbola 16x\(^{2}\) - 9y\(^{2}\) = 144.
Solution:
The given equation of the hyperbola is 3x\(^{2}\) - 6y\(^{2}\) = -18.
The equation of the hyperbola 3x\(^{2}\) - 6y\(^{2}\) = -18 can be written as
\(\frac{x^{2}}{6}\) - \(\frac{y^{2}}{3}\) = 1 ……………… (i)
The above equation (i) is of the form \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) - \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = -1, where a\(^{2}\) = 6 and b\(^{2}\) = 3.
Therefore, the length of the transverse axis is 2b = 2 ∙ √3 = 2√3 and the length of the conjugate axis is 2a = 2 ∙ √6 = 2√6.
● The Hyperbola
- Definition of Hyperbola
- Standard Equation of an Hyperbola
- Vertex of the Hyperbola
- Centre of the Hyperbola
- Transverse and Conjugate Axis of the Hyperbola
- Two Foci and Two Directrices of the Hyperbola
- Latus Rectum of the Hyperbola
- Position of a Point with Respect to the Hyperbola
- Conjugate Hyperbola
- Rectangular Hyperbola
- Parametric Equation of the Hyperbola
- Hyperbola Formulae
- Problems on Hyperbola
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Transverse and Conjugate Axis of the Hyperbola to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Number | Long Division |Worksheet Answer
Apr 24, 24 03:46 PM
Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Numbers are discussed here step-by-step. How to divide 3-digit numbers by single-digit numbers? Let us follow the examples to learn to divide 3-digit number by one-digit nu… -
Symmetrical Shapes | One, Two, Three, Four & Many-line Symmetry
Apr 24, 24 03:45 PM
Symmetrical shapes are discussed here in this topic. Any object or shape which can be cut in two equal halves in such a way that both the parts are exactly the same is called symmetrical. The line whi… -
Mental Math on Geometrical Shapes | Geometry Worksheets| Answer
Apr 24, 24 03:35 PM
In mental math on geometrical shapes we will solve different type of problems on simple closed curves, polygons, basic geometrical concepts, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, circle, terms relates… -
Circle Math | Terms Related to the Circle | Symbol of Circle O | Math
Apr 24, 24 02:57 PM
In circle math the terms related to the circle are discussed here. A circle is such a closed curve whose every point is equidistant from a fixed point called its centre. The symbol of circle is O. We… -
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts | Point | Line | Properties of Lines
Apr 24, 24 12:38 PM
The fundamental geometrical concepts depend on three basic concepts — point, line and plane. The terms cannot be precisely defined. However, the meanings of these terms are explained through examples.