Subscribe to our ▶️YouTube channel🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Properties of Factors
The properties of factors are discussed step by step according to its property.
Property (1):
Every whole number is the product of 1 and itself so
(i) Each number is a factor of itself.
19 x 1 = 19,
So, 19 is the factor of 19.
(ii) 1 is the factor of every number.
We know that a number multiplied by 1 is the number itself. So, 1 is a factor of every number.
For example
21 ÷ 1 = 21. So, 1 is the factor of 21,
96 ÷ 1 = 96, So, 1 is a factor of 96.
31 x 1 = 31, So, 1 is the factor of 31.
Property (2):
Every number is a factor of zero (0)
As, 7 x 0 = 0,
17 x 0 = 0,
93 x 0 = 0
So, 7, 17, 93, ……, etc., are the factors of 0.
Property (3):
1 is the smallest factor of every number.
1 is the smallest factor of a multiple and the greatest factor of a multiple is the multiple itself.
A number is a factor of itself. SO, a number itself is its own greatest factor. For example 73 ÷ 1 = 73 so, 73 and 1 are the factors. 73 is the greatest factors.
Property (4):
Every number other than 1 has at least two factors, namely the number itself and 1.
We know that 1 and the number itself are always the factors of every number. This means that every number has at least 2 factors.
Therefore, the properties of factors are explained above so, that student can understand each property.
Properties of Factors
Property 1: A number has a finite number of factors.
Property 2: 1 and the number itself are the factors of every number.
Property 3: 1 is the smallest factor of any number.
Property 4: The number itself is the greatest factor of every number.
Property 5: Factors of a number are always smaller or equal to the number.
Property 6: Every factor of a number is the exact divisor of the number.
To find that whether a number is a factor of another number, we divide the bigger number by the smaller number. If the remainder is zero, we say that the divisor is a factor of the dividend.
For example:
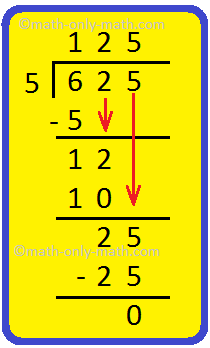
1. Is 5 a factor of 625?
Here, 5 divides 625 exactly. So 5 is a factor of 625.
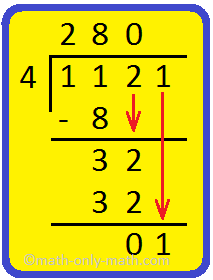
2. Is 4 a factor of 1121?
Here, 4 does not divide 1121 exactly. So 4 is not a factor of 1121.
Related Concept
● Factors and Multiples by using Multiplication Facts
● Factors and Multiples by using Division Facts
● Factors
● Even and Odd Numbers Between 1 and 100
● Examples on Even and Odd Numbers
4th Grade Math Activities
From Properties of Factors to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Worksheet on Area of a Square and Rectangle | Area of Squares & Rectan
Jul 19, 25 05:00 AM
We will practice the questions given in the worksheet on area of a square and rectangle. We know the amount of surface that a plane figure covers is called its area. 1. Find the area of the square len… -
Area of Rectangle Square and Triangle | Formulas| Area of Plane Shapes
Jul 18, 25 10:38 AM
Area of a closed plane figure is the amount of surface enclosed within its boundary. Look at the given figures. The shaded region of each figure denotes its area. The standard unit, generally used for… -
What is Area in Maths? | Units to find Area | Conversion Table of Area
Jul 17, 25 01:06 AM
The amount of surface that a plane figure covers is called its area. It’s unit is square centimeters or square meters etc. A rectangle, a square, a triangle and a circle are all examples of closed pla… -
Worksheet on Perimeter | Perimeter of Squares and Rectangle | Answers
Jul 17, 25 12:40 AM
Practice the questions given in the worksheet on perimeter. The questions are based on finding the perimeter of the triangle, perimeter of the square, perimeter of rectangle and word problems. I. Find… -
Formation of Square and Rectangle | Construction of Square & Rectangle
Jul 16, 25 11:46 PM
In formation of square and rectangle we will learn how to construct square and rectangle. Construction of a Square: We follow the method given below. Step I: We draw a line segment AB of the required…










New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.