Elimination Method
Follow the steps to solve the system of linear equations by using the elimination method:
(i) Multiply the given equation by suitable constant so as to make the coefficients of the variable to be eliminated equal.
(ii) Add the new equations obtained if the terms having the same coefficient are opposite signs and subtract if they are of the same sign.
(iii) Solve the equation thus obtained.
(iv) Substitute the value found in any one the given equations.
(v) Solve it to get the value of the other variable.
Worked-out examples on elimination method:
1. Solve the system of equation 2x + y = -4 and 5x – 3y = 1 by the method of elimination.
Solution:
The given equations are:
2x + y = -4 …………… (i)
5x – 3y = 1 …………… (ii)
Multiply equation (i) by 3, we get;
{2x + y = -4} …………… {× 3}
6x + 3y = -12 …………… (iii)
Adding (ii) and (iii), we get;
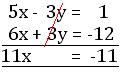
or, x = -11/11
or, x = -1
Substituting the value of x = -1 in equation (i), we get;
2 × (-1) + y = -4
-2 + y = -4
-2 + 2 + y = -4 + 2
y = -4 + 2
y = -2
Therefore, x = -1 and y = -2 is the solution of the system of equations 2x + y = -4 and 5x – 3y = 1
2. Solve the system of equation 2x + 3y = 11, x + 2y = 7 by the method of elimination.
Solution:
The given equations are:
2x + 3y = 11 …………… (i)
x + 2y = 7 …………… (ii)
Multiply the equation (ii) by 2, we get
{x + 2y = 7} …………… (× 2)
2x + 4y = 14 …………… (iii)
Subtract equation (i) and (ii), we get
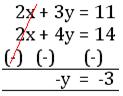
Substituting the value of y = 3 in equation (i), we get
2x + 3y = 11
or, 2x + 3 × 3 = 11
or, 2x + 9 = 11
or, 2x + 9 – 9 = 11 – 9
or, 2x = 11 – 9
or, 2x = 2
or, x = 2/2
or, x = 1
Therefore, x = 1 and y = 3 is the solution of the system of the given equations.
3. Solve 2a – \(\frac{3}{b}\) = 12 and 5a + \(\frac{7}{b}\) = 1
Solution:
The given equations are:
2a – \(\frac{3}{b}\) = 12 …………… (i)
5a + \(\frac{7}{b}\) = 1 …………… (ii)
Put \(\frac{1}{b}\) = c, we have
2a – 3c = 12 …………… (iii)
5a + 7c = 1 …………… (iv)
Multiply equation (iii) by 5 and (iv) by 2, we get
10a – 15c = 60 …………… (v)
10a + 14c = 2 …………… (vi)
Subtracting (v) and (vi), we get
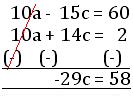
or, c = \(\frac{58}{-29}\)
or, c = -2
But \(\frac{1}{b}\) = c
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{b}\) = -2 or b = -\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Subtracting the value of c in equation (v), we get
10a – 15 × (-2) = 60
or, 10a + 30 = 60
or, 10a + 30 - 30= 60 - 30
or, 10a = 60 – 30
or, a = \(\frac{30}{10}\)
or, a = 3
Therefore, a = 3 and b = - \(\frac{1}{2}\) is the solution of the given system of equations.
4. x/2 + 2/3 y = -1 and x – 1/3 y = 3
Solution:
The given equations are:
x/2 + 2/3 y = -1 …………… (i)
x – 1/3 y = 3 …………… (ii)
Multiply equation (i) by 6 and (ii) by 3, we get;
3x + 4y = -6 …………… (iii)
3x – y = 9 …………… (iv)
Solving (iii) and (iv), we get;
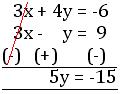
or, y = -15/5
or, y = -3
Subtracting the value of y in (ii), we get;
x - 1/3̶ × -3̶ = 3
or, x + 1 = 3
or, x = 3 – 1
or, x = 2
Therefore, x = 2 and y = -3 is the solution of the equation.
x/2 + 2/3 y = -1 and x - y/3 = 3
● Simultaneous Linear Equations
Solvability of Linear Simultaneous Equations
Word Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Word Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Practice Test on Word Problems Involving Simultaneous Linear Equations
● Simultaneous Linear Equations - Worksheets
Worksheet on Simultaneous Linear Equations
Worksheet on Problems on Simultaneous Linear Equations
8th Grade Math Practice
From Elimination Method to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
What are Parallel Lines in Geometry? | Two Parallel Lines | Examples
Apr 19, 24 04:39 PM
In parallel lines when two lines do not intersect each other at any point even if they are extended to infinity. What are parallel lines in geometry? Two lines which do not intersect each other -
Perpendicular Lines | What are Perpendicular Lines in Geometry?|Symbol
Apr 19, 24 04:01 PM
In perpendicular lines when two intersecting lines a and b are said to be perpendicular to each other if one of the angles formed by them is a right angle. In other words, Set Square Set Square If two… -
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts | Point | Line | Properties of Lines
Apr 19, 24 01:50 PM
The fundamental geometrical concepts depend on three basic concepts — point, line and plane. The terms cannot be precisely defined. However, the meanings of these terms are explained through examples. -
What is a Polygon? | Simple Closed Curve | Triangle | Quadrilateral
Apr 19, 24 01:22 PM
What is a polygon? A simple closed curve made of three or more line-segments is called a polygon. A polygon has at least three line-segments. -
Simple Closed Curves | Types of Closed Curves | Collection of Curves
Apr 18, 24 01:36 AM
In simple closed curves the shapes are closed by line-segments or by a curved line. Triangle, quadrilateral, circle, etc., are examples of closed curves.