Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem states that:
In a triangle, if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides then the angle opposite to the first side is a right angle.
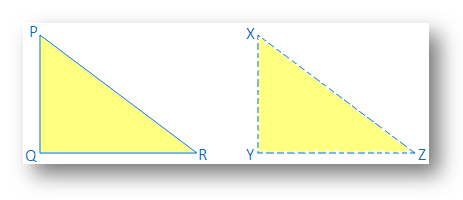
Given: A ∆PQR in which PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
To prove: ∠Q = 90°
Construction: Draw a ∆XYZ such that XY = PQ, YZ = QR and ∠Y = 90°
So, by Pythagora’s theorem we get,
XZ2 = XY2 + YZ2
⇒ XZ2 = PQ2 + QR2 ……….. (i), [since XY = PQ and YZ = QR]
But, PR2 = PQ2 + QR2 ………… (ii), [given]
From (i) and (ii) we get,
PR2 = XZ2 ⇒ PR = XZ
Now, in ∆PQR and ∆XYZ, we get
PQ = XY,
QR = YZ and
PR = XZ
Therefore ∆PQR ≅ ∆XYZ
Hence ∠Q = ∠Y = 90°
Word problems using the Converse of Pythagorean Theorem:
1. The side of a triangle are of length 4.5 cm, 7.5 cm and 6 cm. Is this triangle a right triangle? If so, which side is the hypotenuse?
Solution:
We know that hypotenuse is the longest side. If 4.5 cm, 7.5 cm and 6 cm are the lengths of angled triangle, then 7.5 cm will be the hypotenuse.
Using the converse of Pythagoras theorem, we get
(7.5)2 = (6)2 + (4.5)2⇒ 56.25 = 36 + 20.25
⇒ 56.25 = 56.25
Since, both the sides are equal therefore, 4.5 cm, 7.5 cm and 6 cm are the side of the right angled triangle having hypotenuse 7.5 cm.
2. The side of a triangle are of length 8 cm, 15 cm and 17 cm. Is this triangle a right triangle? If so, which side is the hypotenuse?
Solution:
We know that hypotenuse is the longest side. If 8 cm, 15 cm and 17 cm are the lengths of angled triangle, then 17 cm will be the hypotenuse.
Using the converse of Pythagoras theorem, we get
(17)2 = (15)2 + (8)2⇒ 289 = 225 + 64
⇒ 289 = 289
Since, both the sides are equal therefore, 8 cm, 15 cm and 17 cm are the side of the right angled triangle having hypotenuse 17 cm.
3. The side of a triangle are of length 9 cm, 11 cm and 6 cm. Is this triangle a right triangle? If so, which side is the hypotenuse?
Solution:
We know that hypotenuse is the longest side. If 9 cm, 11 cm and 6 cm are the lengths of angled triangle, then 11 cm will be the hypotenuse.
Using the converse of Pythagoras theorem, we get
(11)2 = (9)2 + (6)2⇒ 121 = 81 + 36
⇒ 121 ≠ 117
Since, both the sides are not equal therefore 9 cm, 11 cm and 6 cm are not the side of the right angled triangle.
The above examples of the converse of Pythagorean Theorem will help us to determine the right triangle when the sides of the triangles will be given in the questions.
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Converse of Pythagorean Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Perimeter of a Triangle | Perimeter of a Triangle Formula | Examples
Apr 25, 24 04:24 PM
We will discuss here how to find the perimeter of a triangle. We know perimeter of a triangle is the total length (distance) of the boundary of a triangle. Perimeter of a triangle is the sum of length… -
Perimeter of a Rectangle | How to Find the Perimeter of a Rectangle?
Apr 25, 24 03:45 PM
We will discuss here how to find the perimeter of a rectangle. We know perimeter of a rectangle is the total length (distance) of the boundary of a rectangle. ABCD is a rectangle. We know that the opp… -
Perimeter of a Square | How to Find the Perimeter of Square? |Examples
Apr 25, 24 12:54 PM
We will discuss here how to find the perimeter of a square. Perimeter of a square is the total length (distance) of the boundary of a square. We know that all the sides of a square are equal. Perimete… -
Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Number | Long Division |Worksheet Answer
Apr 24, 24 03:46 PM
Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Numbers are discussed here step-by-step. How to divide 3-digit numbers by single-digit numbers? Let us follow the examples to learn to divide 3-digit number by one-digit nu… -
Symmetrical Shapes | One, Two, Three, Four & Many-line Symmetry
Apr 24, 24 03:45 PM
Symmetrical shapes are discussed here in this topic. Any object or shape which can be cut in two equal halves in such a way that both the parts are exactly the same is called symmetrical. The line whi…