Common Solid Figures
In third grade geometry we will discuss in
brief about some of the common solid figures named below:
(i) Cube: Definition of cube, parts of a cube, properties of a cube.
(ii) Cuboid: Definition of cuboid
(iii) Cylinder: Definition of cylinder
(iv) Cone: Definition of cone
(v) Sphere: Definition of sphere
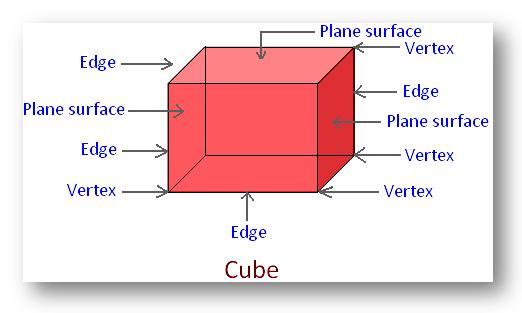
Definition of a cube:
An object which looks like solid box-shaped that has six identical square faces.
A cube has 6 equal and plane surfaces. All the faces of a cube are square in shape.
In a cube there are 6 plane surfaces. There are 8 vertices and 12 edges.
Two adjoining plane – surfaces meet at an edge. There are 12 edges in a cube and all the 12 edges are equal in length. These edges are straight edges.
The meeting point of two edges is called a vertex. In a cube there are 8 such vertices.
Parts of a cube:
(i) Face: Face is also known as sides. A cube has six faces and all the faces of a cube are square in shapes. Each face has four equal sides.
(ii) Edge: When two edges meet each other a line segment formed. There are 12 edges in a cube. All the 12 edges are equal in length because all faces are squares. These edges are straight edges.
(iii) Vertex: When three edges meet each other a point formed. There are 8 vertices in a cube.
(iv) Face Diagonals: Face Diagonals of a cube is the line segment that joins the opposite vertices of a face. There are 2 diagonals in each face so altogether there are 12 diagonals in the cube.
(v) Space Diagonals: Space diagonals of a cube are the line segment that joins the opposite vertices of a cube, cutting through its interior. There are 4 space diagonals in a cube.
Properties of a cube:
Volume: The volume of a cube is s3 where s is the length of one edge.Surface Area: The surface area of a cube is 6s2, where s is the length of one edge.
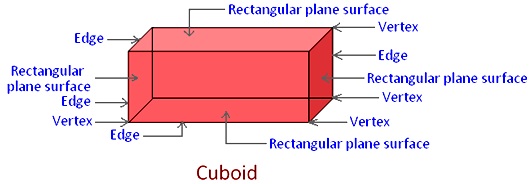
Definition of cuboid:
The cuboid has 6 rectangular faces. The opposite rectangular plane surfaces are identical (equal in all respects). It has 8 vertices and 12 edges.
In a cuboid there are 6 rectangular plane surfaces. There are 8 vertices and 12 edges.
A cube is also a cuboid having all its 6 faces equal and square. Thus, a cube has all the six faces identical, whereas a cuboid has the opposite faces identical.
Properties of a cuboid:
Formulas for the above rectangular box:
Volume: The volume of a cuboid is lwh, where l is the length, w is the width and h is the height.
Lateral Surface Area: The lateral surface area of a cuboid is 2lh + 2wh, where l is the length, w is the width and h is the height.
Surface Area: The surface area of a cuboid is 2lw + 2lh + 2wh, where l is the length, w is the width and h is the height.
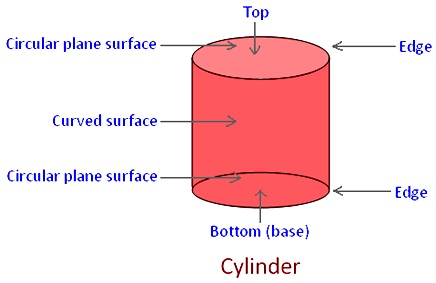
Definition of cylinder:
A cylinder stands on a circular plane surface having circular plane surfaces on its top and bottom. Thus a cylinder has two circular plane surfaces, one at its base and another at its top. It has a curved surface in the middle.
It has two edges, at which the two plane surfaces meet with the curved surface. These edges are curved edges.
In a cylinder there are 2 plane surfaces and 1 curved surface. There are 2 edges and no vertices.
The base and top of a cylinder are of the same shape (circular) and size. Thus, both are identical.
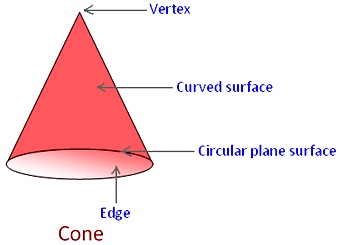
Definition of cone:
A cone has one plane circular surface, i.e. its base and only one curved surface. In a cone there is 1 plane surface and 1 curved surface. There are 1 edge and 1 vertex.
It has one edge which is formed by the circular plane surface meeting with the curved surface. The edge of a cone is a curved edge.
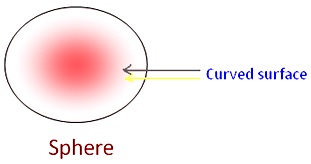
Definition of sphere:
The ball-like shape is called a sphere. In sphere there is curve surface, no edge and no vertex.
Some of the common solid figures are explained above in brief with the labeled diagram to get the basic ideas of the solid shapes.
Note:
(i) The surface of solid is called face.
(ii) Edge is formed when two faces meet.
(iii) The point where 3 faces meet is called the corner.
Related Concepts
● Geometrical Design and Models
From Common Solid Figures to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
What are Parallel Lines in Geometry? | Two Parallel Lines | Examples
Apr 19, 24 04:39 PM
In parallel lines when two lines do not intersect each other at any point even if they are extended to infinity. What are parallel lines in geometry? Two lines which do not intersect each other -
Perpendicular Lines | What are Perpendicular Lines in Geometry?|Symbol
Apr 19, 24 04:01 PM
In perpendicular lines when two intersecting lines a and b are said to be perpendicular to each other if one of the angles formed by them is a right angle. In other words, Set Square Set Square If two… -
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts | Point | Line | Properties of Lines
Apr 19, 24 01:50 PM
The fundamental geometrical concepts depend on three basic concepts — point, line and plane. The terms cannot be precisely defined. However, the meanings of these terms are explained through examples. -
What is a Polygon? | Simple Closed Curve | Triangle | Quadrilateral
Apr 19, 24 01:22 PM
What is a polygon? A simple closed curve made of three or more line-segments is called a polygon. A polygon has at least three line-segments. -
Simple Closed Curves | Types of Closed Curves | Collection of Curves
Apr 18, 24 01:36 AM
In simple closed curves the shapes are closed by line-segments or by a curved line. Triangle, quadrilateral, circle, etc., are examples of closed curves.