4th Grade Math Worksheets
4th grade math worksheets is carefully planned and thoughtfully presented on mathematics for the students. Teachers and parents can also follow the worksheets to guide the students. All the topics are covered in the 4th grade worksheets. These worksheets can be used for home work practice also. All types of questions are covered in the homework sheets for example Numbers, Fractions, Four Fundamental Operations, Measurement, Data handling and Geometry.
If a student have any doubts in any of the particular question in the worksheets or in any questions he/she can contact me through the comment box with that particular question. As soon as I see your question I will surely reply within 24 hours with the step by step solution along with the explanation of that particular question.
I request all the visitors to fill the comment box with your valuable suggestions, so that I can keep in mind and do the needful changes.
● Practice Test - Worksheets
- 4th Grade Worksheet 1
- 4th Grade Worksheet 2
- 4th Grade Worksheet 3
- 4th Grade Worksheet 4
- 4th Grade Worksheet 5
- 4th Grade Worksheet 6
- 4th Grade Worksheet 7
- 4th Grade Worksheet 8
- 4th Grade Worksheet 9
- 4th Grade Worksheet 10
- 4th Grade Worksheet 11
- 4th Grade Worksheet 12
● Geometry - Worksheets on Simple Shapes & Circle
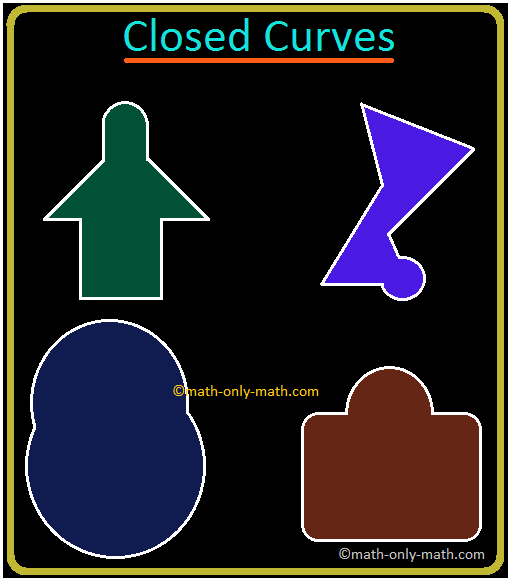
Worksheet on Closed Curves and Open Curves.
Worksheet on Symmetrical Shapes.
● Numbers - Worksheets
Worksheets on Comparison of Numbers.
Worksheet on Successor and Predecessor.
Worksheet on Arranging Numbers.
Worksheet on Numbers in Words.
Worksheets Showing Numbers on Spike Abacus.
Worksheet on Expanded form of a Number.
Worksheet on Formation of Numbers.
Worksheet on Forming Numbers with Digits
Worksheet on Rounding off Numbers.
Worksheet on Rounding Numbers.
● Roman Numerals - Worksheets
● Factors and Multiples - Worksheets
Worksheet on Even and Odd Numbers.
● Fractional Numbers - worksheets
Worksheet on Equivalent Fractions.
Worksheet on Comparison of Like Fractions.
Worksheet on Conversion of Fractions.
Worksheet on Changing Fractions.
Worksheet on Types of Fractions.
Worksheet on Reducing Fraction.
Worksheet on Addition of Fractions having the Same Denominator.
Worksheet on Subtraction of Fractions having the Same Denominator.
Worksheet on Add and Subtract Fractions.
Worksheet on Fractional Numbers.
● Four Fundamental Operations - worksheets
Worksheet on Word Problems on Addition.
Worksheet on Mixed Addition and Subtraction.
Worksheet on Word Problems on Addition and Subtraction.
Worksheet by Adding or Subtracting.
Worksheet on Addition and Subtraction.
Worksheet on Estimating Sums and Differences.
Worksheet on Multiplication of a Number by a 2-Digit Number.
Worksheet on Multiplication of a Number by a 3-Digit Number.
Worksheet on Estimating Products.
Worksheet on Word Problems on Multiplication.
Worksheet on Estimating the Quotient.
Worksheet on Dividing Numbers.
Worksheet on Division by Two-Digit Numbers.
Worksheet on Word Problems on Division.
Worksheet on Four Fundamental Operations.
Worksheet on Systems of Numeration.
● Measurement - Worksheets
Worksheet on Measurement of Length.
Worksheet on Perimeter of a Figure.
Worksheet on Measurement of Mass or Weight.
Worksheet on Measurement of Capacity.
Worksheet on Measurement of Time.
Worksheet on Antemeridian and Postmeridian.
Worksheet on Interpreting a Calendar.
● Data Handling - Worksheets
Worksheet on Interpreting a Pictograph.
I. State whether the following statements are true or false:
(i) Fractions having denominator 1 are called unit fractions.
(ii) \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(iii) \(\frac{9}{15}\) = \(\frac{11}{17}\)
(iv) \(\frac{2}{5}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{1}\)
(v) \(\frac{1}{3}\) × 0 = 0
(vi) \(\frac{3}{10}\) = 0.03
(vii) \(\frac{86}{1000}\) = 0.86
(viii) 335 rupees 8 paise = 335.8 rupees
(ix) 26 km 190 m = 26.190 km
(x) 1 litre = 100 millilitres
(xi) 1 decametre = 100 hectometres
(xii) 10 decilitres = 100 centilitres
(xiii) 1 tonne = 10 quintals
(xiv) 3 km 4 hm 5 dm 1 m = 3451 m
(xv) 1629 gm = 16.29 kg
II. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Fractions having same denominators are called ………………………….
(ii) \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = ………………………….
(iii) \(\frac{5}{7}\) = \(\frac{35}{……}\)
(iv) A fraction in which the denominator is greater than the numerator is called ………………………….
(v) A …………………………. is the sum of a whole number and a proper fraction.
(vi) \(\frac{6}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\) + ………………………….
(vii) …………………………. of a fraction is the fraction inverted.
(viii) A …………………………. is a fraction whose denominator is 10 or powers of 10
(ix) 2 and 35 thousandths is written as ………………………….
(x) 28.56 m = …………………………. cm
(xi) 21 kg 75 g = …………………………. g
(xii) 1 litre = …………………………. ml
(xiii) Milli stands for ………………………….
(xiv) 752 quintals = …………………………. kg
(xv) 7 hl 5 dl = …………………………. l
III. Reduce the fractions to their lowest terms:
(i) \(\frac{72}{216}\)
(ii) \(\frac{168}{840}\)
IV. Arrange the following sets of fractions in the ascending order.
(i) \(\frac{5}{9}\), \(\frac{5}{11}\), \(\frac{5}{17}\), \(\frac{5}{12}\), \(\frac{5}{21}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{15}\), \(\frac{5}{15}\), \(\frac{8}{15}\), \(\frac{2}{15}\), \(\frac{7}{15}\)
V. Arrange the following sets of fractions in the descending order.
(i) \(\frac{8}{16}\), \(\frac{9}{16}\), \(\frac{7}{16}\), \(\frac{11}{16}\), \(\frac{16}{16}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{7}\), \(\frac{2}{6}\), \(\frac{5}{6}\), \(\frac{8}{3}\)
VI. Add the following fractions:
(i) \(\frac{2}{9}\) + \(\frac{4}{9}\) + \(\frac{1}{9}\) =
(ii) \(\frac{7}{13}\) + \(\frac{1}{13}\) + \(\frac{2}{13}\) + \(\frac{3}{13}\) =
VII. Subtract the following:
(i) \(\frac{7}{10}\) - \(\frac{3}{5}\) =
(ii) 15\(\frac{1}{3}\) - 6\(\frac{2}{5}\) =
VIII. Simplify using prime factorisation:
(i) \(\frac{28}{49}\) × \(\frac{27}{48}\) × \(\frac{36}{18}\)
(ii) \(\frac{16}{18}\) × \(\frac{15}{20}\) × \(\frac{25}{30}\)
IX. Multiply the following:
(i) \(\frac{3}{5}\) × 9
(ii) 35 × \(\frac{2}{5}\)
X. Divide the following:
(i) \(\frac{4}{27}\) ÷ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(ii) 5\(\frac{3}{6}\) ÷ 2\(\frac{7}{24}\)
XI. Convert the following into decimals:
(i) 29\(\frac{56}{100}\)
(ii) \(\frac{29}{1000}\)
XII. Add the following:
(i) 38.3 + 56.28 + 49.5 + 75.25
(ii) 528.234 + 364.641 + 258.070
XIII. Subtract the following:
(i) 37.070 – 25.180
(ii) 578.125 – 287.209
XIV. Workout the following:
(i) 235 km 528 m + 513 km 743 m + 28 km 050 m
(ii) 78 l 750 ml – 64 l 280 ml
(iii) 78 m 83 cm × 16
(iv) 36.500 kg ÷ 12
XV. Workout the following word problems:
(i) A factory produces 5340 soaps in 4 days. How many soap do the factory produce in 10 days?
(ii) Sharon walked \(\frac{2}{3}\) km. Shelly walked \(\frac{8}{18}\) km. Who walked farther? How much farther did one walk than the other?
(iii) The length and breadth of a rectangular plot of land are \(\frac{4}{7}\) m and \(\frac{3}{5}\) m. Find its area.
(iv) In a grocery shop, there was 3525 kg 780 g of rice in the morning. During the day 1683 kg 500 g of rice was sold out. How much of rice was left in the shop in the evening?
XVI. Fill in the blanks:
(i) A leap year has ………………………. days.
(ii) A figure bounded by straight lines is called a ………………………. figure
(iii) The length of the boundary of a closed figure is called its ……………………….
(iv) An angle greater than 90° and lesser than 180° is a ……………………….
(v) SP – CP = ……………………….
(vi) 12 midnight is ………………………. hours in 24 hour clock.
(vii) An ………………………. is formed when two rays meet at a point.
(viii) A triangle has ………………………. vertices.
(ix) An angle greater than ………………………. is called a reflex angle.
(x) 15 minutes is ………………………. seconds.
XVII. Convert the following into hours and minutes.
(i) 755 minutes
(ii) 235 minutes
XVIII. Convert the following into minutes.
(i) 11 hours 35 minutes
(ii) 15 hours 56 minutes
XIX. Convert the following into years and months:
(i) 92 months
(ii) 85 months
XX. Add the following:
|
1. days 34 + 46 + 52 |
hours 23 14 17 |
2. hours 12 + 18 + 13 |
minutes 46 53 26 |
seconds 37 28 35 |
XXI. Subtract the following:
|
1. days 17 - 13 |
hours 12 22 |
2. hours 18 - 15 |
minutes 53 38 |
seconds 28 49 |
XXII. Workout the following problems:
(i) Sam bought a two wheeler for $52,000 and sold it at a loss of $13,528. Find the selling price.
(ii) Roma sold her car for $275,000 at a profit of $25,820. Find the cost price of the car.
(iii) A shopkeeper purchased a bag of rice for $1425. He sold it for $1725. What is his gain?
(iv) A square has a perimeter of 256 cm. What is the length of each side?
(v) The length and breadth of a rectangular field is 96 m and 47 m respectively. Find the cost of fencing the field if the cost of fencing is $12 a metre.
XXIII. Construct an angle measuring 125°.
Math Homework Sheets
From 4th Grade Math Worksheets to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
What are Parallel Lines in Geometry? | Two Parallel Lines | Examples
Apr 19, 24 04:39 PM
In parallel lines when two lines do not intersect each other at any point even if they are extended to infinity. What are parallel lines in geometry? Two lines which do not intersect each other -
Perpendicular Lines | What are Perpendicular Lines in Geometry?|Symbol
Apr 19, 24 04:01 PM
In perpendicular lines when two intersecting lines a and b are said to be perpendicular to each other if one of the angles formed by them is a right angle. In other words, Set Square Set Square If two… -
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts | Point | Line | Properties of Lines
Apr 19, 24 01:50 PM
The fundamental geometrical concepts depend on three basic concepts — point, line and plane. The terms cannot be precisely defined. However, the meanings of these terms are explained through examples. -
What is a Polygon? | Simple Closed Curve | Triangle | Quadrilateral
Apr 19, 24 01:22 PM
What is a polygon? A simple closed curve made of three or more line-segments is called a polygon. A polygon has at least three line-segments. -
Simple Closed Curves | Types of Closed Curves | Collection of Curves
Apr 18, 24 01:36 AM
In simple closed curves the shapes are closed by line-segments or by a curved line. Triangle, quadrilateral, circle, etc., are examples of closed curves.